First, let us see the OSI reference mode. In OSI we have seven layers. They are application layer, presentation layer, session layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer, and physical layer. Let us see the layers in the TCP IP model by a comparing with the OSI reference model. There are four layers in the TCP IP model. They are network access layer, Internet layer, transport layer, and application layer.
To purchase any IT related software or hardware please visit: https://www.xtechbuy.com/
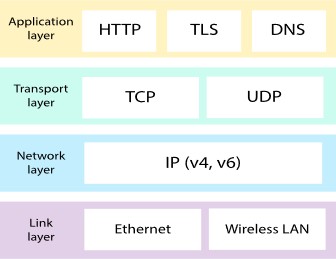
The TCP IP protocol suite was developed prior to the OSI model, and the functionalities of the physical layer and datalink layer are combined into a single layer called network access layer. The network layer is equivalent to Internet layer of the OSI model. The transport layer is the same as in OSI model and the functionality of the session layer, presentation layer and application layer are merged into a single layer called application layer. If TCP IP model is with 5 layers, just break network access layer into physical layer and data link layer separately. There are some protocols that are there in every layer of the TCP IP model because of that protocol only does the functionality of that layer if you take network access layer point to point protocol simply PPP frame relay is popular in network access layer. Ethernet is a popular protocol in the network access layer. In the Internet layer, we have IP protocol- IP simply means IPV4 or IPV6, ICMPV4 or ICMPV6. In the transport layer, we have TCP and UDP and in the application layer we have HTTP, DNS, DHCP, and FTP.
For general IT Support services for Businesses please visit: https://www.benchmarkitservices.com.au
TCP IP model
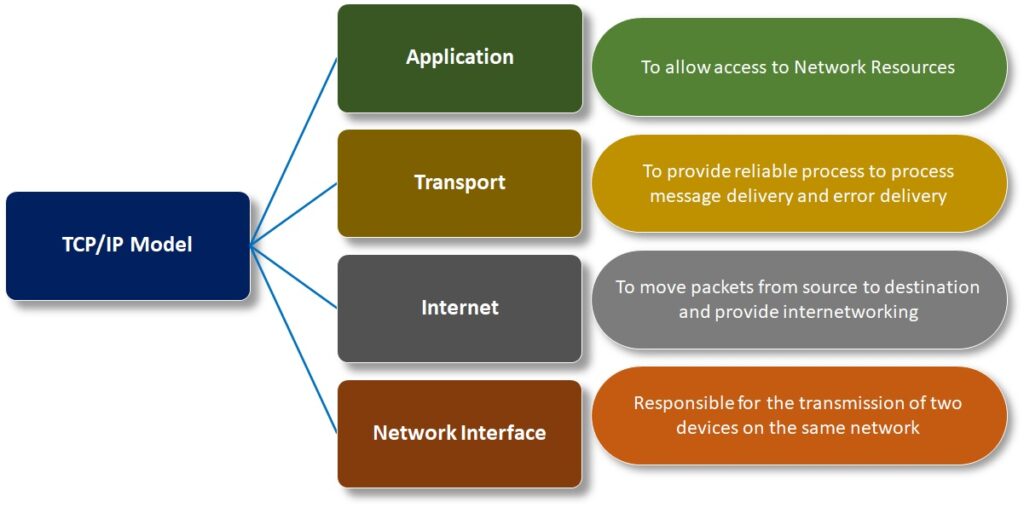
TCP IP model has four layers. They are network access layer which controls the hardware because physical layers are part of network access layer. Next is the Internet layer, this is the network layer, it determines the best path through the network. The transport layer, it supports communication between diverse devices across diverse network. Simply transport layer deals with process-to-process communication. In the application layer, this layer is dealing with the users so representing the data to the user plus encoding dialogue control. The functionalities of application layer, presentation layer, and session layer are combined into a single layer.
For general support issues of home users please visit: https://www.computerepaironsite.com.au/
TCP IP protocol suite
The network access layer has protocols like point-to-point protocol PPP, Ethernet protocol and there are many interface drivers that work on this network access layer and coming to the Internet layer, the routing protocols will come in the Internet layer, routing protocols like RAP, OSPF, EAGRP, BGP and we have IP support protocols like ICMP and NAT- network address translation. The transport layer the widely used transport layer protocols are TCP and UDP. TCP means transmission control protocol and UDP means User datagram protocol. In the application layer protocol, we have domain name servers or Domain Name System, there are host configuration protocols like boot-P or bootstrap protocol, dynamic host configuration protocol or simply DHCP and we have email related protocols like simple mail transfer protocol SMTP, post office protocol or simply PO, Internet message access protocol IMAP, and we have file transfer protocols like FTP file transfer protocol and trivial file transfer protocol, In order to access the web or web pages we have HTTP. These are the popular protocols in the application layer this is the TCP IP protocol suite.
For Data security related issues of businesses please visit: https://www.benchmarkitservices.com/backup/
Protocol Data Unit PDU
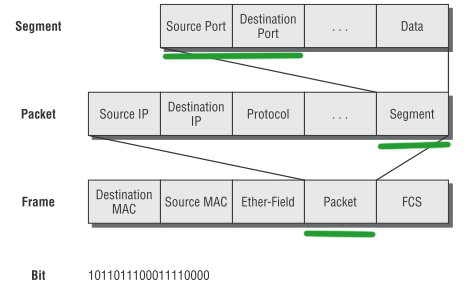
Protocol data units are named according to the protocols of the TCP IP suite. It means the pda can be data, segment, packet, frames, and bits. The application layer information or that application layer pdu is called as data. The transport layer pdu is called a segment after adding the transport layer information. By adding the network layer information, the network layer pdu is called as a packet. With this network layer will be adding the data link layer part that is the header and the trailer, so the data link layer pdu is called as a frame. These frames are converted into zeros and ones in the physical layer, so the physical layer pdu are called as bits.
For cyber security related issues of businesses please visit: https://www.benchmarkitservices.com/cyber-security/
Let us see an example, suppose there is a user who is accessing a mail server somewhere on the Internet. Let us assume that it is gmail.com, he has opened a gmail.com list browser and he is generating the application layer data, so this email data generating is simply called as data. The application layer pdu is called as data. if it is a big, data is broken into smaller pieces now each of these smaller pieces are added with the transport header in the transport layer. The transport layer pdu is now called as segment. Now this segment is the segment after adding the network layer header, we call this network layer pdu as a packet. With this information we are going to add a header and a trailer in the data link layer, this data link layer pdu is called a frame. Now this frame is a medium dependent frame, because if this is an Ethernet cable, this frame is going to be different. If it is a Wi-Fi frame, it is different, so Ethernet frames have different and Wi-Fi frames are different and that is why the frames are medium dependent. The data link layer information is converted into zeros and ones, so the physical layer is called as bits. The application layer pdu is called as data, the transport layer pdu is called as segment, the network layer pdu is called as packet, the data link layer pdu is called as frames, and the physical layer pdu is called as bits.
For cloud-based solutions for the businesses like Google, AWS and Azure please visit: https://www.benchmarkitservices.com/google-cloud-service-providers/