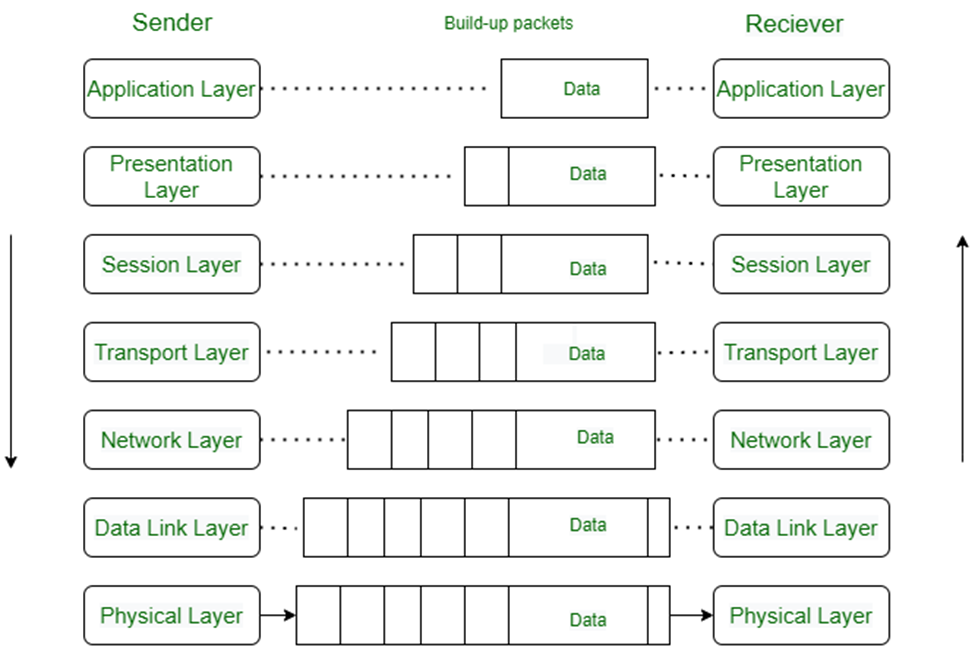
OSI Layers: Open system inter connection layers developed in 1984 to transfer data from one system to across all over the global. It has seven layers. This mode provides theoretically to understand how the network communicates.
[1]
OSI mode consists of 7 layers are:
- Physical layer
- Datalink layer
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Session layer
- Presentation layer
- Application layer
Physical Layer: Physical layer is the very last layer of OSI and it is physically transferring the data in form of signals from one end to other. And converts signals into 0s and 1s transfer the data to nextlayer data link. Data at this layer is called bits.
[1]
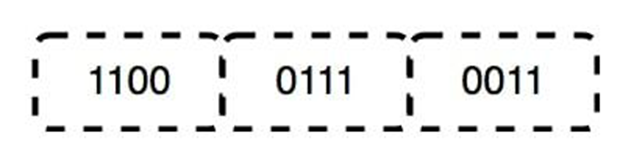
Bit synchronization, bit control are the some functions of physical layer.
In physical layer for the transmission purpose 2 types of medias are there. Guided media and unguided media. Guided media such ad UTP, coaxial cables and optical fibers are using. Where as unguided media wire less or open air space is considered as unguided media. To connect the devices in physical layer medium there are some topologies have been introduced .
- Mesh topology
- Ring topology
- Bus topology
- Star topology
- Hybrid topology [2]
2. Data link layer: The main function of the layer is delivering the data error free from one node to others. And also, responsible to transmit the data over a mac address to the host. Switches are operating on this layer. Switches transfer the data using the mac address which is also called as burnt in address is a 12 digit hexa decimal number broken into 6 pairs of hexa-decimal number. Here first six digits are represents the OUI ( Organizationally Unique Identifier) last six are for unique purpose to identify the device. When the data wants to transfer by a switch, it uses the mac address of the system to transfer the data which helps it to faster transmission. [3]
[4]
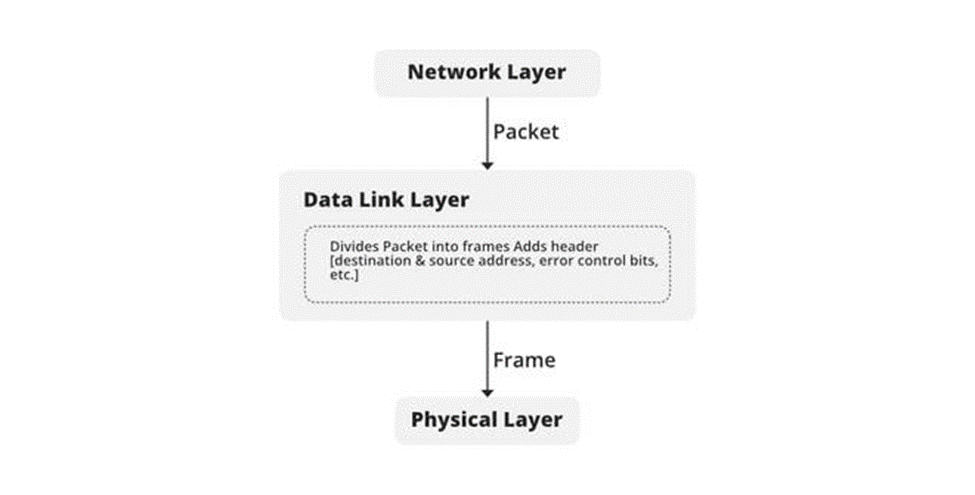
Layer 2 uses the Arp protocol to find the mac address of a system. For example, when a computer wants to transfer the data to another computer. First it transfers data to a switch. Then switches use arp-protocol to find the mac address of that particular devices using the IP address. The process for find the mac address the switch floods the Arp request to all other port except the one it received. Then it gets a request from where is supposed to transfer the data after matching its Ip address. Data in this layer is called frame. In old days hubs were used. The disadvantage with hubs is they flood the data instead of transfer to the one it needs to send. Where as switch send to only to the ports it has to send. [5] [6]
3. Network layer: Routers and layers 3 switches are, operating in network layer. Here the data is called as packets. So, to transfer the packets in between routers it needs an Ip address which is to identify as unique overall the network. To transfer these packets there are some protocols IP, RIP, EIGRP, OSPF are some of the protocols using in layer 3 OSI model. Protocol is set of rules or procedure governing by an organization.
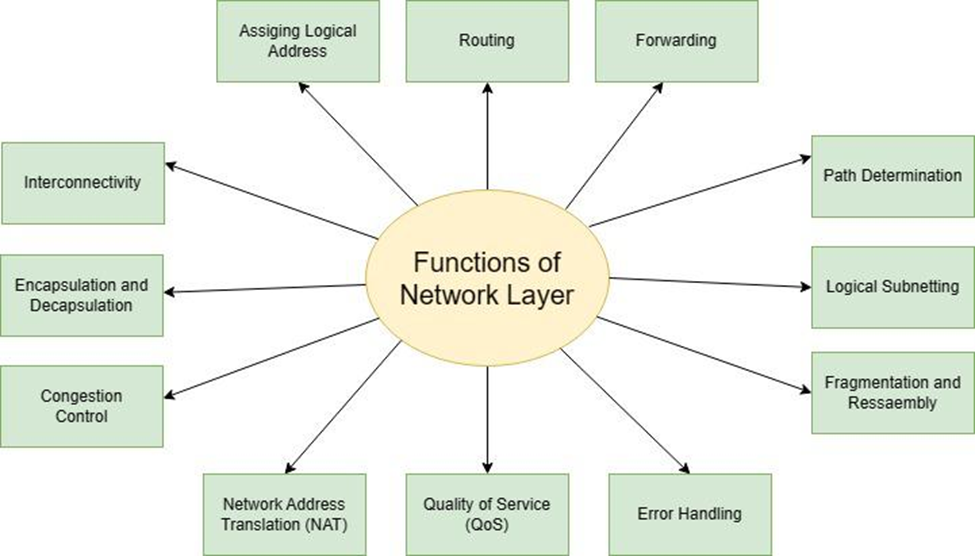
[4] it is responsible to assign the host id and network id. Using the host id it can confirm was sent by the authorized user or not. Here are some of the functions performed by the network layer
a. assigning logical address
b. routing
c. host – host delivery
d. logical subnetting
e. error handling
f. QoS
g. NAT (network Address Translator) [4]
4. Transport Layer: In this layer data is called as segment. Transport layer is responsible for end-to-end communication of data packets. TCP/IP and UDP are the protocols most often uses for data communication. TCP/IP is most reliable protocol which provides packet sequencing, connection orientation, flow control, error detection, retransmission the data. Unlike TCP/IP, UDP uses live communication which is not a connection oriented. [5]
5. Session Layer: session layer is to control and maintain connection between to share data. In case of network error, it provides authenticity and provides recovery option and also manages synchronizes the data. Here are some functions of session layer.
i. Session establishment
ii. Data transfer
iii. Dialog Management
iv. Synchronization
v. Authentication [7]
6. Presentation layer: Presentation layer is responsible for to ensure data is understandable for the end system. Based on applications of data formats and syntax it translates and also manages encryption and decryption of data. In this layer programmers considers structure and presentation rather than sending data in form of packets or datagrams between users. Although each levels have their own encryption, presentation layer also has decryption and encryption. Example when logging into bank sites this layer decrypts the data it receives. [8]
7. Application layer: Application layer is the top layer of OSI model. This implemented by the network applications and produced to be transferred the data over the networks. Here are the functions of application layer.
Mail services, Directory services, FTAM (Files Transfer Access and Management), Network Virtual Terminal (NVT) allows user to logon virtually.
| Layer No. | Layer Name | Responsibility | Information Form | Device or Protocol |
| 7 | Application layer | Identifies client and communication synchronization | Massage | SMTP |
| 6 | Presentation layer | Extracts and manipulates the data into requested format | Message | JPEG, MPEG, GIF |
| 5 | Session layer | Connection maintenance establishes | Encrypted message | Gateway |
| 4 | Transport layer | Provides information to application layer | Segment | Firewalls |
| 3 | Network layer | Transmission of data between hosts | Packet | Router |
| 2 | Datalink layer | Node to node delivery | Frame | Switch, bridge |
| 1 | Physical layer | Physical connection between devices | Bits | Repeater, modem, cables |
[4]
References
| [1] | 05 05 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/open-systems-interconnection-model-osi/. |
| [2] | “edukedar project,” 05 05 2024. [Online]. Available: https://edukedar.com/physical-layer/#gsc.tab=0. |
| [3] | “how-to-greek,” 5 5 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.howtogeek.com/764868/what-is-a-mac-address-and-how-does-it-work/. |
| [4] | “geeksforgeeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/open-systems-interconnection-model-osi/. [Accessed 05 05 2024]. |
| [5] | “geeksforgeeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/network-layer-in-osi-model/. [Accessed 05 05 2024]. |
| [6] | “datalinklayer,” [Online]. Available: https://osi-model.com/data-link-layer/. [Accessed 05 05 2024]. |
| [7] | “javapoint,” [Online]. Available: https://www.javatpoint.com/session-layer-in-osi-model. [Accessed 05 05 2024]. |
| [8] | “layer6PresentationLayer,” [Online]. Available: https://osi-model.com/presentation-layer/. [Accessed 05 5 2024]. |
