Network Devices: Network devices nothing but network hardware which uses to communicates with other network devices to share data. Examples are repeaters, routers, switches, NIC, etc.
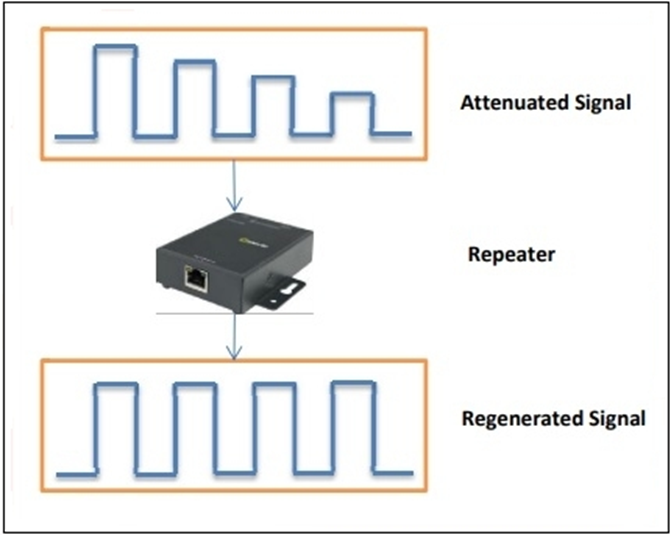
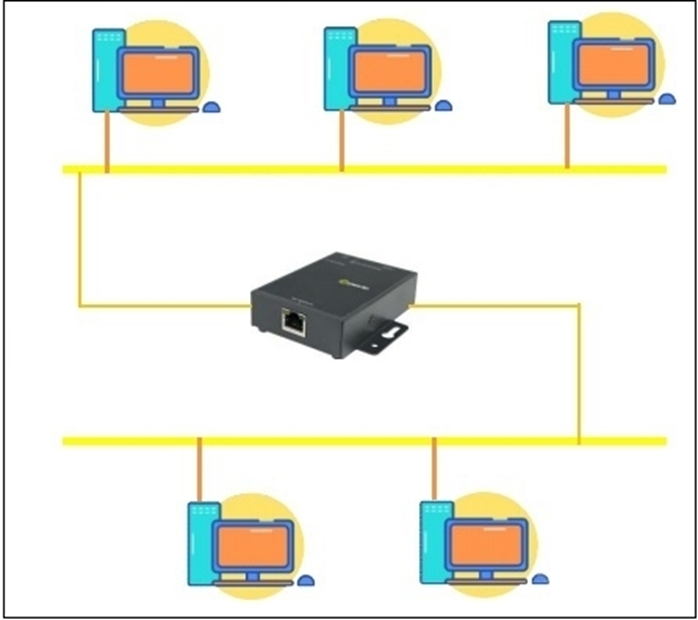
Repeaters: The repeater is a physical device to transfer the signal over the network. Its job is to regenerate the signal when it is becoming week or corrupted. Repeaters job is not only amplifying the signal but also to regenerate it. It is a port 2 device.
[1]
Repeaters can solve the problem of the loss or corrupted signal. When signal is transmitting with in the Lan area, the signal gets attenuated upon the nature of the technology. Over certain distances or periods repeaters has been using in between the lans.
Types of repeaters:
Analog repeaters
Digital repeaters
Wires repeaters
Wireless repeaters
Local repeaters
Remote repeaters
Repeaters are cost effective and so simple to install. But they can separate the signal and noise.
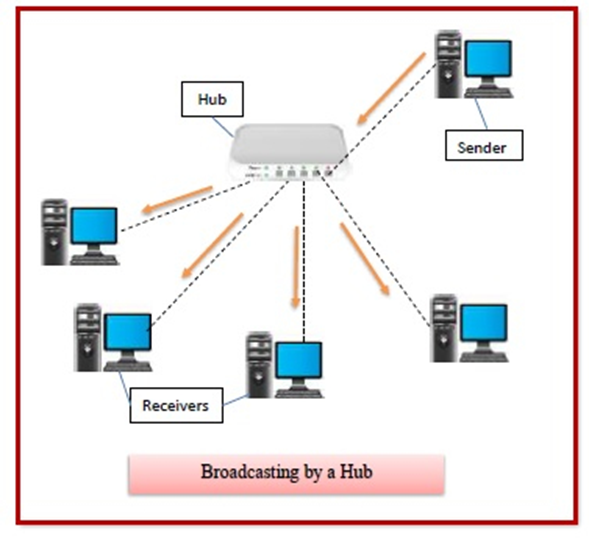
Hub: Hub uses to connected the devices from multiple branches. Basically, it is a multi-port device. When the data received by the hub device, it just forward to all other devices it is connected to unlike switch. Hubs does not know to finding out the best path.
[1]
Hubs operates in OSI physical layer. Hubs can not filter data these are non-intelligent network devices. Half duplex mode used in hubs and is passive devices.
Types of hubs:
Passive Hubs: Passive hubs are limited in area of network and can not amplify the signals. The nodes are connected in a form of star and just forward the data without amplifying it.
Active Hubs: Active hubs have their own power supply so it can amplify and regenerates the signal before broadcast. Active hubs use for longer distances purpose because of its amplification and regeneration properties.
Intelligent hubs: These hubs act like active hubs also have remote management capabilities.
Bridge: Bridge is a 2-port device having single input and single output. It works as repeater and based on the MAC address it forwards the data. Bridges are operates on layer 2 of the OSI model.
[2]
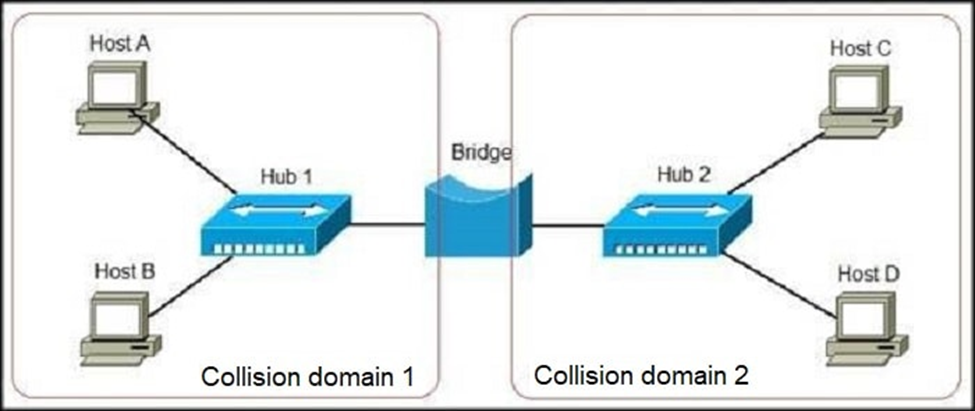
Above example has 4 computers and divided the network into several segments by the bridge. Example A wants to communicates with C. The frame or the data will be inspected by the bridge and the forwarded it. Most of the bridges has either 2 or 4 ports. Bridges are software based and switches are hardware and chips based.
Types of bridges:
Transparent Bridges and Source Routing Bridges.
Switch: Switch is layer 2 device has many ports that are connected to the devices. Switch performs the operations like forwarding the packets to the correct device by mac address and in case of corrupted packets it just drops it rather than forwarding it. Switches one of the functions is error checking and redundancy check. Switches have multiple collision domains in different VLANS.
[3]
Types of switches: Here some types of switches.
a. Managed Switches: Most commonly seen in commercial and enterprise companies. It uses to split network into smaller sub divisions by creating VLANS.
b. Unmanaged switches: Basically, used to forward the data in between devices by mac address. These are cheap switches and unsuitable for many corporates.
c. Power Over Ethernet: POE switches provide DC power to low power across the lan wire. Some IoT devices works on very low power. So, these ports are suitable for low power IoT devices.
d. Layer 3 Switches: Layer 2 switches are operating on data link layer of OSI layer. Basically, its operations are forwards the ethernet frame. Layer 3 switches are hybrid of layer 2 and 3. They have complex software design than layer 2 switches. [3]
e. Desktop Switches: These switches used for small office environment purpose. They are smaller in size.
Routers: Routers are the devices like switch that routes the path for IP packets. They operate on layer 3 of OSI model. Routers normally connects between LAN and WAN. They dynamically find the best path for the packets
Core Router: Usually, service providers use these routers. They provide maximum bandwidth to routers which are connected to core router. Small businesses no need of core routers.
Edge Router: Edge routers also called as gateway routers to distribute data to end users. They have ethernet ports to connect to internet and additional routers.
Distribution Router: Distribution router takes the information from edge router over wired connection and forward it to end user over Wi-Fi or additional routers.
Wire less Routers: These are combination of edge and distributed routers for home usage. They provided by the service providers. [4]
[5]

Gateway: As the name implies, gateway means connecting two networks which operates distinct networking models. They carry out message, transferring functions and interpreting data from system to other system. Gate way functions at network layer and also a protocol. Another name for gateway is protocol converter.
Simple steps how gateway works:
1. Obtain the data from network
2. Received data gets intercepted and analyzed
3. Forwards the data to destination address
4. Data is converted so that it used by the receiver network.
5. Last bit of data sends over the inside network.
[6]
NIC (Network Interface Card): A computer is connected to a network using a network adapter known as a network interface card, or NIC. It is installed on the computer in order to construct a LAN. It has a connection on it for connecting the cable, and the chip has a unique id etched on it. The cable acts as an interface between the computer and the router or modem. NIC cards operate on both the physical and data link tiers of the network model since they are layer 2 devices.
[1]
References
| [1] | “tutorials point,” [Online]. Available: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-are-repeaters-in-computer-network. [Accessed 05 05 2024]. |
| [2] | “studyccna,” [Online]. Available: https://study-ccna.com/network-bridge-explained/. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
| [3] | “spiceworks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/networking/articles/what-is-network-switch/. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
| [4] | “cisco,” [Online]. Available: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/small-business/resource-center/networking/what-is-a-router.html. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
| [5] | “geeksforgeeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-of-a-router/. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
| [6] | “geeksforgeeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-are-gateways-in-computer-network/. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
| [7] | moumita, “tutorialspoint,” 22 07 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-are-hubs-in-computer-network. [Accessed 06 05 2024]. |
