What is Edge computing?
Edge computing is a networking philosophy that aims to get computation as close as feasible to the data source to minimize latency and bandwidth consumption. In simple terms, edge computing is shifting fewer processes from the cloud to local locations, such as a user’s PC, an IoT device, or an edge server. As a result of moving computing to the edge of the network, it will be reduced the long-distance communication between a client and server.
If further explained, instead of running on a centralized server or in the cloud, edge computing is a distributed computing approach in which processing happens close to the actual site where data is being gathered and analyzed. As part of this new infrastructure, various devices, such as laptops and cellphones, are connected to the network, and edge servers securely handle data locally in real time.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
In a traditional environment, data is often created on a user’s computer or another client program. The information is subsequently transferred to the server, where it is stored and processed via channels like the internet, intranet, LAN, etc. This still stands as a classic and proven method for client-server computing.
However, the exponential growth in the amount of data produced and the number of internet-connected devices has proven difficult for traditional data center infrastructures to handle. By 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will be made outside of centralized data centers, which a report by Gartner predicts. This amount of data puts a heavy burden on the internet, causing congestion and outages. The idea behind edge computing is straightforward: rather than bringing the data near the data center, it brings the data center close to the data. The data center’s computing and storage capabilities are installed as close as possible (preferably in the same place) to the data generation site.
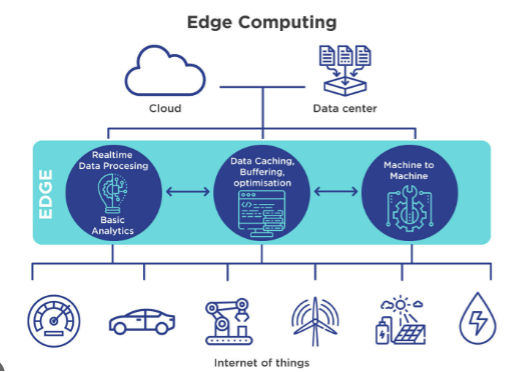
Applications of Edge computing
Edge computing will be applicable and provide value to different industries. Enterprises benefit from increased productivity, excellent security, and performance. Following are some top applications of edge computing in enterprises.
Banking and Finance Industry
By incorporating image recognition into ATMs, edge AI can be used to examine video feeds and increase ATM security. There is no requirement for human involvement. Additionally, transferring the data to the cloud is optional first. Even if the ATM loses its cool, it will immediately shut down to prevent any wrongdoing. The bank is then informed so they can take appropriate action by contacting law enforcement.
When it comes to the data privacy of the banking and finance industry, to lessen the likelihood of data theft, it is essential to go by the privacy and security requirements when transferring data to a centralized location utilizing cloud computing. However, there is still a danger of data loss. It makes this task easier. It helps banks and financial institutions distribute applications around regional branch offices, lowering the demand for cloud computing and the risk of data loss.
Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturing edge AI offers quick response times to handle on-site accidents and stop them before they happen. The biggest challenge that manufacturers are having is accessing data. However, data generated by the machine in manufacturing can help the manufacturer follow data patterns and make their choice more valuable and precise. The central server is overloaded by the enormous volume of raw data machines produce. It is beneficial to sanitize the data at the edge and only send what is necessary to the cloud. As a result, it lessens the load on the cloud and makes moving the only valuable data fast. Manufacturers can create new revenue streams by remotely monitoring the condition of their assets, such as maintenance services that allow customers to pay for services only when they are available.
Retail Industry
Inventory management services must be secure and effective to give retail customers a positive user experience. When a client requests a product, it must be made available while considering the customer’s availability and demand. AI can monitor the inventory system using in-store intelligent video image recognition and respond appropriately. Flash sales, for instance, may be made available to in-store customers if overstock items are available. It can still function when there is a poor network connection.
Automobile Industry
Edge AI in the car has produced some encouraging results. A self-driving automobile is a simplified example. All the decisions are taken under a hood, from the vehicle’s speed to the likelihood of a collision, controlling the steering wheel, assessing engine health, and transmitting battery health. AI can identify hazardous circumstances. To avoid a collision, it can warn the driver or take emergency control of the car. Driver assistance steering, cross-traffic detectors, emergency braking, and blind-spot monitoring can all help prevent collisions and save lives.
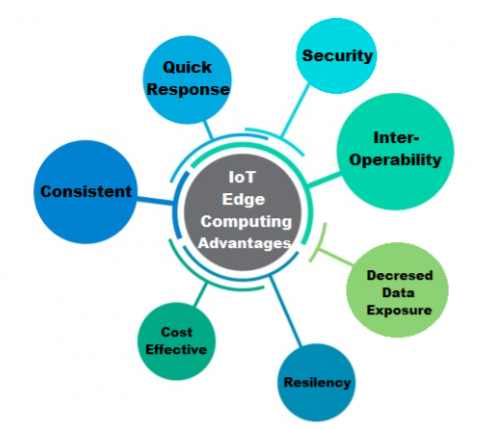
Advantages of Edge Computing
There are some key benefits of this technology.
Reduced latency
Edge computing can offer substantially faster performance, given that the data doesn’t need to travel very far to be processed. Information will be processed considerably more quickly if it is positioned close to its network. In some sectors, such as transportation or healthcare, even a second delay can cause millions of dollars worth of harm.
Safety
Edge computing enables businesses to retain some control over data by storing the crucial parts of data locally.
Scalability
Edge computing enables the storage of growing volumes of data both on the edges of networks and in distant centers. The company can transfer some of the files stored on remote storage if the local network can no longer handle all the data collection at some time. In this scenario, files essential for a team’s operation are left on the local network. Data centers get the secondary data.
Versatility
Edge computing strikes a balance between local storage and traditional, centralized cloud data storage. Businesses can concentrate on performance speed while sending specific data to the network’s edges.
Reliability
Edge computing reduces the possibility that a malfunction on a third-party network will impair the system’s overall functionality. Additionally, even when the solution is offline, locally saved data can be viewed, and once the connection is restored, that data is synced into the data storage. Edge computing improves corporate independence and reduces risks related to security problems and power outages.