Neuromorphic computing is a type of computing that is based on the structure and function of the human brain. It involves using specialised hardware and software that mimics how neurons and synapses work in the brain. The goal of neuromorphic computing is to create computing systems that are more energy-efficient and capable of handling complex, unstructured data, such as images, videos, and audio.
Neuromorphic chips, also known as neuro-synaptic chips, are designed to mimic the structure and function of neurons and synapses in the brain. These chips are made up of small, simple processing units called “neurons” connected by “synapses” that can change their strength over time. This architecture allows neuromorphic chips to process information in a highly parallel and distributed manner, similar to how the brain processes information.
Advantages:
Energy efficiency: Neuromorphic computing systems are designed to be highly energy-efficient, as they consume less power compared to traditional computing systems. This is because neuromorphic chips comprise small, simple processing units that consume less energy than conventional processors.
Handling complex data: Neuromorphic computing systems can handle complex, unstructured data, such as images, videos, and audio, in real-time. This is because the architecture of neuromorphic chips is based on the structure and function of the human brain, which is highly parallel and distributed.
Real-time processing: Neuromorphic computing systems can process information in real-time, which is crucial in fields such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and self-driving cars.
Adaptability: Neuromorphic systems can learn and adapt to new situations, similar to how the human brain learns and adapts.
Disadvantages:
Limited scalability: Neuromorphic computing systems are currently limited in terms of scalability, as the number of neurons and synapses on a chip is limited.
High development costs: Developing neuromorphic computing systems is costly and time-consuming.
Limited application areas: Currently, neuromorphic computing systems are only being used in a limited number of applications.
Challenges:
Developing neuromorphic chips: Developing neuromorphic chips is challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of how the human brain works and how to replicate it in a computing system.
Programming neuromorphic systems: Programming neuromorphic systems is also challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of the architecture of neuromorphic chips.
Limited availability of neuromorphic systems: Neuromorphic systems currently need to be widely available and are only used in a limited number of application areas.
Fields of application:
Artificial Intelligence: Neuromorphic computing systems have the potential to revolutionise the field of artificial intelligence, as they are capable of handling complex, unstructured data in real time.
Robotics: Neuromorphic computing systems have the potential to revolutionise the field of robotics, as they are capable of processing information in real time and adapting to new situations.
Self-driving cars: Neuromorphic computing systems have the potential to revolutionise the field of self-driving vehicles, as they are capable of processing information in real time and adapting to new situations.
Healthcare: Neuromorphic computing systems have the potential to revolutionise the field of healthcare, as they could help analyse medical images and improve the accuracy of diagnoses.
Cybersecurity: Neuromorphic computing systems have the potential to revolutionise the field of cybersecurity, as they are capable of handling complex, unstructured data in real time and could be used for threat detection and response.
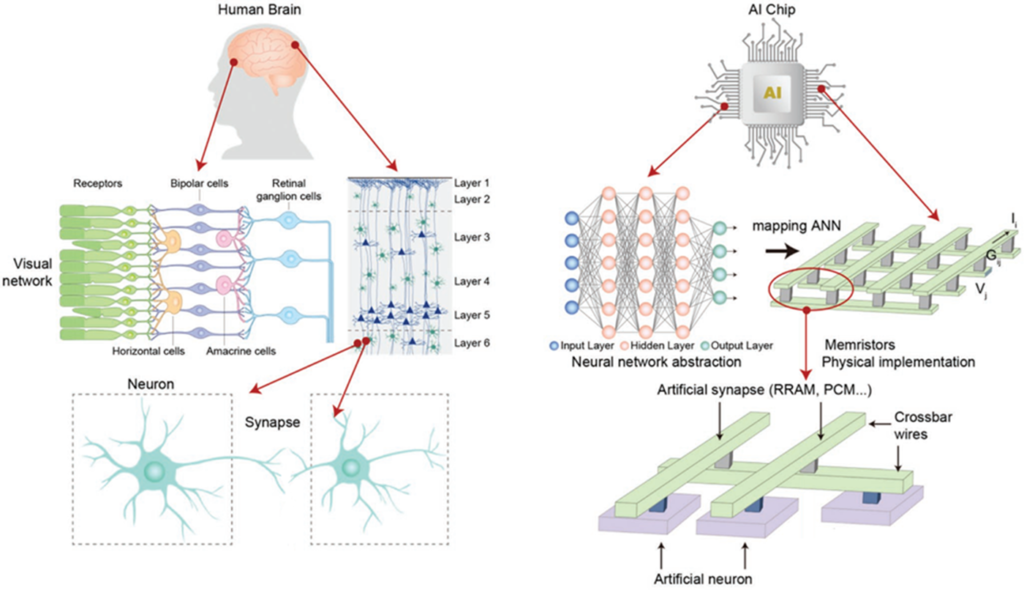
The advancements in neuromorphic computing are just starting to be explored, and it’s a promising field that could lead to new and innovative technologies shortly. However, it is still in its early stages of development, and there’s still a lot of research and development that needs to be done to realise its potential fully.
Neuromorphic Computing and Engineering
Neuromorphic computing and engineering are interrelated fields that aim to create computing systems that mimic the structure and function of the human brain. Neuromorphic engineering is designing and developing hardware and software that can replicate the brain’s functionality. This involves using specialised chips, called neuromorphic chips, that mimic the structure and function of neurons and synapses in the brain.
Overall, neuromorphic computing and engineering are interrelated fields that have the potential to revolutionise the way we process information and solve complex problems. However, it is still in its early stages of development, and there’s still a lot of research and development that needs to be done to realise its potential fully.