Cryptography: Securing Information in the Digital World
In the digital age, information security has become a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and governments. The rise of the internet and the increasing amount of sensitive information that is transmitted and stored online has made it easier for hackers to steal valuable data. As a result, cryptography has become an essential tool for securing information in the digital world.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice of protecting information by transforming it into an unreadable format. It is a technique that is used to ensure that only authorized parties can access sensitive data. Cryptography uses mathematical algorithms and protocols to convert plaintext into ciphertext. This process makes the data unreadable to anyone who does not have the proper key to decrypt it.
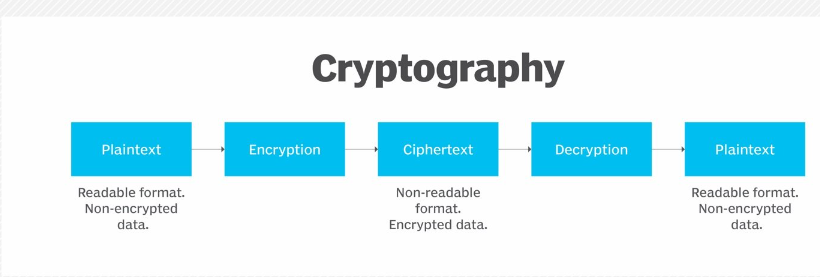
How Does Cryptography Work?
Cryptography works by using mathematical algorithms to transform plaintext into ciphertext. The process involves two steps: encryption and decryption.
Encryption: This is the process of converting plaintext into ciphertext. In encryption, a mathematical algorithm is used to transform the plaintext into an unreadable format. The resulting ciphertext can only be read by someone who has the decryption key.
Decryption: This is the process of converting ciphertext back into plaintext. In decryption, the decryption key is used to transform the ciphertext back into its original plaintext format.

Types of Cryptography
There are two main types of cryptography: symmetric-key cryptography and public-key cryptography.
Symmetric-Key Cryptography: Symmetric-key cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This means that both parties must have the same key to communicate securely. The most common symmetric-key cryptography algorithm is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Public-Key Cryptography: Public-key cryptography uses two different keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt the data, and the private key is used to decrypt the data. This means that anyone can encrypt the data, but only the person with the private key can decrypt it. The most common public-key cryptography algorithm is the RSA algorithm.
Applications of Cryptography
Cryptography has many applications in the digital world. Some of the most common applications include:
Secure Communication: Cryptography is used to ensure that communication between two parties is secure. This is essential for online transactions, email communication, and messaging apps.
Data Protection: Cryptography is used to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. This includes personal information, financial information, and medical records.
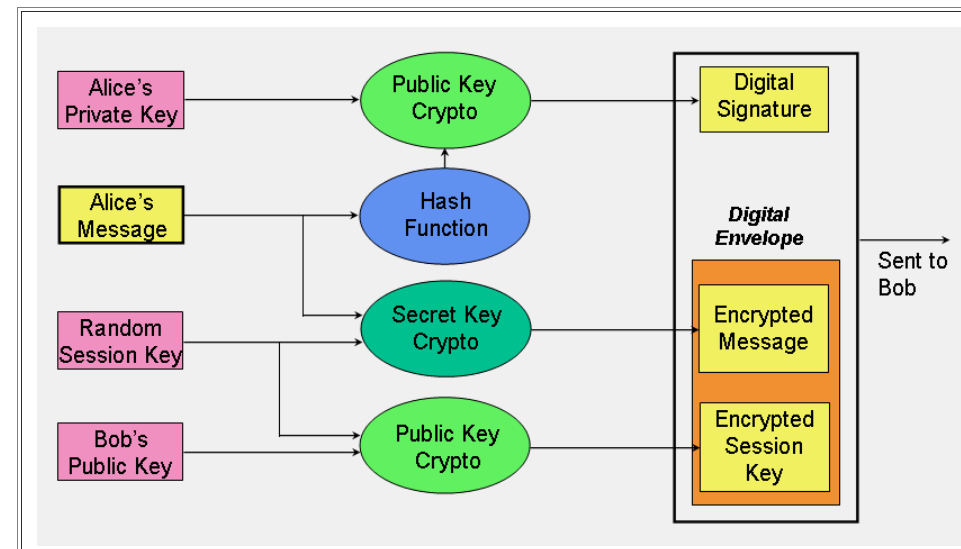
Digital Signatures: Cryptography is used to create digital signatures, which are used to verify the authenticity of digital documents.
Benefits of Cryptography
- Security: The primary benefit of cryptography is that it provides a secure method for protecting sensitive data. By encrypting data, it becomes unreadable to unauthorized parties. This ensures that the data remains confidential and cannot be accessed or tampered with by hackers or other unauthorized parties.
- Authentication: Cryptography provides a way to verify the identity of users, devices, and services. This is done through digital signatures, which provide a secure way to confirm the authenticity of data.
- Integrity: Cryptography ensures the integrity of data by providing a mechanism to detect any modifications made to the data during transmission. This ensures that the data is not tampered with and remains intact.
- Non-Repudiation: Cryptography provides a mechanism for preventing the denial of sending or receiving data. This is done through digital signatures, which ensure that the sender cannot deny having sent the data and the receiver cannot deny having received it.
- Compliance: Cryptography is often required by regulatory bodies and industry standards to ensure compliance with data security requirements. This is particularly important for organizations that handle sensitive data, such as financial institutions and healthcare providers.
Disadvantages of Cryptography
- Complexity: Cryptography is a complex field that requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Implementing cryptography correctly can be challenging, and any mistakes can lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Key Management: Cryptography requires the management of encryption keys, which can be challenging, particularly in large organizations. Keys need to be protected and stored securely, and proper key management procedures need to be followed to ensure the integrity of the encryption process.
- Performance: Cryptography can have an impact on performance, particularly for resource-constrained devices. Encryption and decryption can take up significant processing power and can slow down devices, leading to slower performance.
- Cost: Implementing cryptography can be expensive, particularly for organizations that require specialized hardware and software to implement encryption and decryption processes.
- Human Error: Cryptography relies on human input for key management and other processes. Human error can lead to security vulnerabilities, such as using weak passwords or storing encryption keys insecurely.
Conclusion
Cryptography plays a vital role in securing information in the digital age. It is a technique that is used to ensure that only authorized parties can access sensitive data. Cryptography uses mathematical algorithms and protocols to convert plaintext into ciphertext, making the data unreadable to anyone who does not have the proper key to decrypt it. There are two main types of cryptography: symmetric-key cryptography and public-key cryptography. Cryptography has many applications in the digital world, including secure communication, data protection, and digital signatures. In conclusion, cryptography is an essential tool for ensuring the security of information in the digital age.
