3D printing is a technology that enables the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital model. The process starts by creating a digital model of the object using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This digital model is then sliced into thin layers and sent to a 3D printer where each layer is printed and then stacked on top of one another to create the final object.
There are various types of 3D printing technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), PolyJet, and Directed Energy Deposition (DED), among others. Each of these technologies has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and they are used to create objects from a variety of materials including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even human tissues.

The applications of 3D printing are numerous and cover a wide range of industries including healthcare, aerospace, automotive, construction, and many more. In healthcare, 3D printing has been used to create prosthetics, implants, and even human organs. In aerospace, 3D printing is being used to create complex parts for aircraft and rockets, reducing the time and cost of production. In the automotive industry, 3D printing is being used to create prototypes, custom parts, and even entire cars.
With its numerous applications, 3D printing is set to play a crucial role in shaping the future of a wide range of industries and will continue to have a significant impact on our daily lives.
Applications of 3d printing:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates a three-dimensional object by layering material based on a digital model. The technology has been used in a wide range of industries, including engineering, architecture, manufacturing, and medicine, among others. Here are some of the most prominent applications of 3D printing.
Manufacturing: 3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling companies to produce complex parts and prototypes quickly and at a lower cost. This has led to an increase in innovation and product development, as well as a reduction in production time and costs.
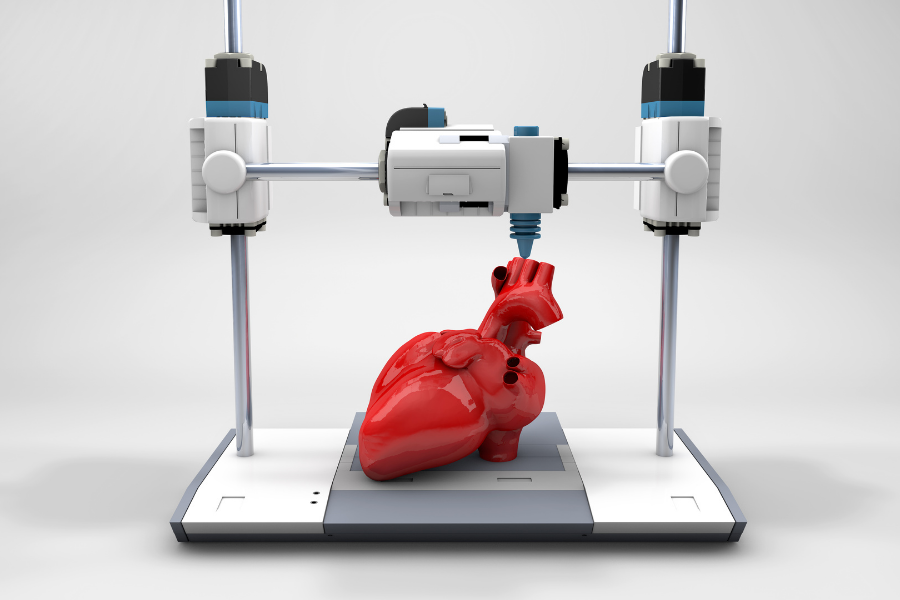
Healthcare: In the medical field, 3D printing has been used to create customized prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools. For example, doctors can use 3D printing to create a model of a patient’s heart to plan for a complicated procedure, or to create a customized prosthetic limb.
Architecture: 3D printing has been used in the construction industry to create scale models, prototypes, and full-sized building components. This has allowed architects and engineers to test designs and make changes before construction begins, resulting in more efficient and effective building processes.
Education: 3D printing has been used in education as a tool for teaching students about design, engineering, and manufacturing concepts. It allows students to experiment and create prototypes, which can help to increase their creativity and problem-solving skills.
Art: 3D printing has been used in the creation of art, including sculptures and jewelry. It has allowed artists to create complex shapes and designs that would have been difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, 3D printing has been used to produce complex parts for spacecraft and aircraft, reducing the time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing processes.
Consumer goods: 3D printing has been used to create a variety of consumer goods, including toys, phone cases, and even furniture. This has allowed for greater customization and personalization of products, and has made it possible to produce small batches of products at a lower cost.
Food: 3D printing has been used to create food, such as desserts and chocolate, allowing for greater creativity and innovation in the culinary arts.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of 3D printing. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that new applications will emerge, transforming the way we live, work, and play.
Pros:
Customization: 3D printing offers the ability to create customized products with intricate designs and shapes that would be difficult to produce with traditional manufacturing methods.
Speed and Efficiency: 3D printing can greatly reduce the time required for product development and prototyping. The speed of the printing process and the ability to quickly iterate designs makes it a valuable tool for product development.
Cost Savings: By reducing the need for expensive tooling and molds, 3D printing can lead to significant cost savings in product development and production. It can also allow companies to produce small quantities of parts at a lower cost, reducing the need for large production runs.
Sustainability: 3D printing produces less waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods and has the potential to reduce the need for shipping products long distances.
Cons:
Quality and Durability: While 3D printing has come a long way, the quality and durability of 3D printed parts can still be an issue compared to traditionally manufactured parts.
Material Options: Currently, there are limited options for materials that can be used in 3D printing, and the cost of these materials can be high.
Post-Processing: 3D printed parts often require additional post-processing, such as sanding or painting, to meet desired specifications.
Limited Scale: Currently, the size of parts that can be produced with 3D printing is limited. While large-scale 3D printers have been developed, they are still relatively expensive and less widely available.
While 3D printing has many benefits and offers exciting possibilities, it’s essential to carefully consider the pros and cons before investing in this technology.
The future of 3d printing:
The future of 3D printing is looking very promising and holds a lot of potential for innovation and disruption across a wide range of industries. Here are a few ways that 3D printing is expected to continue to evolve and shape the future:

Increased production speed: With advances in technology, 3D printing is becoming faster and more efficient, allowing for quicker production times and larger quantities of printed parts.
Wider range of materials: 3D printing has traditionally been limited to certain types of materials, but with ongoing research and development, the range of materials that can be used for printing is expanding. This will increase the versatility of the technology and open up new applications.
Greater precision: 3D printing technology is becoming increasingly precise and accurate, allowing for finer details and more intricate designs. This will enable the creation of higher-quality, more functional printed parts.
Wider adoption: As 3D printing technology becomes more accessible and affordable, it is expected to become increasingly widespread, particularly in manufacturing and industry. This will enable companies to reduce costs, streamline production processes, and create new products more quickly and efficiently.
Development of new business models: 3D printing has the potential to disrupt traditional business models and create new ones, such as on-demand production, local production, and even distributed production networks.
The future of 3D printing is exciting, as new developments in the technology are being made all the time. This includes the use of new materials, the development of multi-material printing, and the integration of 3D printing into other technologies such as AI and IoT. As 3D printing technology continues to advance, it is likely to have an even greater impact on our lives and the way we live and work.
