Title: An Examination of Cloud Networking: Structure, Mechanisms, and Safety
Overview of Cloud Networking
The architecture, implementation, and management of networks have changed dramatically as a result of cloud networking. It uses the concepts of cloud computing to provide services and network infrastructure that are affordable, adaptable, and scalable. We’ll dive into the world of cloud networking in this in-depth guide, covering its architecture, important technologies, security issues, and practical applications.
Cloud networking architecture:
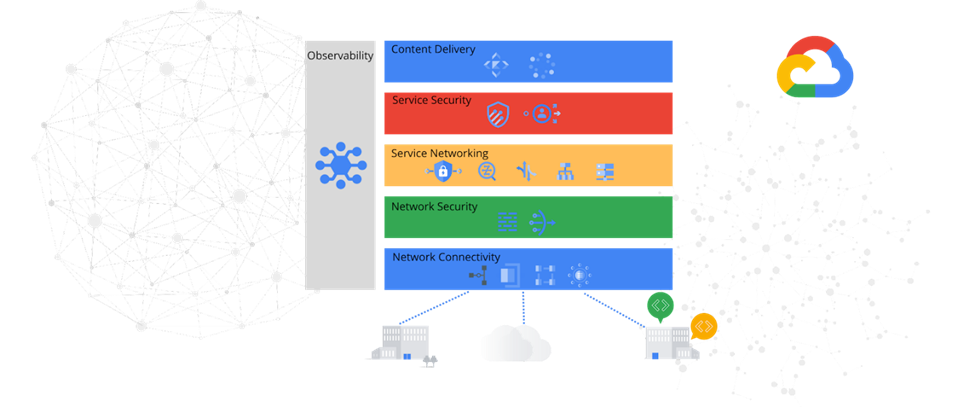
[1]
Virtualization, which abstracts physical network resources and offers them as on-demand services, is the fundamental idea behind cloud networking. Typically, cloud networking architecture is made up of the following essential elements:
1. Virtualized Infrastructure: The foundation of cloud networking is virtualized infrastructure, which abstracts physical network components like firewalls, switches, and routers into virtual entities. This makes it possible to manage and allocate network resources dynamically in response to demand.
2. Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Offering centralized control and programmability of network infrastructure, SDN is a crucial technology that facilitates cloud networking. SDN enables dynamic configuration and network traffic flow optimization by separating the control plane from the data plane.
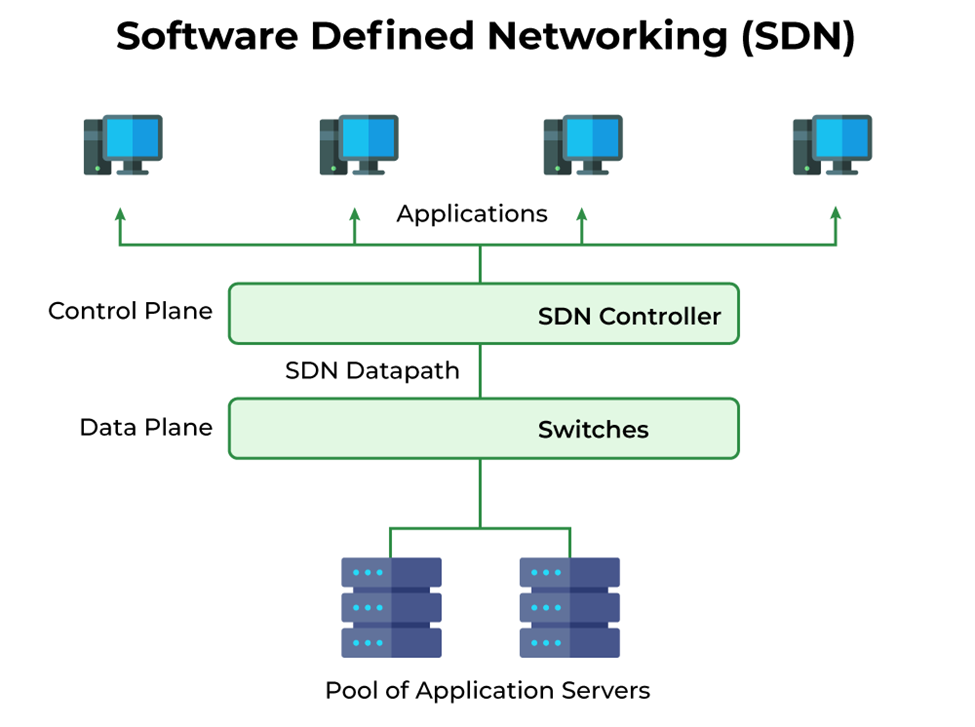
[2]
Importance of SDN :Better Network Connectivity: Sales, services, and internal communications all benefit greatly from SDN’s improved network connectivity. SDN additionally helps in quicker information sharing. Better Application Deployment Software-defined networking can speed up the deployment of new applications, services, and numerous business models. Better Security: Programming characterized network gives better perceivability all through the organization. Administrators can make separate zones for gadgets that require various degrees of safety. SDN networks give more opportunity to administrators. Better Control with Fast: Programming characterized organizing gives preferred speed over other systems administration types by applying an open standard programming based regulator.
3. Network function virtualization, or NFV, is a technology that enables software-based instances of network functions like intrusion detection systems, load balancers, and firewalls to operate on commodity hardware. This improves network service deployment’s scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
4. Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs): VPCs let businesses divide their network resources and impose security regulations by offering segregated virtual network environments inside a public cloud infrastructure. VPCs take advantage of the cloud’s scalability and agility to provide the advantages of private networking.
5. Edge Computing: As real-time applications and Internet of Things (IoT) devices proliferate, edge computing is becoming an essential part of cloud networking. By bringing computational resources closer to end users or devices, edge computing lowers latency and uses less bandwidth.
Essential Cloud Networking Technologies:
The functionality and capabilities of cloud networking are supported by multiple technologies:
- Virtualization: Resource abstraction and optimization are made easier by the creation of virtual network devices and services made possible by virtualization technologies like hypervisors and containerization platforms.
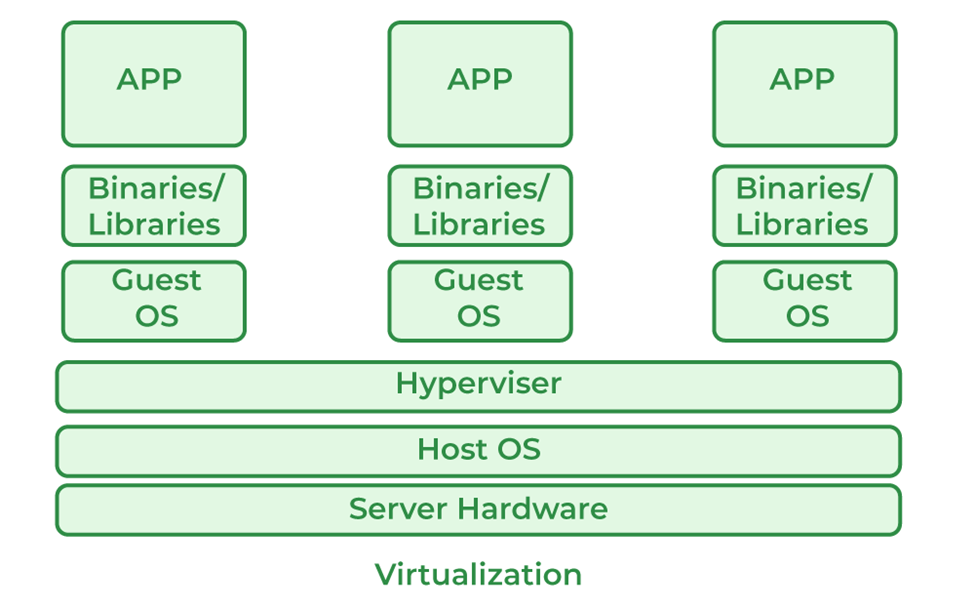
[3]
2. Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN controllers offer centralized network infrastructure management and orchestration, facilitating dynamic configuration and policy enforcement. One example of an SDN controller is OpenFlow-based controller.
3. Network function virtualization, or NFV, allows for on-demand provisioning and scalability by virtualizing network functions and services. Examples of NFV platforms are OpenStack and VMware NSX.
4. Container Networking: Platforms for container orchestration, such as Kubernetes and Docker Swarm, offer networking features for applications running in containers. These features facilitate communication among containers and allow for service discovery.

[4]
5. Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN): By utilizing the principles of software-defined networking to dynamically route traffic over multiple WAN links, SD-WAN solutions improve branch offices’ and remote sites’ connectivity and performance.
A Look Into Security Aspects of Cloud Networking
Because cloud environments are shared and dynamic, security in cloud networking is critical. Important security factors consist of:
1. Data encryption: Preventing unwanted access and interception of sensitive information is made easier by encrypting data both in transit and at rest. In cloud networking, IPsec and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are two popular encryption protocols.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access cloud resources requires the implementation of strong IAM policies and access controls. Two crucial IAM mechanisms are role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
3. Network Segmentation: By separating network traffic into isolated segments and utilizing virtual LANs (VLANs) or network security groups (NSGs), it is possible to contain potential breaches and inhibit lateral network movement.
4. Early detection and response to security incidents are made possible by continuous network traffic monitoring and the logging of security events. Platforms for security information and event management, or SIEM, offer centralized logging and analysis features.
Applications of Cloud Networking in the Real World:
Cloud networking finds use in a range of sectors and scenarios:
1. Business networking: Businesses use cloud networking to establish scalable and resilient network infrastructure, allow employees to work remotely, and connect geographically dispersed offices.
2. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): By caching content at edge locations to lower latency and boost performance, CDNs leverage cloud networking to effectively deliver content to users worldwide.
- IoT and Edge Computing: Real-time applications and analytics at the network edge are supported by cloud networking, which makes connectivity and data processing possible for IoT devices and edge computing environments.
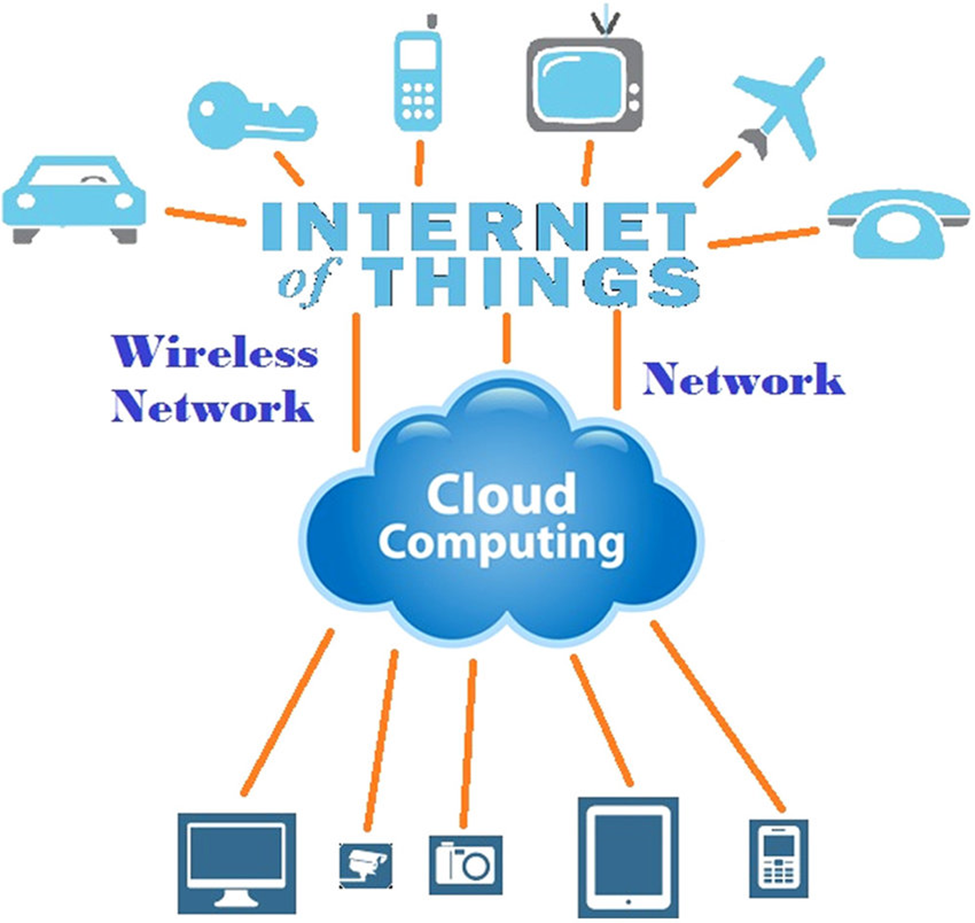
[5]
4. Telecommunications: Cloud networking is used by telecom providers to offer network services like software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN), virtual private networks (VPNs), and voice over IP (VoIP).
In summary:
Unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and agility in the deployment and management of network infrastructure and services are provided by cloud networking. Through the utilization of virtualization, SDN, NFV, and other essential technologies, establishments can construct robust and safe networks that fulfill the requirements of contemporary digital commerce. However, to reduce risks and protect sensitive data in cloud environments, strong security measures and best practices are necessary. Cloud networking will become more and more important in determining the future of networking services and infrastructure as cloud adoption increases.
References
| [1] | 03 06 2024. [Online]. Available: https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/developers-practitioners/6-building-blocks-cloud-networking-networking-architecture. |
| [2] | “geeks for geeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-defined-networking/. [Accessed 03 06 2024]. |
| [3] | “geeksforgeeks,” [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/virtualization-cloud-computing-types/. [Accessed 03 06 2024]. |
| [4] | [Online]. Available: https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=FamCBqlq&id=C4A5A7014D3C447501EA18A60364F660FA1DE3E7&thid=OIP.FamCBqlqK17LbrrOqa0VxAHaDt&mediaurl=https%3a%2f%2fwww.cloudoye.com%2fimages%2fblog%2fContainerization+in+Cloud+Computing.JPG&exph=400&expw=. [Accessed 03 06 2024]. |
| [5] | [Online]. Available: https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=3OBtDz8U&id=F828A285C9EC4F1640E0B3B22C47E5663F2643B3&thid=OIP.3OBtDz8U5LU5sqesEGfdBgHaHA&mediaurl=https%3a%2f%2fwww.researchgate.net%2fprofile%2fKostas_Psannis%2fpublication%2f311065854%2ffigure%2ffig3. [Accessed 03 06 2024]. |
