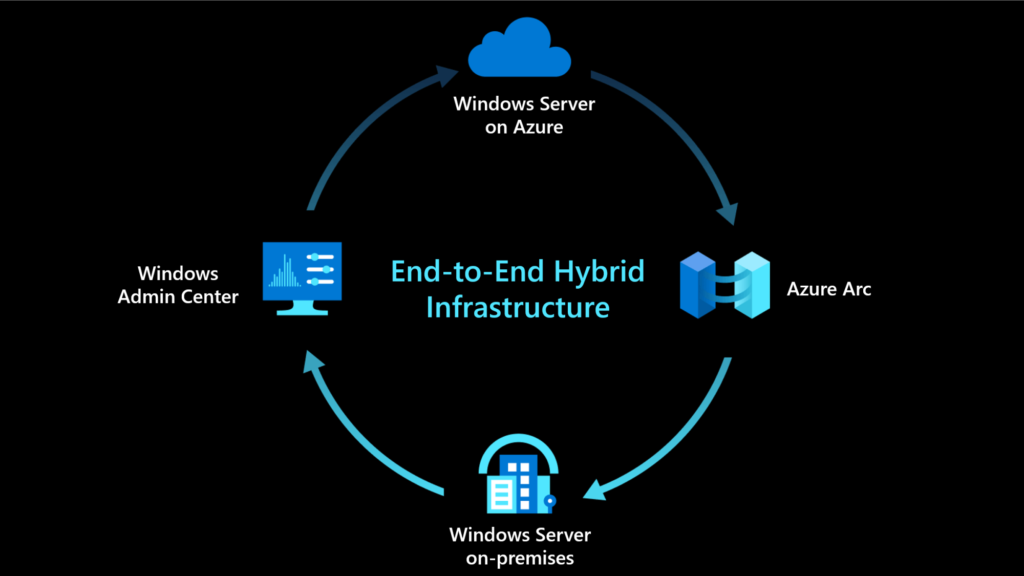
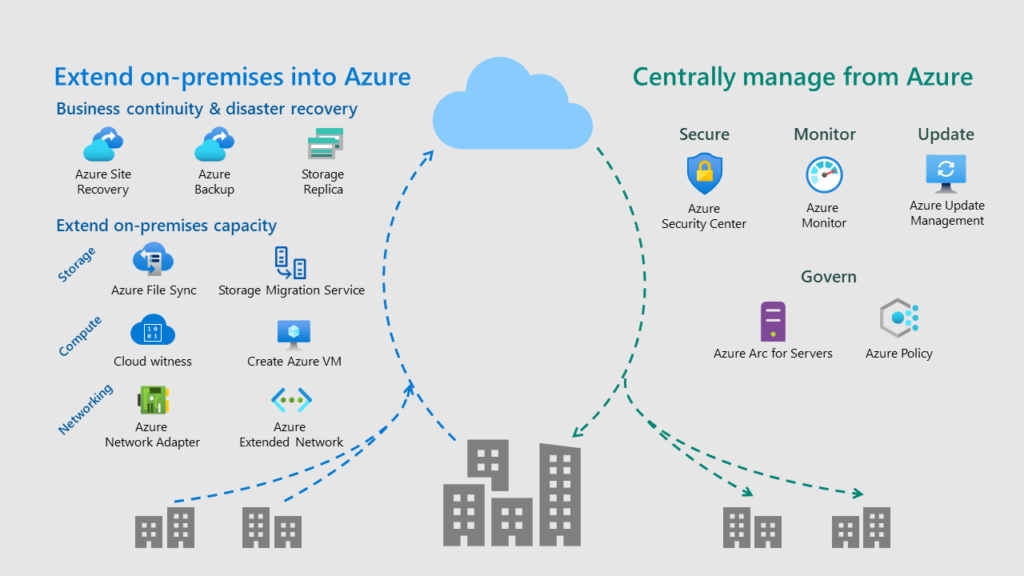
Harnessing the Power of Windows Server in the Cloud: A User-Friendly Guide
In the rapidly evolving landscape of IT infrastructure, the combination of Windows Server with cloud technology has become a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. As more organizations transition to the cloud, the integration of Windows Server offers a robust foundation for improved scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the marriage of Windows Server and the cloud, unraveling the multitude of benefits and providing insights into best practices for a smooth integration.
Demystifying Windows Server in the Cloud
Windows Server Essentials:
Windows Server is the unsung hero of many enterprises, offering a comprehensive suite of services, from file sharing and user management to network services and security features. When these capabilities extend to the cloud, businesses can unlock the full potential of Windows Server in a scalable and cost-effective manner.
Cloud Dynamics:
The cloud, with its on-demand resources and pay-as-you-go model, transforms traditional IT operations. It allows businesses to scale their infrastructure dynamically, responding to changing demands without the need for significant upfront investments. Windows Server, when hosted in the cloud, aligns perfectly with this paradigm, offering an agile and adaptable solution.
Benefits of Marrying Windows Server with the Cloud
1. Scalability:
One of the standout advantages of deploying Windows Server in the cloud is scalability. Cloud environments empower businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down based on workload fluctuations. Windows Server seamlessly adapts to these changes, ensuring optimal performance without the need for extensive manual adjustments.
2. Cost Efficiency:
Cloud computing introduces a cost-efficient model with its pay-as-you-go approach. Windows Server in the cloud follows suit, enabling organizations to optimize costs by only paying for the resources they use. This marks a significant departure from traditional server setups that often involve substantial upfront costs.
3. Flexibility and Mobility:
With Windows Server in the cloud, the geographical constraints of traditional server setups are eliminated. Users can access resources and applications from anywhere, promoting flexibility and mobility. This becomes particularly relevant in the context of the modern workforce, which often operates across different locations.
4. Enhanced Security:
Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures to safeguard their infrastructure. When Windows Server is deployed in such environments, businesses benefit from the provider’s robust security protocols. Additionally, Windows Server itself brings a suite of security features, creating a layered defense against potential threats.
Integration with Popular Cloud Platforms
1. Microsoft Azure:
As the cloud arm of Microsoft, Azure offers seamless integration with Windows Server. Organizations leveraging Azure can deploy virtual machines running Windows Server, utilize Azure Active Directory for identity management, and take advantage of various Azure services to enhance their infrastructure.
2. Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS provides a robust platform for hosting Windows Server instances in the cloud. Users can benefit from AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for scalable virtual servers, Amazon RDS for managed databases, and other AWS services to build a comprehensive and scalable IT environment.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP also supports Windows Server workloads, offering solutions for compute, storage, and networking. Businesses can harness the power of GCP’s global infrastructure to run Windows Server applications with the flexibility and scalability required for modern IT environments.
Best Practices for a Seamless Integration
1. Plan for Hybrid Deployments:
Consider a hybrid deployment strategy that combines on-premises servers with cloud resources. This approach allows for a gradual transition to the cloud while maintaining certain workloads locally.
2. Optimize Resource Usage:
Regularly assess resource usage and optimize configurations to ensure cost-effectiveness. Cloud platforms often provide tools for monitoring and adjusting resource allocations based on actual usage.
3. Embrace Automation:
Leverage automation tools to streamline deployment and management processes. Automation enhances efficiency, reduces manual errors, and ensures consistent configurations across the infrastructure.
4. Implement Robust Security Measures:
Adopt a comprehensive security strategy that combines built-in security features of Windows Server with the security offerings of the chosen cloud provider. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
5. Ensure Regular Backups:
Implement a robust backup strategy to protect critical data. Most cloud providers offer backup solutions, and Windows Server has built-in features like Windows Server Backup to facilitate data protection.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Full Potential
The integration of Windows Server with the cloud heralds a new era in IT infrastructure management. Businesses can now enjoy the best of both worlds – the familiar and powerful capabilities of Windows Server complemented by the agility and scalability of the cloud. As organizations embark on this transformative journey, careful planning, adherence to best practices, and a commitment to ongoing optimization will ensure they harness the full potential of Windows Server in the cloud.
The synergy between these two technological stalwarts represents a cornerstone in building a resilient, efficient, and future-ready IT ecosystem. Embrace the power of Windows Server in the cloud, and let it redefine the way your organization operates in the digital realm. Whether you are a small business