Ever since the era of the personal computer began there has been debate on which operating system is better. Like the programmers prefer Linux for security and handling while gamers prefer windows whereas the industrials or professionals prefer macOS for better performance. To understand the difference between the file system of windows and macOS we must first understand what is a file system?
Have you ever wondered where the saved files go, or how is it accessed? Every file has a designated path and directory dedicated to it. These are known as the file system. If we talk about accessing like downloaded files in windows, we must go through a long route like my PC then the library, and then downloads whereas in macOS one needs just to click on download either from the menu bar or from anywhere. The outcome would still be the same. The filing structure is responsible for these access methods. But when there are so many ways of accessing one data how can we choose which is better or faster? What of the concern about data security? And the biggest question among the questions is how do file systems even work? Let us now discuss windows and macOS file systems and understand them even further.
File Systems in Windows:
Windows have a compound file system. It has two principal methods to maintain its file system. One is the file allocation table or FAT in short. The first repetition of the FAT system was named FAT12 with 12 denoting the number of bits that are inside the block. With passing time, the prior file system was taken over by the newer ones that were more efficient than the prior ones. For reference, we can see that FAT12 could support only 212 blocks whereas for the latest that is FAT32 can support 232 blocks which is a huge improvement. Though being one of the most widely used file systems in devices such as flash drives and DVDs, the FAT32 system is becoming obsolete as we progress toward Blu-ray discs and 1TB memory card sticks. FAT32 is being phased out in favor of the exFAT file system, which stands for “Extended File Allocation Table.”
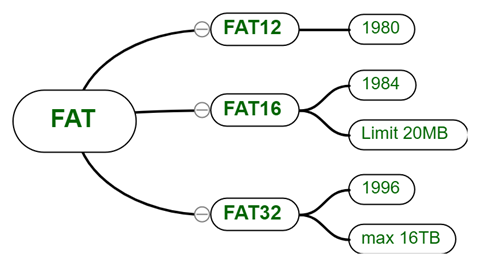
Fig. Link: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20200302205141/FAT-File-System-11.png
FAT32 is incompatible with macOS supporting devices and even in a Linux system, we would require special software to access the drive. But the new exFAT is compatible with macOS but still needs special software for Linux.
NTFS:
Another file system that was adapted by windows is New Technology File System, NTFS in short.
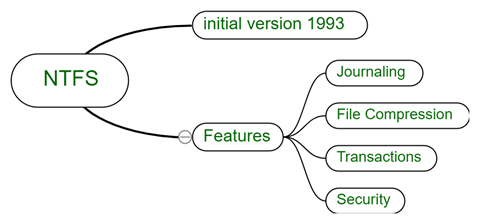
Fig. Link: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20200302205148/NTFS-File-System-11.png
NTFS is attempted to be made free from the compatibility limitations that FAT faces. Up until now, there have never been any specific limitations recorded in terms of size. Microsoft has done everything to make sure that NTFS fulfills modern-day technology. The NTFS file system can be read on Mac or Linux all the same.
ReFS:
The latest development in the file system has been ReFS that stands for Resilient File System. It was introduced along with windows 8 and it is available for the 10th version as well. This file system has a very different structure than other file systems we have discussed. Due to the new features of this file system, it has a very high tolerance to failures. The best feature is copied to the write feature. Because of this feature, no metadata can be changed in any way without the original data being copied. Since every time any changes occur in the data a new copy of the data is saved in a free area. This results in a large number of backups kept in various places that provide ease in data recovery.
HPFS:
The High-Performance file system was created as a server file system in collaboration between Microsoft and IBM. When compared to the FAT it had better performance. It attempts to arrange the file in continuous blocks, or at the very least to position its pieces as near together as possible. It begins with three control blocks; a boot, the super, and the spare block; that occupy 18 sectors. The residual storage space is split into bands of 8 MB respectively, which are made up of continuous sectors. For storing directories, a specific directory band in the middle of the disc is utilized, whereas the directory structure itself is a balanced tree with alphabetical entries.
File Systems in macOS:
Apple is well-known for creating intelligent and beautiful systems. So, how do we expect anything different from its file systems? Unlike Windows file systems there is no going into any partition to access any file. And there is no complicated code execution to access the file like in Linux. So, how do you access a file in macOS? Accessing a file in macOS is as simple as one can get. You just need to open the hard drive and there you can find everything in a single folder. Basically, there are two types of file systems utilized by the macOS. HFS+ was the first file system developed for macOS compatibility products but was superseded by the APFS.
Fig. Link: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20200302205146/HFS-File-System-11.png
But then HFS+ was not much help because most of the devices had compatibility with the Windows file system that happened to be incompatible with HFS+. So, it was replaced by the new and improved version named APFS.
APFS:
It is made to resolve the issues that were present in HFS+ and are developed to be compatible with modern flash drives and SSDs. This format also uses the COW method utilized by NTFS or ReFS in Windows. It copies the data that is changed to a free storage area saving the old version of data.

Fig. Link: https://blog.fosketts.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/APFS-Structure-500×354.png
The various information about the number of blocks, or the block is all saved in the container superblock. This format that is used by apple is very similar to the NTFS of windows. This latest format can read Windows and Linux supported devices as well but with the help of special software.
Conclusion:
After discussing all the file systems followed by both macOS and Windows we have a broader idea of how both works and their pros as well as limitations. An ideal file system must be the one that supports most of the devices not only their exclusive devices for the benefit of users. But macOS is slowly getting towards that ideal system without being the complicated system followed by Windows.
