Social Engineering
Social engineering is a term that is used for a variety of malicious activities achieved through human interaction. Psychological manipulations can be used to trick users into making security mistakes or providing confidential information.
In other words, Social engineering is the art of using human psychology rather than hacking techniques to gain access to buildings, systems, or data. For example, instead of trying to detect a software vulnerability, a social engineer might call an employee and involve an IT support technician to mislead the employee into revealing their password.
The success of social engineering techniques depends on the ability of attackers to manipulate victims to perform certain actions or provide confidential information. Social engineering is recognized today as one of the most serious security threats facing organizations. If your are facing such security threats please contact experts like BITS .
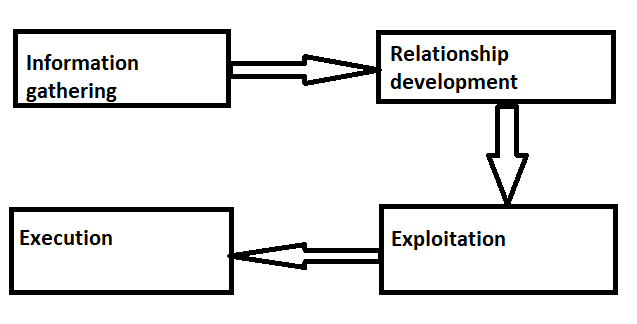
Social engineering phases
Types of social engineering attacks
Phishing
Phishing occurs when an attacker disguises himself as legitimate and fraudulently communicates with a victim from an often claimed or trusted source. It is usually in the form of an email, chat, web advertisement, or website designed to impersonate a real system, individual, or organization. In a phishing attack, the recipient is tricked into installing malware on the device or sharing personal, financial, or business information. Some ask end users to verify their account credentials and include a replica login page that includes the logo and brand to make it look legitimate. Some claim that the end user is the winner of the grand prize or lottery and demand access to a bank account where the prize can be delivered.
To host your emails and use the Google cloud on GSuite, please contact the Google partner “Benchmark IT Services”
Baiting
Trojan Horse Attack It works with physical media (such as pen drives) in the hope that human curiosity and greed will attract it. For example, attackers usually leave flash drives infected with malware – in suspicious areas that are sure to see potential victims. The house looks authentic, for example, showing a label as a company payroll. Victims become curious and inject it into a work or home computer, resulting in the automatic installation of malware on the system. This allows the hacker to access their network.
Quid pro quo
Quid pro quo includes hackers who request the exchange of important data or login credentials in exchange for services. For example, an end user may be called by a hacker who pretends to be a technical expert and offers free computer support or technical upgrades in exchange for login credentials.
Tailgating
Tailgating attack is an effort by cyber threat actors in social engineering in which they manipulate staff to help them obtain unwanted entry to the business premises. In a restricted area where access is regulated by software-based electronic devices, the intruder seeks entry. Because only the authorised individuals can obtain access, cybercriminals literally trick and deceive one of the authorised individuals by following the entry behind them.
Pretexting
To gain private information, pretexting is characterised as the activity of posing oneself as someone else. In certain examples, it will create a whole new identity and then use that identity to exploit the receiving of knowledge, rather than simply making a lie. Pretexting may also be used to impersonate persons in some occupations and positions they have never performed on their own.
Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
Some tips to stop/detect social engineering attacks
There is no precise and straightforward way for social engineering attacks to be carried out, although we may assume that the best way to protect against them is to use common sense. It could be an assault if anything looks odd. Some common indicators of social engineering attack:
- If you believe someone is trying to make you feel like you are the target of a social engineering assault, do not interact further with him.
- If it is someone you do not know who is calling you, hang up the phone.
- If you do not know anyone who is talking with you online, terminate the connexion.
- Delete untrusted emails.
- Any work-related attack, make sure you report it to your support team or security team right away.
- Be suspicious when Someone that induces an enormous sense of urgency to make you make a very swift and anyone demanding data that they do not have access to or may already know about.
Tips to prevent future social engineering attacks
Education
Ensure that you have a robust security awareness training curriculum to periodically update both the general phishing risks and the latest tailored cyberattacks to counter them. It is our primary task to live in a world where security is the most important thing. Go to work and do your best to encourage management to raise the security budget for greater protection.
Think before you click
To make you move first and consider later in phishing attacks, attackers employ a sense of urgency. Be sure to take a second to verify whether the source is legitimate first anytime you get an extremely urgent, high-pressure call. The easiest approach is to find another contact mechanism that is distinct from where the message is from, such as calling the user to see whether an urgent response was sent to you or by an attacker.
Strong passwords
For your accounts, build a secure password and never reveal it. No company will call you and ask for your password at any time. If this is done by another, it is an assault.
Do not share too much
All you have shared with others raises the probability of attack detection and enables the intruder to learn more about you. To build a full image of you, even revealing tiny things of yourself over time can be added together. It is also convenient for adversaries to uncover and mislead you to do just what they want from you.
Verify contacts
Often, you might be called by certain organisations like bank, credit card firm, cell service provider or others to get any information or problem, for legal purposes. If you have any questions as to whether a request for information is genuine, do not offer any personal information and recommend going to an agency and asking the person for their name and extension number. This way, while it seems like a challenge, protecting your identity and sensitive information is worth any additional step.
