“Hello my fellow technology enthusiasts, I wanted to speak about a subject that is recognized in its true nature by all but seldom understood. The topic is “Cloud Computing” and will be addressed in series. So, let ‘s dive into the world of cloud computing. In this blog I am going to focus on Hypervisor which include:
What is Hypervisor
Types of hypervisors
Benefits of using hypervisors
Security risks
What is Hypervisor
Hypervisor is a type of virtualization software used to separate and distribute resources on different pieces of hardware in cloud storage. Hypervisor is a virtualization strategy for hardware that enables multiple guest operating systems (OS) to operate concurrently on a single host device. A Hypervisor is also sometimes called a virtual machine manager (VMM).
The operating systems are isolated by the hypervisor from the primary host machine. A hypervisor ‘s role is to cater to and successfully handle the needs of a guest operating system. Each virtual machine is autonomous, and while they operate on the same host machine, they do not compete. They are not related to one another in any way. The remaining computers continue to operate normally, even at times when one of the virtual machines fails or experiences certain challenges.
In cloud computing, the function of hypervisors is not only limited to control over the data centre, they are now used as “Storage Hypervisors.” The Database Hypervisors functionality is used to build a consolidated storage pool using virtual storage services. This eliminates the question about the storage’s physical location. The ability of the host system to run multiple guest VMs by virtualizing the server is significantly improved by the introduction of hypervisors. Hypervisor makes the VM self-governing and independent of the hardware of the simple server. Click here for general IT Support services for Businesses
Types of hypervisors
Type-1 Hypervisor
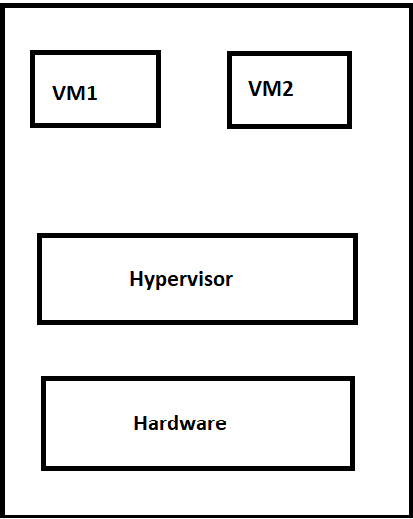
“Hypervisor operates directly on the underlying host machine. It is also referred to as” Native Hypervisor “or” Bare Metal Hypervisor”. No base server operating system is needed. It has direct access to hardware resources. VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer, and Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor are examples of form 1 hypervisors.
Type-2 Hypervisor
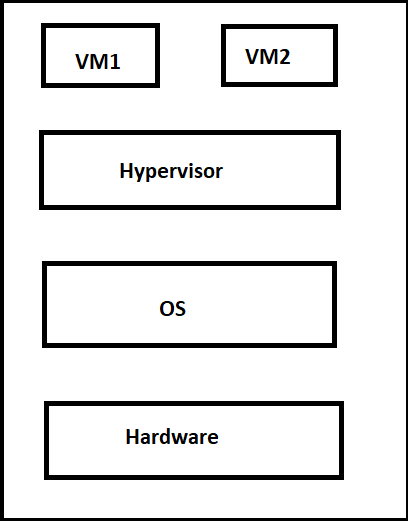
A host operating system operates on an underlying host system. It is often referred to as ‘Hosted Hypervisor.’ Essentially, a programme built on an operating system. Hypervisor asks the operating system to make hardware calls. VMware Player or Parallels Desktop are examples of type 2 hypervisor. Hosted hypervisors on endpoints such as PCs are also found.
Click here to purchase any IT related software or hardware
Type 1 vs Type 2 Hypervisor
Choosing the right type
A comparison of their efficiency metrics is one of the easiest ways to assess which hypervisor suits your needs. These include CPU overhead, full host and guest memory volume, and virtual processor support.
You can go for one of the Type 2 hypervisors for personal use and smaller deployments. If budget is not an issue, every feature you need will be provided by VMware. Otherwise, the VirtualBox Oracle VM is a hypervisor that will have much of the commonly required functionality.
Even though type 1 hypervisors are the way to go, before deciding, you need to take multiple variables into account.
The price of a hypervisor: The hardest part of choosing a hypervisor is to find the best balance between cost and features for many consumers. Although a variety of entry-level options are free, or essentially free, rates can be staggering at the other end of the market. Frameworks for licencing often vary, so it is important to be mindful of precisely what you get for your money.
Performance of virtual machines: The output of their physical counterparts can be matched or surpassed by virtual networks, at least in relation to the programmes within each server. Benefit is all beyond reaching this benchmark.
Click here for cloud based solutions for the businesses like Google, AWS and Azure
Benefits of using hypervisors
Data replication
It is hard to duplicate and recreate virtual machines. Replication approaches dependent on storage enable the full volume of all the virtual machines on the cloud to be repeated. If your server has several virtual machines, so replicating the whole volume takes large volumes of storage space.
For straightforward cloning and duplication, hypervisors may be used. Hypervisor-based replication is faster and more cost-effective than any other virtual machine replication process.
Speed
Unlike bare-metal servers, hypervisors allow virtual machines to be built instantly. This makes it easier for complex workloads to supply resources as needed.
Server consolidation
Inbuilt graphical dashboards are also offered by Hypervisors. For improved visibility, you can also download additional enhancements to the inbuilt dashboards. This ability helps you to centrally consolidate and control the servers even though they are running multiple operating systems.
Flexibility
Bare-metal hypervisors allow several hardware types to operate operating systems and their related applications because the hypervisor distinguishes the OS from the underlying hardware, so the OS no longer depends on hardware devices or drivers.
Desktop virtualization
For desktop virtualization, hypervisors may also be used effectively. On a computer, you can conveniently run a virtual machine, and the machine replicates the actual desktop of the user. This allows employees to access their workstations through client devices over the Internet, allowing them to work remotely.
Security risks
Security researchers believe that hackers will inevitably find a flaw in the programme, while hypervisors are usually well-protected and stable. Few reports of hypervisor hacks have been published so far; but cyber criminals might, in principle, run a programme that can break out of a VM and communicate directly with the hypervisor. From there, from access rights to computational power, they can monitor anything.
Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
Since hypervisors distribute VMs via the company network, if you do not have the correct protections in place, they may be susceptible to removing intrusions and denial-of-service attacks.
Conclusion
Enhanced workloads can be managed by a hypervisor. You can quickly turn such virtual machines onto any other physical nodes in a situation where a single hardware node gets overheated. Virtualization also provides other advantages of protection, debugging and support. For hackers, a Hypervisor is a natural target because its design controls all the hardware resources while managing all the virtual machines residing on it.

1 Comment
Pingback: Google Compute Engine: Machine Types and Feature of GCE – Let's Tech It Easy