What is Cache?
A cache is a reserved place for storage that stores temporary information to help launch websites, browsers, and applications faster. Caching is the method of momentarily storing data so that it does not need to be updated each time by the web, application, or smartphone.
Laptops, tablets, phones, no matter what. To store this sort of data for easy access, all our devices have some degree of reserved space.
If you need any assistance regarding such type of issues contact experts like Benchmarkitservices
Browser cache
To view the websites it visits, a browser cache stores the files needed by your browser. This contains elements such as the HTML file, along with CSS style sheets, JavaScript’s, cookies, and photos that define the website.
When you visit Amazon, for instance, it downloads all the images associated with the product sites you are viewing, the HTML and other script files necessary to make the sites, and layout details, such as your login information and shopping cart content. These files are saved by browsers until their TTL (Time to Live) expires or until the hard disc cache is complete. If needed, users can still clear their tab cache.
A website that loads will load after a browser cache is removed, as if it was the first time the user accessed the website. On the first time if anything has been loaded improperly and stored improperly, clearing the cache will cause it to load properly. Clearing one’s tab cache, however, will briefly delay page load times as well.
Click here for general IT Support services for Businesses
Application cache
Usually, apps also hold their own cache. Apps save files and data that they consider essential, like browsers, so they can easily reload the data as needed. However, each app is different, because the type of data it caches can vary, but may include images, thumbnails of videos, search history, and other user preferences.
Benefits of caches
- The key advantage of a cache is that it boosts the system’s performance. For example, by saving local copies of website content, your browser only needs to import the information when you first visit it and can load local data when you subsequently visit it.
- Caching reduces the use of bandwidth, thereby reducing network traffic and reducing network congestion.
- Recent and commonly used data is saved in the cache for users to further boost performance. This not only helps it to run quicker as described before, but in some situations, it can allow apps to work “offline.” For example, if you do not have internet access, even without a link, an app can rely on cached data to continue to work.
- For later usage, they store data. In only uploading files once, there is a lot of usefulness. If a copy of a file is saved in the cache, the software does not have to waste time, battery power, and other second-time transfer resources. Instead, it is only necessary for the application to import updated or new files.
Downsides of cache
- The major downside to caching is that a consumer might be staring at stale results, which may arise due to a lack to proper proxy updating.
- They will take up a lot of room for storage. A cache is a limited archive of files used by an app, in theory. Some caches, however, can grow incredibly large and restrict the free space on your computer. The files can be deleted, and a significant volume of memory restored by deleting the cache.
- While caching can boost web browsing speed, since web pages are stored in the browser, it can also make you exposed to hackers, because they are likely to contain private and sensitive information.
- A broken cache will cause the app to behave poorly. If a file saved in the cache contains something wrong, it may cause the software to view data wrongly, bug or even crash. That is why clearing the cache is a common solution for browser problems.
- Caches can prevent the current update of a web page or other data from being loaded by apps.
- Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
Should I clear the cache?
If you find that the memory of your mobile device is exhausted from cached records, then you possibly should clear it. Cached info, after all, is not essential to the success of an app or website, it just ensures that it will have to reload the files on it.
But it is not a lasting solution to continuously clear your cache, because you can inevitably reopen apps and revisit websites at some stage. The information will be re-cached, and it will resume the loop.
The cache can grow very large based on your settings and can use a lot of storage space on your computer. And that is even though you never access those websites again. The more data that is stored in the cache, the slower the site can be browsed by your computer. Deleting cache data helps to troubleshoot issues, helps to improve web page loading time, and improves your computer’s performance.
Since the cache saves website records, you can say which places have been visited in the past from the stored information. Clearing the cache may also be interesting for you in terms of privacy and computer protection.
How to clear cache?
Click her to clear cache on Safari web browser
Click her to clear cache on Firefox web browser
In Chrome
- On your computer, open Chrome.
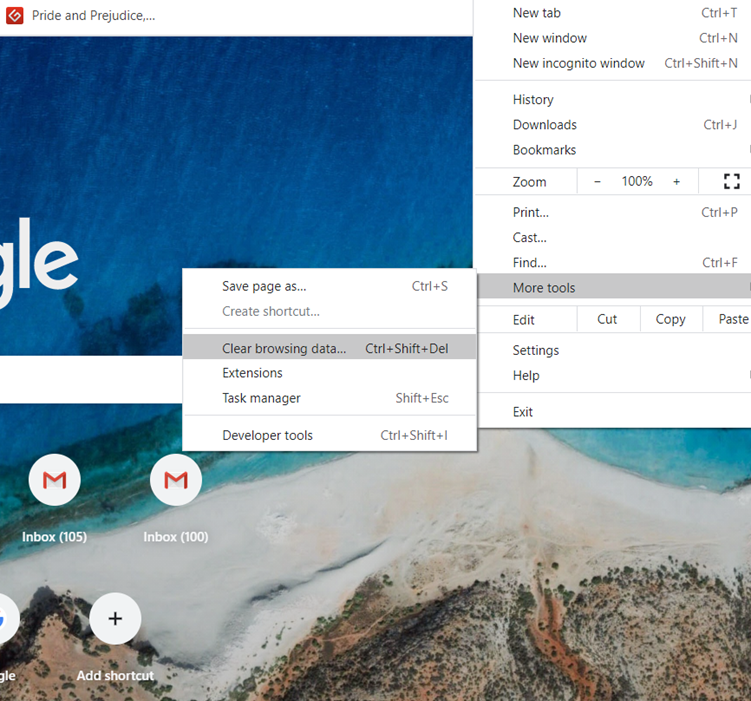
- At the top-right, click More
.
- Click More tools
Clear browsing data.
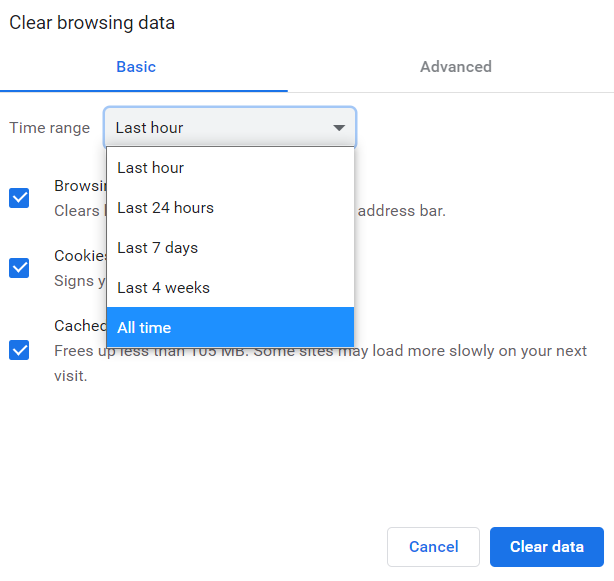
- At the top, choose a time range. To delete everything, select All time.
- Next to ‘Cookies and other site data’ and ‘Cached images and files’, tick the boxes.
- Click Clear data.