Introduction
Application security refers to security measures used at the application level to prevent data or code theft or hijacking. It includes security considerations taken during application development and design, as well as strategies and procedures for safeguarding deployed applications.
What is the definition of application security?
Application security, abbreviated AppSec, encompasses all duties that help development teams implement a secure software development life cycle. Its goal is to enhance security practises and, as a consequence, to detect, rectify, and, ideally, to avoid application security issues. It includes the requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance phases of an application.
Application security may comprise hardware, software, and methods for identifying and mitigating security risks. Hardware application security is a term that refers to a router that prevents a computer’s IP address from being viewed over the Internet. However, application-level security measures, such as an application firewall that imposes strict constraints on which actions are permitted and prohibited, are frequently included into the programme. A process is an example of an application security routine that incorporates protocols such as frequent testing.
Why is Application Security Critical?
Due to the fact that modern apps are usually accessible across several networks and connected to the cloud, they are more susceptible to security threats and breaches. There is growing demand and motivation to ensure security not only at the network level, but also at the application level. One reason for this might be because hackers are concentrating their efforts on applications more than in the past. Application security testing can identify application-level issues, contributing in their prevention.
The more quickly and thoroughly you can identify and address security risks during the software development process, the safer your business will be. Because everyone makes errors, the challenge is to detect them quickly.
Application security technologies that connect with your development environment may significantly simplify and streamline this process and workflow. These techniques are particularly advantageous for compliance audits, since they may help save time and resources by identifying concerns before the auditors do. The changing nature of corporate application development over the last many years has contributed in the industry’s fast growth.
Application Security Types
Application security features include authentication, authorization, encryption, logging, and application security testing. Additionally, developers can utilize code to mitigate application security issues.
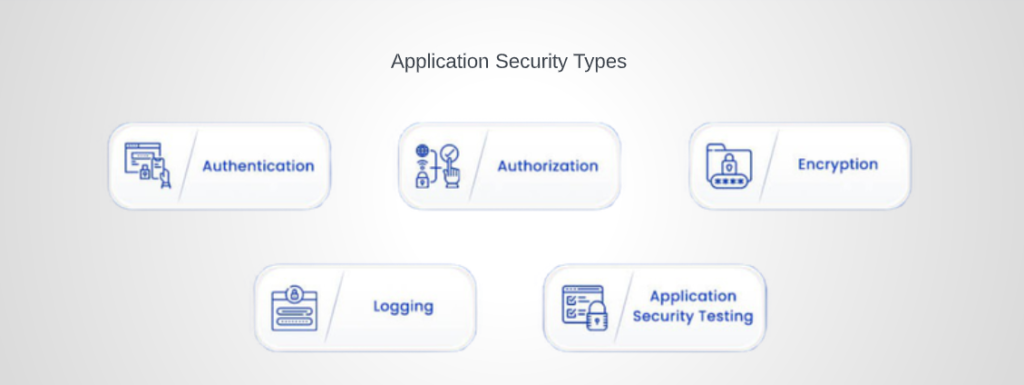
1. Authentication
When developers include protocols into a programme to guarantee that it is only accessible to authorised users. Procedures for authentication ensure that the user is who they claim to be. This may be accomplished by asking the user to give a username and password when login into a programme. Multi-factor authentication requires the use of various authentication methods, including something you know (a password), something you have (a mobile device), and something you are (a biometric).
2. Authorization
After authentication, a user may be granted access to and usage of the programme. The system may verify that the user has authorisation to use the programme by comparing the user’s identify to a list of authorised users. Authentication must occur prior to authorisation in order for the application to match only validated user credentials to the approved user list.
3. Encryption
Other security measures can help prevent sensitive data from being viewed or used by a cybercriminal once a user has been confirmed and the application has been launched. Sensitive data-carrying traffic between the end user and the cloud in cloud-based apps can be encrypted to ensure the data’s security.
4. Logging
If an application suffers a security breach, logging can aid in understanding who obtained access to the data and how they did so. Program log files record which components of the application were accessed and by whom.
5. Testing
A procedure that ensures the effectiveness of all of these security controls.
Application Security Tools
A comprehensive application security strategy assists in identifying, remediating, and resolving a variety of application vulnerabilities and security difficulties. The most successful and advanced application security strategies incorporate solutions for correlating the impact of application security-related events to business consequences. Choosing the appropriate application security solutions for your business is critical to ensuring the efficacy of any security measures implemented by your DevOps or security teams.
Numerous classifications exist for application security:
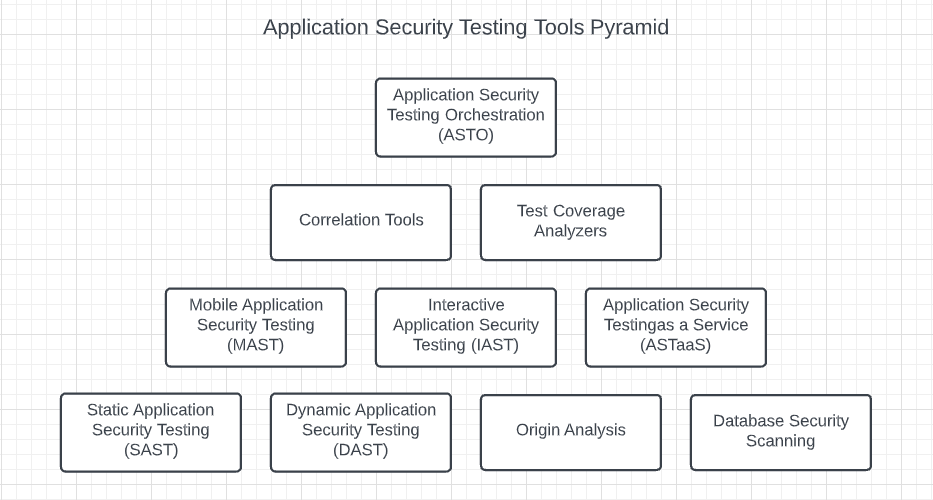
1. Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
SAST assists in the discovery of code defects by searching for the underlying cause in the application’s source files. The ability to compare static analysis scan findings to real-time solutions accelerates the discovery of security issues, lowering mean time to repair and facilitating collaborative troubleshooting.
2. Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
DAST takes a more proactive stance by simulating security breaches on a live web application in order to provide exact information about exploitable issues. Because DAST assesses programmes in production, it is particularly effective for discovering runtime or environment-related issues.
3. Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
IAST combines elements of SAST and DAST by allowing for real-time or point-in-time analysis from within the application throughout the development or production process. IAST has complete access to the application’s code and components, which enables it to deliver more accurate findings and give a greater level of detail than prior versions.
4. Run-time Application Self Protection (RASP)
RASP likewise operates within the application, although its primary focus is on security rather than testing. RASP performs continuous security checks and automatically responds to any breaches, including session termination and notification to IT departments.
Approaches to Application Security
Different methodologies will identify subsets of an application’s security problems, and they will be most successful at certain times of the development lifecycle. They all represent distinct trade-offs in terms of time, effort, cost, and vulnerability.
1. Review of the Design
Before code is written, the application’s architecture and design may be reviewed for security issues. The development of a threat model is a frequently employed method at this phase.
2. White-box security auditing or code auditing
A security engineer goes into the application’s source code, manually checking it for security flaws. Understanding the application enables the discovery of application-specific vulnerabilities.
3. Dark Security Audit
This is performed just by running a program and examining it for security issues; no source code is required.
4. Tooling Automation
Numerous security technologies may be automated by their inclusion in the development or testing process. Automated DAST/SAST tools that are integrated into code editors or continuous integration/continuous delivery systems are examples.
5. Platform for Coordination of Vulnerabilities
Numerous websites and software suppliers provide hacker-powered application security solutions that enable users to be identified and paid for flaw reporting.
For any personal or business related cybersecurity issues, please visit: https://www.benchmarkitservices.com/cyber-security/

