Introduction

Virtualization is a process of creating various virtual versions of something, including but not limited to a virtual computer hardware platform, operating system, storage device, or computer network resources. Virtualization can be applied to many things including:
- Computer hardware
- Operating systems
- Storage devices and data storage
Virtualization can also be applied to many other things as well such as business processes and organizations themselves. In the case of virtualization, software in which the process of creating a virtual version is carried out is called a hypervisor, or virtual machine monitor (VMM). The word virtual might be used by itself in this sense. Virtualization is used to create operating systems for VMs. It also helps run applications within those OS that may not work well together otherwise on shared hardware resources because they have different requirements for CPU power, memory capacity or input/output limitations.
Types of Virtualizations
There are two main types of virtualizations: platform and OS. Platform virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of a hardware platform. Operating system virtualization (OS virtualization) is a server virtualization technology that involves tailoring a standard operating system so that it can run different applications handled by multiple users on a single computer at a time. The operating systems do not interfere with each other even though they are on the same computer. Virtualization can be done at different levels, including the hardware level, the operating system level, or the application level.
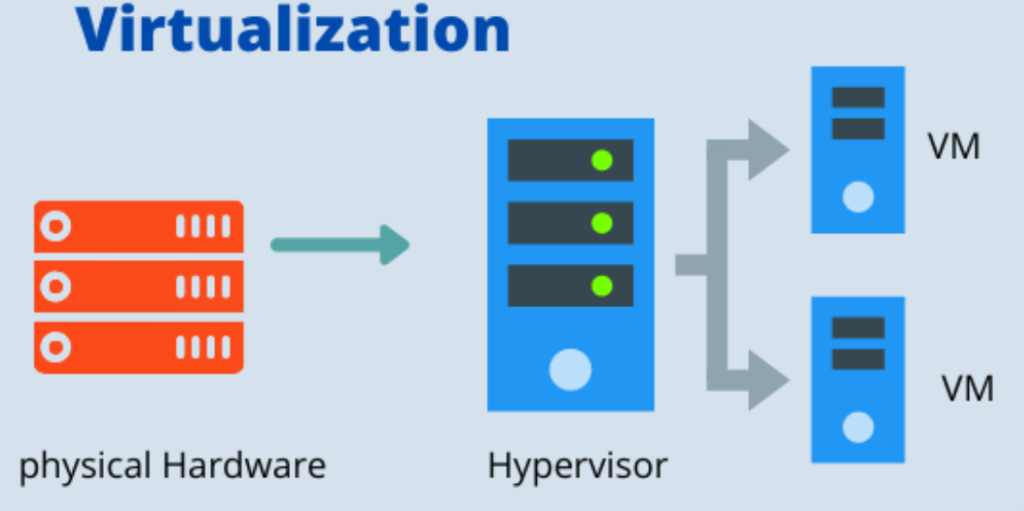
Advantages and Applications of Virtualizations
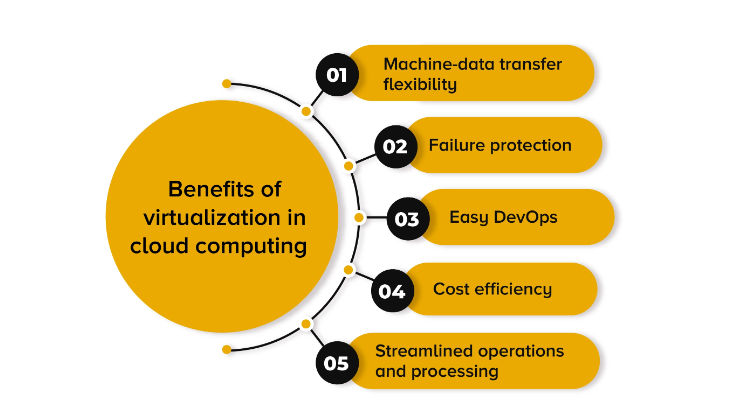
Virtualization is a software-based technology that allows multiple operating systems to run on one physical computer. The advantages of virtualization include:
- Reduced power consumption and heat generation.
- Reduced software license cost.
- High availability and scalability.
- Application isolation, which prevents applications running on the same computer from interfering with each other or corrupting data files (i.e., someone can’t make changes to your banking app without your permission).
- Several operating systems run on one computer at same time, reduced power consumption and heat generation, reduced software license cost, high availability and scalability, application isolation etc.
- You can increase resource utilization by virtualizing applications and infrastructure. This means that more users can access applications at the same time, increasing overall productivity. Using virtualization technologies also simplifies management tasks by making it easier to add new systems, manage software updates across all systems, scale up or down based on business needs, move workloads between physical machines as needed and replicate data in case of a disaster.
In addition, companies can use virtualization to build cloud computing environments for delivering software or services. Cloud computing is a form of computing that provides shared processing resources and data to computers and other devices on demand. Unlike grid computing, cloud computing relies on the Internet for general purpose distributed applications, rather than large high-performance parallel systems. It is an example of a utility computing model in which the end user does not have control over particular machines and their software environment, but uses services provided by the provider (in this case, virtualization).Virtualization allows companies to create one large server from multiple smaller servers. This has several advantages: it increases efficiency since you only need one server instead of many; it reduces costs because you’re sharing hardware; and it provides better security because each part of your network can be isolated from other parts of firewall. Virtualization allows you to reduce the number of physical servers required by consolidating multiple discrete workloads onto each one. This enables dynamic workload balancing, which means that you can optimize the performance of your applications based on the demand for them at any given time.
Example: A web server is a workload. So is an application server and a database server. Each one has different characteristics and uses different resources, but if all three have to be running at full capacity during peak hours, it’s not possible without scaling up your hardware or adding additional servers.
Consolidation is another term for virtualization; it refers to combining multiple discrete applications into one virtual machine (VM). For example, if you used VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) 5 with five VMs running Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition on them—a domain controller, file server, web server, database server, and Exchange mail server—you would consolidate those systems into just two physical servers instead of five separate ones because the VMs run in their own space on a host machine while sharing CPU and memory resources with other VMs on that host or even other hosts altogether.
Environments that allow for server virtualization also often provide the ability to store workloads on virtualized storage systems. This means that you can build cloud computing environments for delivering software or services. The result is greater flexibility and efficiency in data centres because it allows multiple users to share the same resources. The main goal of server virtualization is to manage workloads by abstracting logical storage from physical storage. Server virtualization is a technology that allows multiple operating systems to run on one physical server. The main goal of server virtualization is to manage workloads by abstracting logical storage from physical storage. Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on one physical server. Each guest OS can access a different disk partition, but they all share the same processor and memory resources as well as other resources such as networking interfaces, NIC cards and power supplies.
Disadvantages of Virtualization
If you want to run several operating systems at the same time, then virtualization has some disadvantages:
- High performance requirement(if you want to run several operating systems at once),
- Complex backup procedures,
- Security issues etc.
Conclusion
Virtualization is an integral part of modern InfoTech world. Every layman with a computer knows about virtualization. It is in every field, from medical to military to software development and industry automation. Virtualization as a whole is a useful and powerful tool that can have tremendous effects on businesses. Whether you’re looking to save money by reducing energy costs, enhance your IT operations with cloud computing, or increase the amount of data you can store using storage virtualization, there are many benefits to consider before making a final decision. The next step will be to see how it fits into your business model.
