“Hello my fellow technology enthusiasts, I wanted to speak about a subject that is recognized in its true nature by all but seldom understood. The topic is “Cloud Computing” and will be addressed in series. So, let ‘s dive into the world of cloud computing. In this blog I am going to focus on Virtual private cloud.
What is VPC?
Public cloud VS Private cloud VS virtual private cloud
VPC VS VPN
How is VPC isolated within a public cloud?
Advantages of VPC
Virtual Private cloud
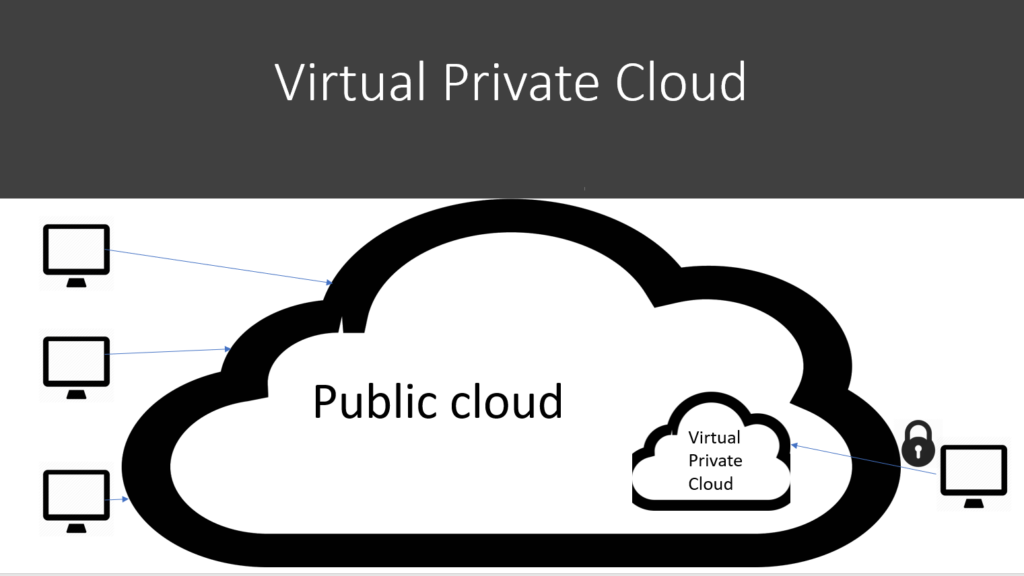
A private cloud computing environment found within a public cloud
is a virtual private cloud (VPC). Essentially, to provide a virtual private environment, a VPC offers logically segregated portions of a public cloud.
A stable, isolated private cloud hosted inside a public cloud is a virtual private cloud (VPC). In an ordinary private cloud, VPC clients can execute code, store data, host blogs, and do whatever else they can do, but a public cloud service hosts the private cloud remotely. (In this sense, not all private clouds are hosted.) VPCs merge public cloud computing ‘s scalability and ease with private cloud computing ‘s data isolation. Click here for cloud based solutions for the businesses like Google, AWS and Azure
Public cloud VS Private cloud VS virtual private cloud
In comparison, a private cloud is a single tenant cloud environment that operates on dedicated servers. This or lie on-site, in a dedicated off-site data centre or with a managed supplier of private clouds. The private cloud is controlled by fixed structures while the public cloud is dynamic and readily scalable. The private cloud ‘s benefit is power and exclusivity. They are yours. There are no neighbours in which to exchange host services.
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is an approach that bridges the two, delivering the best of all versions of the cloud. The VPC operates as a private cloud running on a public or shared platform. Using an individualised, private IP subnet, the VPC isolates the services of one user from others and is interconnected through virtualized networks, like Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) or encrypted channels. SAP VPCs host identical and relatively static workloads, unlike public clouds that support complex environments and all workloads. Since this is SAP, via virtual private networks (VPN), most clients access their environment. Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
VPC VS VPN
By building an encrypted tunnel into which communication passes, a virtual private network (VPN) makes a public Internet link as secure as a link to a private network. To create a stable site-to – site contact channel between your VPC and your on-site environment or any venue, you can deploy a VPN-as-a-Service (VPNaaS) on your VPC. You can link subnets to several VPCs using a VPN, so that they operate as if they were on a single network.
How is VPC isolated within a public cloud?
To separate a VPC from the rest of the public cloud, the main technologies are:
Subnets: A subnet is a set of IP addresses that are reserved within a network such that they are not available to anyone within the network, splitting part of the network for private use in nature. In a VPC, these are private IP addresses that, unlike ordinary, publicly available IP addresses, are not accessible via the public Internet.
VLAN: A LAN is a local area network or a collection of computer machines, both of which are connected to each other without an Internet link. A virtual LAN is a VLAN. Like a subnet, a VLAN is a way to partition a network, except within the OSI paradigm, partitioning takes place on a separate layer.
VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) establishes a private network over the top of a public network using encryption. VPN traffic, but the traffic is scrambled and not accessible to anyone, flows through publicly available Internet infrastructure-routers, switches, etc.
A VPC may have a dedicated subnet and VLAN, accessible only by the user of the VPC. This prohibits someone else from accessing computing services within the VPC within the public cloud- essentially putting the “Reserved” sign on the bar. The VPC customer connects to their VPC via VPN, so that other public cloud users cannot see data passing into and out of the VPC.
Advantages of VPC
Click here for general IT Support services for Businesses
Security: Without crossing the internet, knowledge exchanged through a VPC remains under the hands of a client. Moreover, VPC operators have a highly committed stake in keeping everything running efficiently and safely, while ensuring high levels of uptime, with all users working on the same back-end infrastructure.
Scalability: Since a public cloud service hosts a VPC, users can add additional on-demand computing services.
Flexibility: VPCs are versatile enough to switch with your company as needed, whether your company is increasing or evolving. There are dynamically distributed cloud computing tools, which makes it easier to customise a VPC to your evolving needs.
Savings: Consumers also benefit from economies of scale when VPCs are inside a shared cloud, exchanging expenses with other companies without losing the protection.
Minimized downtime: VPC environments have the redundancy and other functionality needed to achieve requirements of near-100 percent uptime. Your clients will enjoy a high degree of efficiency of almost 100 percent uptime, which will reinforce loyalty and confidence in your brand.

