Before discussing SDN let us know a little about optical networks. Optical networks use signals ciphered in the form of light to share the data. It is a form of visual transmission of information with the help of optical accelerators, lasers, or LEDs, as well as w(ave) d(ivision) m(ultiplexing), to transfer massive amounts of data through fiber-optic wires. Since it has the ability to reach a high bandwidth, it is a system that enables Modern telecommunication networks to transfer the vast bulk of all human and device data.
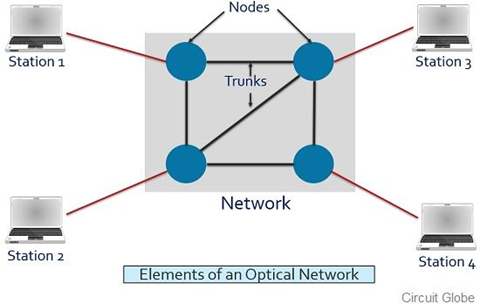
Fig. Link: https://circuitglobe.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/elements-of-optical-network-2.jpg
Types of Optical Networks:
Fiber-optic Networks
Communication infrastructure, mesh networks, and ring networks are by far the most prevalent fiber-optic networks used in urban, local, nationwide, and worldwide organizations.
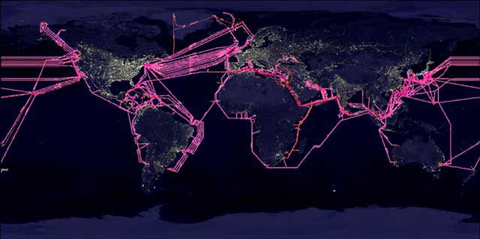
Fig. Link: https://www.thefoa.org/tech/ref/basic/earth-with-cables1.jpg
The passive optical network is yet another type of fiber-optic network that employs unpowered optical splitters to connect one cable to several locations for that last usage.
Free-space optical networks
This category of optical network employs many of the same concepts as a broadband network, but its signals are sent across the open field rather than through fiber. Numerous envisioned satellite networks, including SpaceX’s Starlink for worldwide internet delivery, will employ cordless laser transmission to create optical mesh nodes between orbiting satellites.
Fig. Link: https://steemitimages.com/640×0/https://img.esteem.ws/14qevmnda7.jpg
Unrestricted optical networks can also be used to create temporary ground networks, such as those used to connect LANs on-premises.
Software-Defined Networking
S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) is a connectivity method that employs technology controllers or A(pplication) P(rogramming) I(nterfaces) to connect with underlying physical infrastructure and guide network activity. If you are how is it any different from other networks, other networks use specialized hardware to operate the network traffic whereas S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) can create a virtual network as well as operate it with basic hardware components with the help of software. Since network virtualization is interpreted to component multiple virtual networks inside a single network interface or computing device on distinct physical network systems to share a cohesive virtual network, application networking provides an innovative strategy for controlling incoming packets routing across a centralized server.
Importance of SDN
- It becomes easy to control the networks since there is no need for manually programming various hardware devices, experts can simply program an open platform application controller to control the traffic flow of the network. What is more, they can always have the luxury of choosing the equipment from the wide range of options.
- Executives utilizing an S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) platform may build virtual networks and deploy virtualized resources from a centralized location to update the communications infrastructure in real-time. This allows network administrators to manage data flow via the network and prioritize services that require greater accessibility.
- An S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) system gives transparency throughout the whole network, providing for a more complete view of safety risks. With the proliferation of internet-connected smart devices, S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) offers substantial benefits over traditional networking. Operators can create distinct zones for goods that require differing levels of security, or they can rapidly isolate compromised devices so that they do not pollute the whole network.
SDN for Optical Networks
After knowing all that we can deduce that optical networks are present everywhere in modern time. They are even used commercially in offices or homes. It is quite difficult to provide efficient communication at the same time throughout the four tiers of hierarchy. The traditional approaches of formal management panels and C(ommand) L(ine) I(nterfaces) are no longer appropriate for these elevated, complicated networks. Modern optical systems involve a software-based programmable conceptual model for versatile coordination and monitoring. S(oftware) D(efined) N(etwork) is an interface that makes the control of networks easy for specialists where traditional systems have several platforms to accomplish the same task.
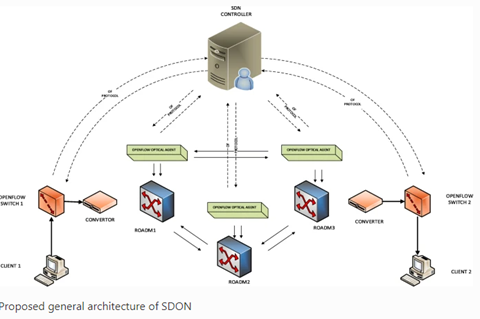
Several modern services and applications, particularly those using the cloud, would be impossible to run without S(oftware) D(efined) N(etwork). It enables data to be readily moved between distant sites, which is essential for cloud services. Furthermore, due to the agility and efficiency provided by SDN, it can accommodate upcoming trends in the industry such as edge computing and the I(nternet) Of T(hings), which requires a significant amount of data to be sent fast and efficiently between various location.
Working of Software-Defined Networking
The application is isolated from the hardware in SDN. The control plane, which decides where to transmit traffic, is moved to software, while the data plane, which normally delivers traffic, remains in devices. This enables network managers who utilize S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) to design and administer the whole network from a single platform instead of the device by device.
A typical S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etworking) infrastructure consists of only three components, it may be located in several physical locations.
- Applications that communicate resource requirements or network-wide data.
- Based on programmed input, controllers make judgments on how to transmit data packets.
- Networking devices that get data transfer instructions from the administrator.
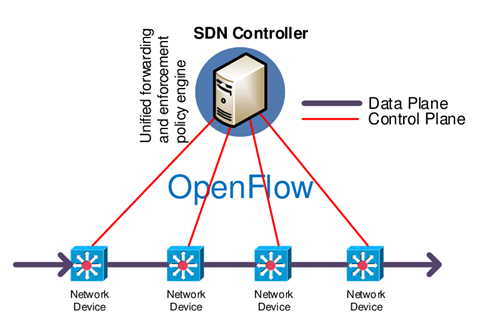
Physical or virtual networking devices transport data over the network. In some cases, virtual switches, which may be implemented into either software or hardware, can take over the functions of actual switches and merge their operations into a single, adaptive switch. Before sending data packets, the switch validates their validity and virtual machine endpoints.
Models of Software-Defined Networks
- Open S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork): The specialists use different open protocols like OpenFlow to operate the movements of the real and digital switches at the ground level.
- S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork) by API: This model does not make use of open protocols but uses A(pplication) P(rogramming) I(nterface) to operate the data movement.
- S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork) Overlay Model: This model creates dynamic gateways to multiple upon or faraway data centers by running a network interface on top of existing hardware architecture. The network connection distributes traffic over several channels and connects devices to each channel while leaving the actual network alone.
- Hybrid S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork): This model is the combination of S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork) and the traditional networking arrangement in a single infrastructure. The traditional one takes care of directing some data while allowing the S(oftware)-D(efined) N(etwork) to direct the rest of the data.
