Quantum computing is a new and emerging field in computer science that has the potential to revolutionize many industries and applications. It differs from traditional computing in several ways and is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy at a very small scale.
In a traditional computer, information is stored and processed using binary digits, or bits, which can have a value of either 0 or 1. In a quantum computer, information is stored and processed using quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states at the same time. This property, known as superposition, allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations much faster than traditional computers.
Quantum computing operates on the principle of quantum parallelism, which means that it can perform multiple calculations simultaneously. In a classical computer, the processing speed is limited by the number of transistors on the chip, but in a quantum computer, the processing speed is limited by the number of qubits. The more qubits a quantum computer has, the more complex and powerful it becomes.
Quantum algorithms are the building blocks of quantum computing. They are designed to exploit the properties of quantum mechanics, such as entanglement and superposition, to perform certain calculations much faster than traditional algorithms. One of the most famous quantum algorithms is Shor’s algorithm, which can factor large numbers much faster than traditional algorithms, making it a powerful tool for cryptography.
Quantum computing also has the potential to revolutionize many industries and applications, such as finance, cryptography, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence. In finance, quantum computers can be used to simulate financial markets, helping to optimize investment strategies. In cryptography, quantum computers can be used to break encryption codes, making it essential for companies and governments to develop new encryption algorithms. In drug discovery, quantum computers can be used to simulate the behavior of molecules and predict how they will interact with each other, speeding up the drug discovery process. In artificial intelligence, quantum computers can be used to process large amounts of data and improve the accuracy of machine learning algorithms.
Quantum computing is still in its infancy, and there are many challenges that need to be addressed before it becomes a mainstream technology. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of reliable and stable qubits. Quantum bits are highly sensitive to their environment and are prone to errors, which can significantly impact their performance. Another challenge is the lack of a robust and scalable quantum computing infrastructure, which is essential for developing and testing quantum algorithms.
It has captured the attention of some of the largest tech companies in the world. These companies are investing significant resources in order to be the first to develop a quantum computer that can perform complex calculations at a speed that far surpasses that of traditional computers. The race to develop a quantum computer is not just about bragging rights, but also about the potential for commercial applications and the billions of dollars in revenue that could result from being the first to market.
At the heart of the race for quantum computing are the major tech companies such as IBM, Google, Microsoft, Intel, and Alibaba. Each of these companies has its own approach to quantum computing and is investing heavily in research and development in this area. IBM is one of the pioneers of quantum computing, and it has been working on the development of quantum computers for over 20 years. The company has already developed several quantum computing systems and is now working on making them available for commercial use.
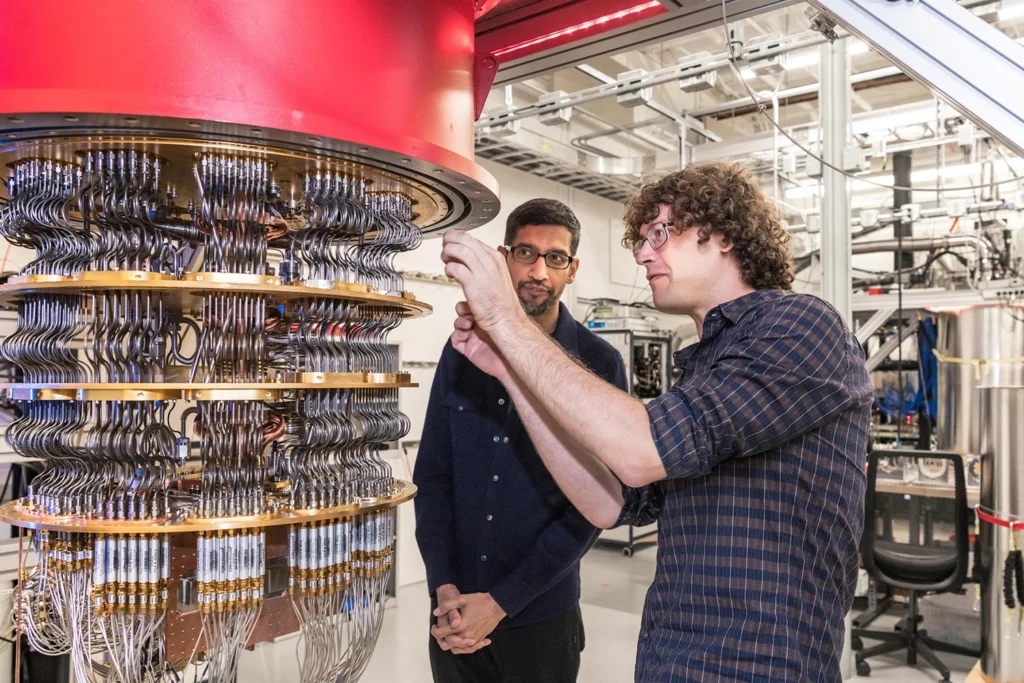
Google, on the other hand, has been focusing on the development of quantum algorithms, as well as the design and construction of quantum processors. The company is hoping that its work in quantum computing will lead to significant advances in the fields of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Google is also working on making its quantum computing technology available for external use through its cloud computing platform.

Microsoft is taking a different approach to quantum computing, focusing on the development of software and tools that will make it easier for developers to build quantum-based applications. The company is also working on the development of quantum-based hardware, which it believes will be key to the future of computing.
Intel is one of the latest tech companies to enter the quantum computing race, but it has made significant investments in this area. The company is working on the development of quantum processors and is also collaborating with other companies to develop quantum-based technologies.
Finally, Alibaba is also investing in quantum computing, with a focus on developing quantum-based technologies for use in finance, healthcare, and other industries. The company is also working on the development of quantum algorithms, as well as the design and construction of quantum processors.
The race to develop a quantum computer is heating up, with some of the largest tech companies in the world investing significant resources in this area. The potential for commercial applications and the billions of dollars in revenue that could result from being the first to market are driving this race. The winner of this race will likely be the company that is able to develop a quantum computer that is both scalable and reliable and can be used for a wide range of applications. The future of computing may well depend on the outcome of this race.
