Private cloud refers to a model of cloud computing where IT services are provisioned over private IT infrastructure for the dedicated use of a single organization. A private cloud is usually managed via internal resources.
The terms private cloud and virtual private cloud (VPC) are often used interchangeably. Technically speaking, a VPC is a private cloud using a third-party cloud provider’s infrastructure, while a private cloud is implemented over internal infrastructure.
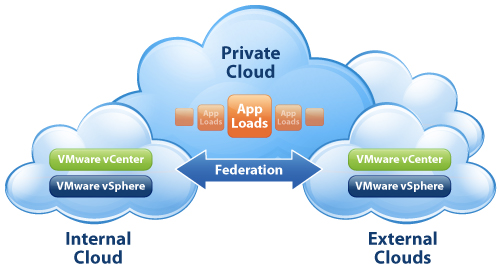
fig: private cloud structure
Private cloud is a computing model that offers a proprietary environment dedicated to a single business entity. As with other types of cloud computing environments, private cloud provides extended, virtualized computing resources via physical components stored on-premises or at a vendor’s datacenter.
One of the chief advantages of a private cloud deployment is the enhanced degree of control offered to the organization. Because the private cloud is only accessible to a single business, that organization has the ability to configure the environment and manage it in a manner that is uniquely tailored to the specific computing needs of the company.
A private cloud strategy may be comprised of hardware hosted locally at a facility owned by a business, or it may be hosted by a cloud service provider. Virtual private clouds are typically paid for on a rolling basis, but provisioned hardware and storage configurations maintain the benefits of a secure, exclusive network.
Private cloud solutions bring value to an enterprise by abstracting computing processes in a manner much more efficient than traditional virtualization. A few of the primary advantages include:
Security and compliance: For businesses operating in heavily regulated industrieshttps://www.benchmarkitservices.com/google-cloud-service-providers/, compliance is paramount. Private cloud infrastructure gives organizations the ability to comply with strict regulations because sensitive data is held on hardware that cannot be accessed by anyone else. This advantage is available through on-site hardware installations as well as in hosted services.
Customization: Private clouds are fully configurable by the organizations using the solution. A fully private cloud is constructed by an on-site cloud architect, which means stakeholders can specify the exact environment needed to run proprietary applications. Hosted private clouds offer the same advantages but require no on-site setup. In that case, the business works with a vendor to set up and manage a cloud for its exclusive use.
Hybrid integration: When an application needs additional computing resources, hybridization extends the resources of the private cloud into a public cloud to maintain uptime without needing to install additional physical servers. This can be a cost-effective solution for organizations that need the security of a private cloud but still want other functions to operate with the power of a public cloud service.
Challenges of private cloud
A private cloud can introduce challenges if an organization does not have consistent computing needs. When resource demand is in flux, a private cloud may not be able to scale effectively, costing the organization more money in the long run. Here are key considerations IT stakeholders should review:
Up-front costs: Fully private clouds hosted on-site require a substantial outlay of capital before they can bring value to the organization. The hardware required to run a private cloud can be very expensive and it will require an expert cloud architect to set up, maintain and manage the environment. Hosted private clouds, however, can mitigate these costs substantially.
Capacity utilization: Under the private cloud computing model, the organization is wholly responsible for maximizing capacity utilization. An under-utilized cloud deployment can cost the business significantly.
Scalability: If the business needs additional computing power from the private cloud, it may take extra time and money to scale up the private cloud’s available resource. Typically, this process will take longer than scaling a virtual machine or requesting additional resources from a public cloud provider.
