Near Field Communication (NFC)
Near Field Communication is referred to as NFC in short. It is used for short-range data communication between two devices known as initiator (e.g., an NFC reader) and target, as its name implies (i.e., NFC Tag)NFC has many uses, including data transfer between cellphones, identity verification at government offices and other locations, ticket purchasing, etc. It uses low data rates of 106, 212, or 424 kbps and runs at a frequency of 13.56 MHz Both the NFC reader and the NFC tag have active and inactive modes. When two devices are touched or brought within a few millimeters of one another, near-field communication (NFC), a short-range wireless networking technology, employs magnetic field induction to permit communication between them. This covers credit card authentication, granting physical access, transmitting tiny files, and launching more powerful wireless networks. In general, it expands and improves upon the work of current ecosystems and standards surrounding radio frequency ID tags (RFID).It was initially meant to be used to send files using Android Beam between phones. NFC is used by contemporary services like Google Nearby Share to set up wireless services on speedier networks like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi direct.
NFC is an addition to other wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi direct, Ultrawideband (UWB), and QR codes. Its main benefit is that it is the most user-friendly wireless technology for establishing connections, making it suitable for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. However, it struggles to sustain a connection over large distances or for extended periods of time.
How does NFC work?
The technology is surprisingly straightforward: an NFC chip functions as a component of a wireless network and was developed from radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. Small quantities of data can be exchanged between the two devices when held a few millimeters apart once it has been activated by another chip. It employs chips that run on extremely little power (or passively, requiring even less power) and requires no pairing code to connect, making it far more power-efficient than other wireless communication kinds.
NFC uses magnetic field induction to transmit data. NFC data is transmitted at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, or a wavelength of twenty-two meters. The fact that the field fades away much more quickly than radio waves make using induction coupling to convey data more advantageous than using radio waves. This is helpful in preventing eavesdropping on private conversations concerning the use of credit cards, door access codes, and other sensitive information. The second important NFC breakthrough is the use of contactless credit card processing that is encrypted. Due to public-key cryptography, the card may produce a unique authentication code for each transaction without disclosing the card’s internal data or the three-digit back code. This makes sure that the original card information would never be obtained, even if someone were to listen in or a hacker checked a card on a crowded metro. On top of this, smartphone providers are beginning to include certain fundamental application execution features. A smart tag in the Google ecosystem may open a progressive web app that is currently running in the browser. Apple recently introduced Apple App Clips, which allow users to open apps with minimal functionality, such as ordering in a restaurant or unlocking a scooter rental kiosk, without downloading a full-fledged app, using an NFC tag or QR code. Access to confidential data on the phone is restricted for certain apps. The diagram for how NFC works in mobile payment is shown below
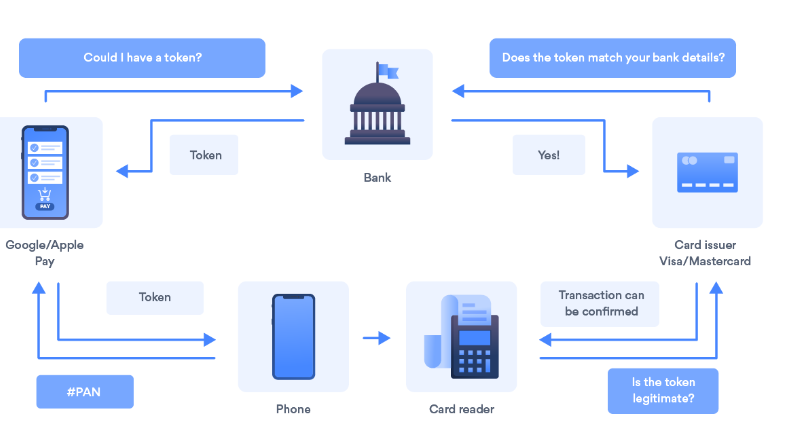
Real Life Examples and application of NFC
Access authentication for doors or offices, unlocking car doors or rental scooters, mobile payments like Apple Pay, Samsung Pay and Google Pay, transit card payments, ticket redemption at concerts or theatres, venue or location check-in to notify friends on social media, device pairing smartphones and headsets by tapping them together, automatic setup for Wi-Fi connectivity by tapping a phone to a router or internet gateway, and connection via smartphone to a radiator to configure are all examples of NFC.
Advantages of NFC
The following are some of the advantages or benefits of NFC:
- Wallet apps on smartphones make it incredibly easy to conduct payments and other transactions.
- It has numerous uses in many different industries, including banking, reservations, ticket booking, redemption, entry/exit passes, etc.
- It benefits both consumers and businesses.
- It offers employees and students secure access to their facilities.
- Compared to debit and credit cards with magnetic strips, it offers additional security. PIN is also utilized
- Unlike Bluetooth and other techniques, it does not require a search and pair process to establish connectivity.
- No unique software is required. Additionally, it does not need human configurations or adjustments.
- It is appropriate for use with current RFID networks.
- NFC communications are challenging to intercept at a distance
- It makes easier to access back-end data.
Disadvantages of NFC
The following are some difficulties with NFC technology:
- Few inches of range limits many use cases
- slower than other protocols
- may restrict smartphone app usage for sensitive data-requiring apps.
- Apple and Google’s limits and tech implementations stifle app innovation,
- unsuitable for location monitoring and
- less universal and simple to integrate into venue ticketing apps than QR codes.
- Because of the complicated processes compared to other simple solutions, adopting NFC-enabled devices is quite expensive for businesses.
- Although it is more secure than a system based on credit or debit cards, there are still some risks involved.
- Due to the availability of the most innovative tools and techniques that grant complete access to smart devices, mobile-based hacking is becoming common today.
- In comparison, NFC-enabled devices consume more power.
Conclusion
The future of electronic devices in people’s lives is already starting to take form thanks to near field communication. It is likely that NFC-enabled mobile phones will become the norm and their uses will become ingrained in daily life as chip production costs decline. A survey revealed that individuals preferred NFC technology to other forms of technologies like QR codes and Bluetooth Beacons. NFC technology is said to be based on RFID technology, which employs magnetic field induction as a medium to communicate and create communication between close-proximity, 13.56 MHz-operated electronic devices due to its unlicensed frequency and maximum 424 kbps data transmission rate. Like Never other technology has advantages and disadvantages. However, when compared to alternative technologies Although it is not as popular right now, the number of Android applications is growing, so soon it will.
