
Image Link: http://surl.li/sveap
In today’s digital age, where information is exchanged at lightning speed across vast distances, ensuring the security and privacy of data has become paramount. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as a crucial tool for safeguarding sensitive information, enabling secure communication over public networks like the internet. Understanding how VPNs work is essential for anyone concerned with protecting their online activities and data integrity. In this blog, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of VPNs, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and applications.
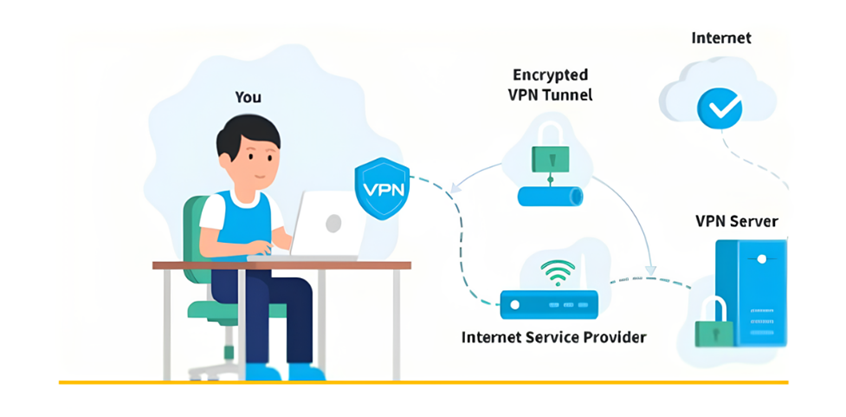
Image Link: http://surl.li/svejx
Understanding Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
At its core, a VPN is a technology that establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s device and a remote server. This connection, known as a tunnel, encrypts all data passing through it, effectively shielding it from unauthorized access or interception. By rerouting internet traffic through this encrypted tunnel, VPNs provide users with privacy, anonymity, and security, regardless of their location or the network they’re using.
How VPNs Work
1. Encryption
Encryption lies at the heart of VPN technology. When a user initiates a connection to a VPN server, all data transmitted between their device and the server is encrypted using robust encryption protocols. This encryption scrambles the data into a format that can only be deciphered by someone with the appropriate decryption key, effectively rendering it unreadable to anyone intercepting the transmission.
2. Tunneling
The concept of tunneling forms the basis of VPN functionality. Through tunneling, VPNs encapsulate data packets within another data packet, creating a secure pathway or tunnel through which information can travel safely between the user’s device and the VPN server. This process ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
3. Protocols
VPNs utilize various protocols to facilitate secure communication and data transmission. Common VPN protocols include OpenVPN, IPSec, L2TP/IPSec, and PPTP, each offering different levels of security, speed, and compatibility. These protocols govern how data is encrypted, authenticated, and transmitted across the VPN connection, ensuring optimal performance and security.
4. Authentication
Authentication mechanisms are employed to verify the identities of both the user and the VPN server before establishing a connection. This ensures that only authorized users and trusted servers can access the VPN network, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Authentication protocols such as username/password authentication, digital certificates, and multi-factor authentication enhance the security of VPN connections, bolstering user confidence in the system.
5. VPN Clients and Servers
In a typical VPN setup, users employ VPN client software installed on their devices to initiate connections to VPN servers. These servers, often located in geographically diverse locations, act as intermediaries between the user’s device and the internet. By connecting to a VPN server, users can effectively mask their true IP addresses and browse the web as if they were accessing it from the server’s location.
Benefits of VPNs
1. Enhanced Privacy
One of the primary benefits of VPNs is their ability to safeguard user privacy by encrypting internet traffic and masking IP addresses. This prevents ISPs, governments, hackers, and other malicious entities from monitoring or tracking users’ online activities, ensuring their anonymity and protecting sensitive information from prying eyes.
2. Security
VPNs provide an additional layer of security for internet users, particularly when accessing public Wi-Fi networks or conducting sensitive transactions online. By encrypting data transmissions, VPNs mitigate the risk of eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and other cyber threats, thereby safeguarding user data and preserving the integrity of communication channels.
3. Access Control
VPNs enable users to bypass geographic restrictions and access region-locked content by connecting to servers in different countries. This allows individuals to circumvent censorship, geo-blocking, and content limitations imposed by streaming services, social media platforms, and other online entities, expanding their access to information and entertainment on a global scale.
4. Data Protection
With the proliferation of cybercrime and data breaches, ensuring the security of sensitive information has never been more critical. VPNs help mitigate the risk of data theft and unauthorized access by encrypting data transmissions and providing secure channels for data exchange. This is especially important for businesses, remote workers, and individuals handling confidential or proprietary information.
Applications of VPNs
1. Remote Work
In an increasingly remote work environment, VPNs play a vital role in facilitating secure and seamless communication between remote employees and corporate networks. By establishing encrypted connections over the internet, VPNs enable remote workers to access company resources, collaborate with colleagues, and conduct business operations securely from any location.
2. Personal Privacy
Individuals concerned about their online privacy and security can benefit greatly from using VPNs to encrypt their internet traffic and conceal their IP addresses. Whether browsing the web, accessing public Wi-Fi networks, or engaging in online banking, VPNs provide peace of mind and reassurance that personal data remains protected from malicious actors and unauthorized surveillance.
3. Geo-Spoofing
VPNs are commonly used to bypass geographic restrictions imposed by streaming services, gaming platforms, and content providers. By connecting to servers in different countries, users can circumvent region-locking and access a wider range of content, including movies, TV shows, games, and websites that may be unavailable in their region.
4. Security Testing
In cybersecurity, VPNs are invaluable tools for conducting penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security audits. By simulating different network environments and masking IP addresses, security professionals can assess the resilience of systems and applications to various cyber threats, identify potential vulnerabilities, and implement robust security measures to safeguard against attacks.
Conclusion
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) represent a powerful solution for safeguarding online privacy, enhancing security, and bypassing geographic restrictions in today’s interconnected world. By encrypting internet traffic, establishing secure connections, and masking IP addresses, VPNs enable users to protect sensitive information, preserve anonymity, and access a wealth of online resources without constraints. Understanding the mechanisms and benefits of VPN technology is essential for individuals, businesses, and organizations seeking to navigate the digital landscape safely and securely. As the demand for secure communication and data protection continues to grow, VPNs will undoubtedly remain indispensable tools for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in an ever-evolving digital ecosystem.
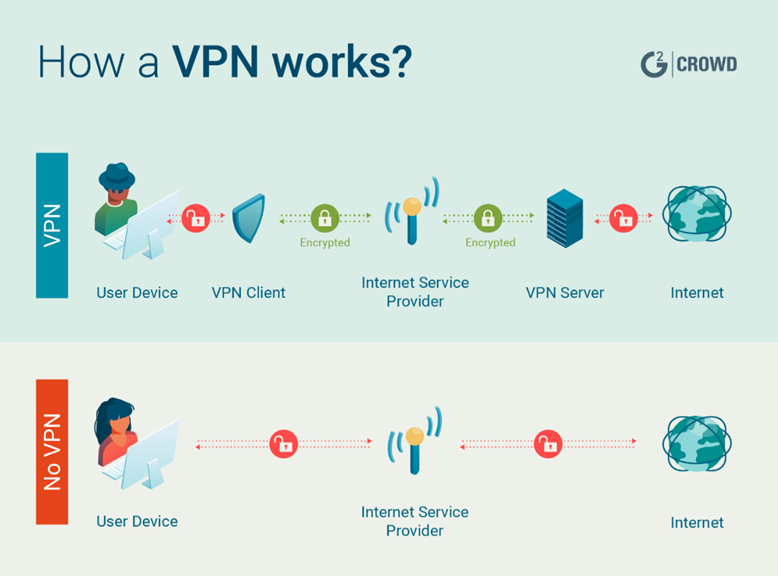
Image Link: http://surl.li/svemb
