INTERNET
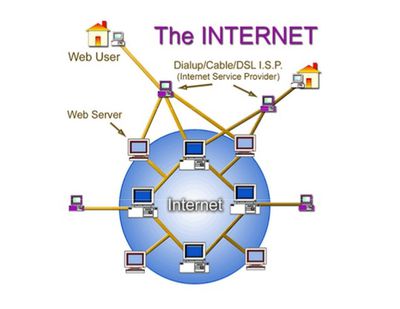
The INTERNET is a worldwide network of interconnected computer networks. A network is formed when two or more electronic devices are linked so that they can communicate with one another. The Internet is a worldwide interconnection of such networks belonging to companies, governments, and individuals, allowing all devices connected to these networks to communicate with one another.
One metric is the amount of data that passes through it each day, which is approximately five Exabyte’s. That’s 40,000 two-hour standard definition movies per second. It takes some tinkering. Hundreds of thousands of miles of cable cross countries, with more being laid along sea floors to connect islands and continents. The modern internet is supported by approximately 300 submarine cables, the deep-sea variant of which is only as thick as a garden hose. Most are made up of bundles of hair-thin fibre optics that transmit data at the speed of light.
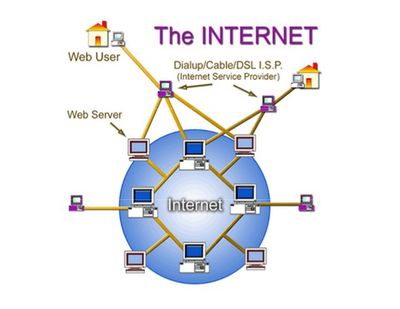
How does the Internet work?
This is an intriguing question that may arise in everyone’s mind! I’m here to relieve some of that tension. The Internet has become an indispensable part of our lives, and a thorough understanding is required to make the best use of this new tool. This blog explains the underlying infrastructure and technologies that enable the Internet to function. It is not in-depth, but it covers enough of each topic to provide a basic understanding of the concepts involved.
It is critical to understand that the Internet is a global network of physical cables, which can include copper telephone wires, television cables, and fibre optic cables. Even wireless connections, such as Wi-Fi and 3G/4G, rely on physical cables to connect to the Internet.
When you visit a website, your computer sends a request to a server via these wires. A server is where websites are stored and functions similarly to your computer’s hard drive. When a request is received, the server retrieves the website and returns the correct data to your computer. What’s amazing is that all of this happens in a matter of seconds!
Communication between the computers:
Computers must be able to understand each other in order to communicate. Communication is possible on the Internet because all devices use the same “language” or protocol, namely the Internet Protocol (IP), creating a “single market” with no physical, technical, or national barriers. It serves as the foundation for all other Internet communication systems.
Sending any kind of communication via the Internet using the Internet Protocol is akin to mailing a book’s pages in a variety of envelopes. The sender and destination addresses are the same on all of the envelopes. Even if some envelopes are delivered by ship and others are delivered by air, all envelopes eventually arrive at their destination. Anyone can create their convention or protocol and use it on the Internet as long as it is based on the Internet Protocol. To put it another way, the only constraint is the human imagination, and the only constraint is that the address on the envelope must be in a standard format. The system’s openness is what makes the Internet such a worldwide phenomenon.
Every restriction on the Internet’s openness limits its future development potential. There are several significant benefits to using a single protocol for all communications. Routers, the machines in charge of delivering Internet data, do not need to be programmed differently to handle different sorts of data. They don’t even need to know what data they’re delivering as long as it’s all done over the Internet Protocol.
There are some technical points to be covered in order to learn about internet they are IP address, www, URL, HTTP, Google and lot more but for now let’s get deep into these parameters,
- IP Address:
A device on the internet or a local network is identified by its IP address, which is a unique address. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a collection of rules that regulate the format of data transferred over the internet or a local network. IP addresses, in essence, are the identifiers that allow data to be transmitted between devices on a network: they contain location information and make devices reachable for communication. The internet requires a method of distinguishing between various computers, routers, and web pages. IP addresses are a crucial aspect of how the internet operates and provide a means of doing so.
Because the Internet is a worldwide network of computers, each computer that connects to it must have its own address. The format of Internet addresses is xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where xxx must be a number between 0 and 255. An IP address is a type of address. As a result, every device connected to the Internet is given an IP address, which is a numerical address. IP addresses can be used to identify a company or person who has purchased Internet Service Provider services in order to connect one or more devices to the Internet. A router, on the other hand, has only one IP address, regardless of how many users are connected to it. As a result, we are unable to identify the culprit in this case.
There are two types of website IP addresses for website owners that do not run their own server and instead rely on a web hosting package – which is the case for most websites. These are dedicated and shared.
A) IP addresses that are shared
Websites that use shared hosting plans from web hosting providers are usually only one of several that share the same server. Individual or small-business websites, where traffic volumes are controllable and the sites themselves are constrained in terms of page count, etc., tend to be like this. The IP addresses of the websites hosted in this manner will be shared.
B) IP addresses that are shared
Websites that use shared hosting plans from web hosting providers are usually only one of several that share the same server. Individual or small-business websites, where traffic volumes are controllable and the sites themselves are constrained in terms of page count, etc., tend to be like this. The IP addresses of the websites hosted in this manner will be shared.
2. World Wide Web (WWW):
The World Wide Web, also known as WWW, W3, or the Web, is an interconnected network of public web pages accessible via the Internet. The Web is not the same as the Internet: it is one of many applications that are created on top of it.
When we enter a website address into a browser, we use the WWW keyword. Have you ever considered what this meant? I believe many of us had that thought, and many of us knew the answer. But we are not as smart as those who already know the answer. So, let’s see what it is, shall we? WWW is a hypertext document that combines text, images, and hyperlinks – a hyperlink points to another document. It may also include moving images, active program’s, and so on. This hypertext document is written in HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language), which is based on SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) and describes the structure of a document. Based on the structure description in HTML the WWW browser determines how to display the document.
3. URL:
The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) stands for Uniform Resource Locator. A URL is simply the address of a specific unique resource on the Internet. Each valid URL, in theory, points to a distinct resource. These resources can include an HTML page, a CSS document, an image, and so on. There are some exceptions in practice, the most common being a URL pointing to a resource that no longer exists or has moved. Because the Web server handles both the resource represented by the URL and the URL itself, it is up to the web server’s owner to carefully manage that resource and its associated URL.
Let’s consider an example of URL as,” HTTPS://LETSTECHITEASY.COM/”
Here in this URL, “https” is called as “Scheme”. The scheme is always the first element of the URL, and it specifies the protocol that the browser must use to request the resource (a protocol is a set method for exchanging or transferring data around a computer network). HTTPS or HTTP is the most common protocol for web pages (its unsecured version). Although one of these two is required to address a web page, browsers are also capable of handling other schemes such as mailto: (to launch a mail client) or ftp: (to transfer files), so don’t be shocked if you see such protocols.
Next follows the “Authority”, which is separated from the scheme by the character pattern ://.
And the next one “LETSTECHITEASY” is called “DOMAIN NAME”. The domain specifies which Web server is being accessed.
4. HTTP:
The “Http:” prefix is used when creating a web address. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer System) is a straightforward protocol for transferring files over the internet. The session is started by the client (browser) connecting to the server. The server does not send data by itself. To retrieve a file from the server, the client uses the GET command. In addition, more data is passed. The server delivers information about the file as well as the file’s contents. When a user visits a website, the request is sent through the HTTP or HTTPS (protected) protocol, and the web page is displayed. The amount of time it takes to display a webpage is determined by a number of factors, including internet speed, server performance, and network latency.

(Image reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0OrmKCB0UrQ)
5. GOOGLE:
We ask GOOGLE a lot of questions in our daily lives. What exactly is GOOGLE? It’s a search engine, after all. A web search engine is a computer program that searches the World Wide Web for information. The search results are typically shown in a list format known as search engine results pages. Web pages, pictures, and other sorts of files may be used to store the data. Some search engines also scour databases and open directories for information. Unlike web directories, which are maintained solely by human editors, search engines keep real-time data by using a web crawler to execute an algorithm.

(Image reference: https://www.thurrott.com/cloud/microsoft-365/242307/google-rebrands-g-suite-introduces-new-integrated-experience)
INTERNET HARDWARE:
To setup the internet and the connections required related to all the internet accessories we have to buy it all of those in a top and trusted place and that trusted place where most of the people prefer is “x-tech buy”. this is the biggest hub where we get A to Z all it related hardware and software accessories. the process of buying the accessories there is the easiest process compared to other store i.e just by visiting there website, https://www.xtechbuy.com/ .
CONCLUSION:
In simple words, the Internet is used to share information. The data can be transferred between two locations that are thousands of miles apart. The internet is also used to disseminate information. We have easy access to information about what is going on in other regions of the world. In today’s world, the internet is used to complete 90% of tasks. We have machines that cannot function without internet access. Today, even aeroplanes have internet access.if you still know more about this, or need help regarding any of your issues with your systems you can contact the customer friendly experts team,“Computer Repair Onsite (CROS)” from their website here.

A large number of businesses conduct business on the internet. They market their goods over the internet. All payments are also made through the internet by the buyer. The bill is likewise generated entirely through the internet. The Internet can also be used as a learning tool. On the internet, data is updated on a regular basis. Students can use the internet to read their study materials. If you like, you can also conduct research on the internet. E-mailing is another popular internet activity now. E-mail is used by businesses to communicate and share information. The Internet has shown to be extremely beneficial to society. dealing with internet without any knowledge is hard and risky, problems may occur at any point in the network, if we feel stuck any point, we can solve it simply by taking an expert advice like “BENCHMART IT SERVICES” by clicking here .