Hyper-V Virtualization-Windows OS
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform from Microsoft that allows users to create and run virtual machines on Windows OS. Hyper-V was first introduced in Windows Server 2008, and it has been included in all versions of Windows since then. In this article, we will discuss how to install Hyper-V on Windows, how to create virtual switches and virtual machines, and its usability in detail. We will also compare Hyper-V with two other popular virtualization platforms: VMware and VirtualBox.
Installing Hyper-V
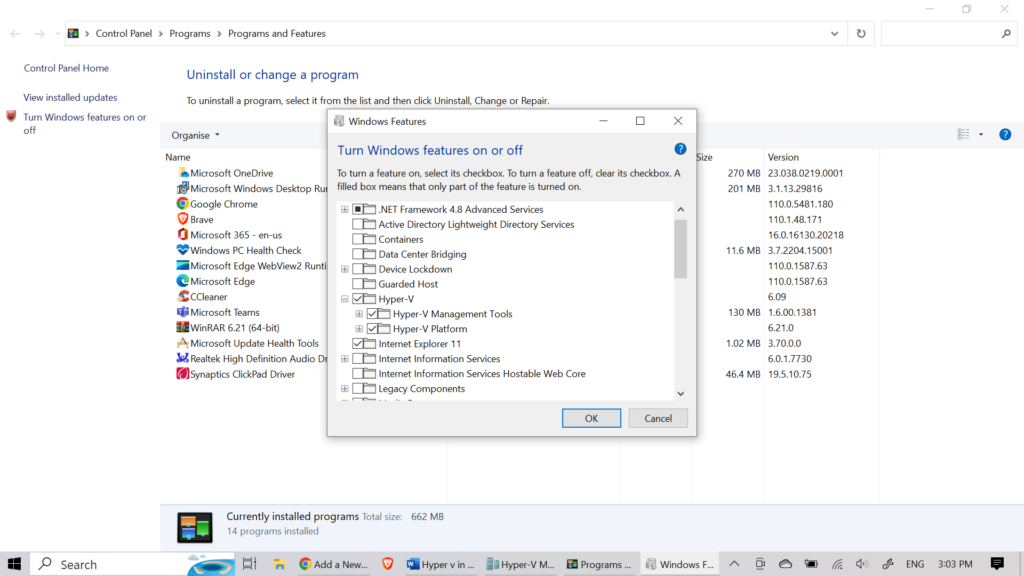
Installing Hyper-V on Windows OS Hyper-V is included in Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. To install Hyper-V on your Windows OS, follow the steps below:
- Press the Windows key + X on your keyboard to open the Power User menu, and then click on “Apps and Features.”
- Click on the “Programs and Features” link on the right-hand side of the window.
- Click on the “Turn Windows features on or off” link on the left-hand side of the window.
- Check the box next to “Hyper-V” and click “OK.”
- Windows will install the necessary components for Hyper-V, and your computer will need to restart to complete the installation.
Creating Virtual Switch
Creating Virtual Switches in Hyper-V A virtual switch is a software-based network switch that allows virtual machines to communicate with each other and the host computer. Hyper-V supports two types of virtual switches: external and internal.
To create a virtual switch in Hyper-V, follow the steps below:
- Open Hyper-V Manager by typing “Hyper-V Manager” in the Start menu.
- In the Actions pane, click on “Virtual Switch Manager.”
- SSelect the type of virtual switch you want to create (external or internal) and click “Create Virtual Switch.”
- Follow the wizard to configure the virtual switch settings, such as the name, connection type, and VLAN ID.
Creating Virtual Machines
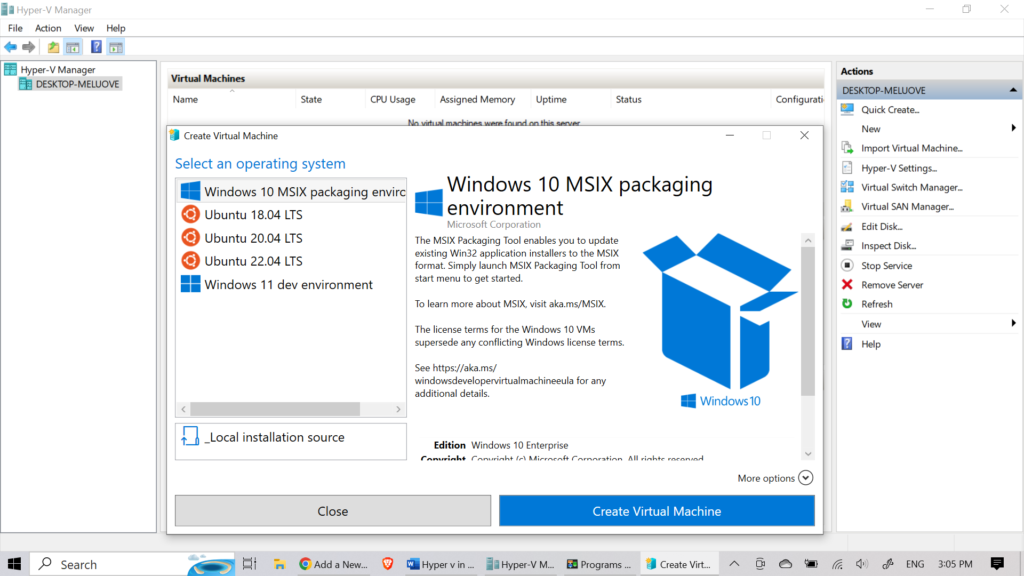
Creating Virtual Machines in Hyper-V Once you have created a virtual switch, you can create virtual machines in Hyper-V. To create a virtual machine in Hyper-V, follow the steps below:
- Open Hyper-V Manager.
- In the Actions pane, click on “New” and then “Virtual Machine.”
- Follow the wizard to create the virtual machine. You will need to specify the name, location, and disk size of the virtual machine.
- After the virtual machine is created, you can start it by selecting it in the Hyper-V Manager and clicking “Start.”
Usability of Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a powerful virtualization platform that offers several benefits to users. Some of the key benefits of using Hyper-V include:
- Isolation: Hyper-V allows you to isolate different operating systems and applications, which helps to reduce the risk of security breaches and system crashes.
- Resource optimization: With Hyper-V, you can easily allocate resources such as CPU, memory, and storage to different virtual machines, which helps to optimize the use of resources on your physical machine.
- Easy migration: Hyper-V allows you to move virtual machines between physical hosts with ease, which is useful for disaster recovery, load balancing, and other scenarios.
Hyper-V, VMware and VirtualBox
Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox are virtualization programs that enable users to create and manage virtual machines on a host computer. The strengths and weaknesses of each program vary, and the user’s choice depends on their specific needs.
Hyper-V is a native hypervisor that is built into Windows OS. It offers features such as live migration, high availability, and support for failover clustering. It also has the ability to isolate virtual machines from each other, providing an added layer of security. Hyper-V is typically used in enterprise environments and is optimized for running Windows operating systems.
VMWare
VMware is one of the most popular virtualization software programs available, and it offers a wide range of features and capabilities. It supports a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and MacOS. VMware offers advanced features such as live migration, high availability, and support for clustering. It also offers a range of management tools that allow users to manage their virtual machines and hosts from a single interface.

Virtual Box
VirtualBox is an open-source virtualization software program that is free to use. It supports a wide range of operating systems and offers features such as snapshotting and the ability to create and manage virtual networks. VirtualBox is often used by developers and hobbyists to test and develop software on different operating systems.

Comparison of Hyper-V with VMware and VirtualBox
When comparing Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox, there are a few key differences to consider. Hyper-V is a native hypervisor that is tightly integrated with Windows, making it the best choice for running Windows operating systems. VMware is a more mature and feature-rich virtualization platform that supports a wider range of operating systems and offers advanced features such as clustering and high availability. VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization platform that is best suited for developers and hobbyists who need a simple and easy-to-use platform for testing and developing software.
In terms of performance, Hyper-V and VMware are generally considered to be the most efficient and reliable virtualization platforms. VirtualBox is slower and less reliable than Hyper-V or VMware, but is still a suitable option for users not needing advanced features.
When it comes to usability, Hyper-V and VMware both offer a range of management tools and interfaces that make it easy for users to create and manage virtual machines. VirtualBox, on the other hand, is a bit more basic and does not offer as many advanced management tools.
Overall, the choice of which virtualization software program to use depends on the specific needs of the user. Hyper-V is best for Windows OS, while VMware has more features and supports more OS.. VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization platform for developers and hobbyists.

