Data Security
Data security is a collection of standards and technologies that protect data from damage, alteration, or leakage by deliberate or unintended means. Data protection can be implemented using several techniques and technological tools, including administrative safeguards, physical monitoring, conceptual tests, operational norms, and other techniques that prohibit access to unauthorised or malicious users.
Importance of Data Security
All the businesses work towards results. Results that come from efforts and data. From the finance giants trading with vast amounts of personal and financial data to the one-man company holding his customers’ contact information on a cell phone, technology is at stake with both big and small enterprises.
Data protection is mainly directed at securing the data, that a business entity captures, saves, produces, receives, or transmits during the course of its business practices. Enforcement is a major concern, too. Every computer, system, or process is used to handle, store, or capture data, it must be secure, regardless. Infringements of data will result in legal cases and large fines, let alone harm to the credibility of an entity.
Data Security Technologies
Data encryption technology comes in multiple ways and sizes and defends data from can attacks. Many of these attacks come from outside sources, but organisations should still work on defending their data from within.
Data encryption: Data encryption applies a code to a single piece of data and does not allow access to encrypted data without providing an acceptable key.
Data resilience: Through making data backup backups, companies may restore data should it be unintentionally lost or corrupted or compromised during a data breach.
Data erasure: There are periods when data need to be erased from all the devices that are no longer functioning or used. For example, if a customer demands removal of their name from a mailing list, the data should be permanently removed.
Data masking: Masking individual data areas will protect it from access to external unauthorised parties, as well as internal employees who may possibly exploit the data. The first 12 digits of a credit card number, for example, may be hidden within a database.
Why are small businesses more vulnerable to Data and Security breach issues?
Australian small businesses represent 97% of businesses. As a group, this means they are increasing the volume of personal and business data. This creates an increasing number of errors as different agencies gather information. These errors include identity theft and fraud. The threatening environment for small businesses is characterized by technical and human errors. The problem is that the small business environment has encouraged the government to accept e-commerce but lack the resources to secure its online business. This article analyses the threats of this situation and finds that personal corporate and government liability issues are fundamental to protecting small business information. Ultimately, this increases the likelihood of major undetected and undetected major vulnerability to Australia.
Use of device
Almost 90 per cent of small businesses use Microsoft Office for their day-to-day operations with barely less the usage of some shape of anti-virus software. Data suggests that 22 per cent of small businesses use a password manager, and these who rated themselves with an ‘above average’ grasp of cybersecurity is twice as likely to use a password supervisor than those who rated themselves with ‘average’ or ‘below average’ perception of cyber security.
According to the survey conducted by Australian Cyber security Centre. Small businesses using a Mac, around one in five are unaware what operating system they use. Small businesses using a PC, one in four use an operating system version that is Windows 7 or older (Which became unsupported from January 2020).
Outsource to specialists, or adopt the DIY approach
The Survey indicates almost half of small businesses spend less than $500 dollars yearly on cyber security. This suggests that many Small businesses take a DIY approach. However, cyber safety is a complicated subject with swiftly evolving technology and increasingly sophisticated cybercriminals pushing boundaries.
The Survey sought to apprehend whether small businesses that undertake the DIY approach commonly put in force the primary steps that will minimise their hazard of a cyber incident. Further, the Survey sought to understand how tons outsourcing buys peace of thought for small businesses when they may no longer be as protected as they believe.
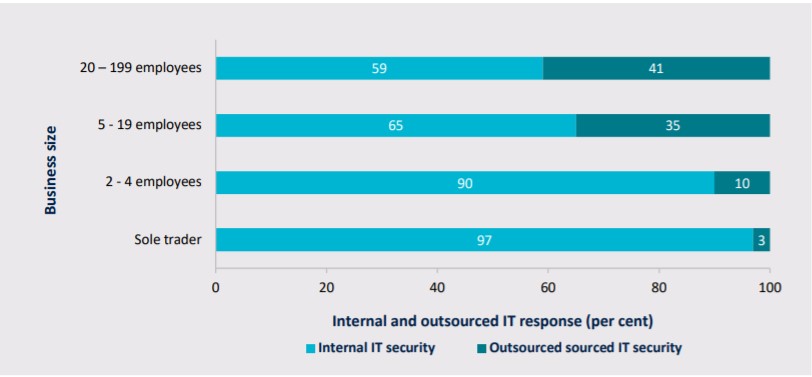
Can small businesses accurately evaluate their cyber-expertise?
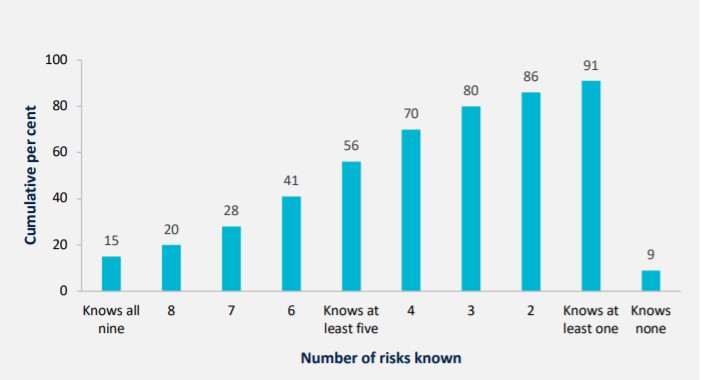
Data shows that Malware, Phishing and Ransomware are the most usually understood cyber security risks. Nearly one in ten respondents feel they are unable to provide an explanation for any of the cyber dangers listed: these being Malware,
Phishing, Ransomware, Trojan, Key logger, Insider Threat, Drive through download, Spear phishing, and Person-in-the-middle attack. Conversely, solely 15 per cent feel they can provide an explanation for all nine cyber risks recognized through the survey. Overall, knowledge of cyber protection risks among Australian small businesses is low.
Lack of Back-up plan
Most of the small businesses do not use cloud services for the data backup. Cloud backup safeguard your apps and data from local disturbances and outages. They provide reliable disaster recovery.
Small businesses are comparatively easy to attack
Due to absence of protection, hackers can easily access valuable data by finding entry points. They also use business credentials to attack big targets like financial institutions and suppliers.
Step-by-step Guide for Data Security
A security incident that impacts small businesses can be devastating. Small businesses should understand, act, and increase their security resilience against ever-evolving security threats.
Malicious Software (Malware)

Malware is an unauthorised software designed to cause harm. This software includes viruses, spyware, trojans and worms.
Malware gains access to important information such as bank or credit cards and passwords. Criminals can take control or spy on a user’s computer using Malware. They can easily access cheap tools to use malware against you.
Protecting against Malware
- Update your operating system automatically
- Automatic software application updates
- Backup your business data regularly
Scam Emails (Phishing)
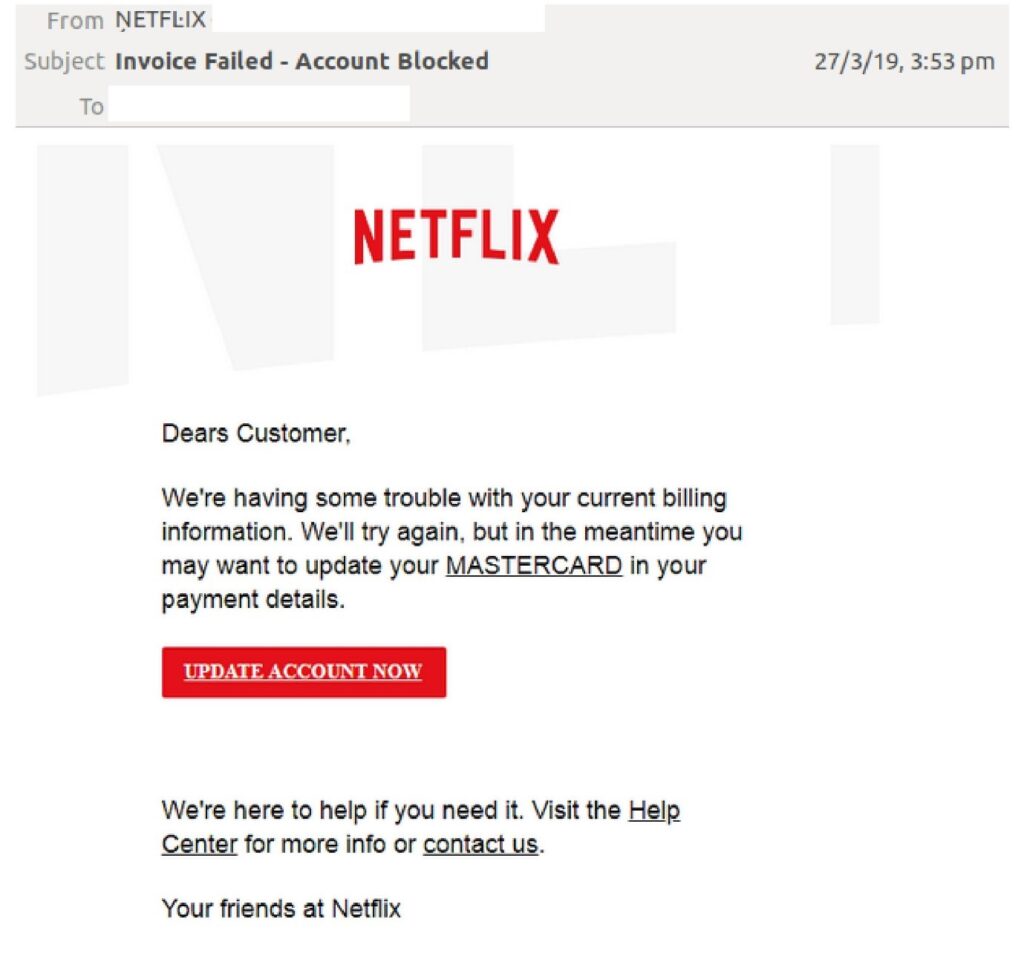
Dodgy emails designed to trick businesses out of money and data. They defraud users by asking them to provide personal information or to pay a fake account. They also scent attachment that looks genuine, with malware inside. Phishing emails are sent to thousands of people. Even if small of users fall for the scam, they can net significant data from the users.
These scams are not only limited to emails, users can receive via SMS, Messengers, and social media.
Be cautious of:
- Attachments
- Requests to check or confirm login details
- Bank account changes
Ransomware

Certain malware that locks your computer and data until you pay a ransom. You are vulnerable to second attack pay a ransom. This attack is typically carried out via email links or attachments. When downloaded or opened it encrypts your files, then demand ransom to restore access. Ransomware offers cyber criminals low-risk and high rewards. They target small businesses because they are unprepared to deal with ransomware attacks and they spend less on security measures.
Prevent and recover from ransomware
- Update your operating system automatically
- Automatic software application updates
- Backup your business data regularly
Software Considerations
Keeping your software organized can dramatically enhance your company’s protection against the most common types of cyber threats. For example, the most important software on a computer is the operating system. It manages your computer’s hardware and all its programs and requires updates, backups, and maintenance. Improve resilience, stay up to date, and stay safe with these small business software considerations.
Automatic Updates
An update is a new, improved, or secure version of software (a program, app, or operating system (such as Microsoft Windows or Apple iOS)) installed by a company on a computer or mobile device. Automatic Updates is a default or “set and forget” system that updates your software as soon as it is available. Automatic updates provide better online security, improve protection from loss of data and identity and enhance features and efficiencies for programs and applications.
- Turn on auto-updates foe operating system
- If auto updates not available, regularly check for updates, and install ASAP.
- If using Anti-virus software, make sure automatic updates are turned on
Automatic Backups
A backup is a digital replica of your business most important information e.g. consumer details, income figures. This can be to an external, disconnected tough power e.g. USB or to the Cloud. An automated backup is a default or ‘set and forget’
system that backs up your information automatically, without human intervention.
Automatic backups get your business back up and running quicker and safer. Protect credibility of your business. You will have peace in mind, that you can you are always protected so you can focus on your business efforts and values.
- Choose a backup system that suits your business
- Use cloud for your backup plan
- Test that are you able to back up your data regularly
- Make sure you safely disconnect and remove your back up storage device after each backup
Multi-Factor Authentication
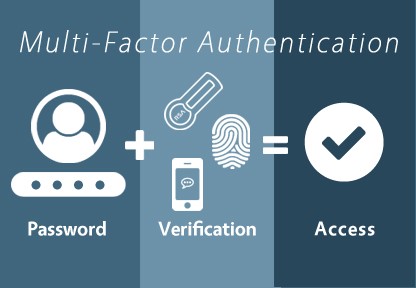
A secure method that requires two or more proof of identity to grant access. It typically requires a combination of something the knows (pin, question), Physical process (card, token) or inherently possesses (fingerprint, retina).
The couple of layers make it much more difficult for criminals to attack your business. Criminals would possibly manage to steal one proof of identification e.g. PIN, but they nevertheless want to obtain and use the other proofs of identity. Two-factor authentication is the most frequent type of MFA. Small business should implement multi-factor authentication wherever possible. Some of the options include token, random pin, email, SMS, fingerprint, etc.
People and Procedures
Businesses, however small, must be aware of and implement cybersecurity measures at all levels. Since small businesses often lack the resources for dedicated IT staff, this section describes how you can manage who can access and who can control your business information and employee training. it is. Your internal processes and workforce are critical and one of the most important lines of defence in protecting your business from cybersecurity threats.
Access Control
The process of controlling who can access in your corporate IT environment is one way to limit access to a computer system. It allows business owners to determine who they would like to give access to privileges to and to enforce access control to staff.
This process minimises risk of unauthorised access to important information. Small businesses outsource work to external suppliers, access control can help them to protect business by limiting the access to network, files, data, etc.
Employee Training
Educate your staff to protect your business against threats. Create a security incident response plan which educates staff how to avoid, recognise, report the threats. This training program is vital foe small businesses to protect the business from cyber-attacks. Unauthorised access to the business depends on how update your staff are, because cyber security is ever evolving.
Move to Cloud

Storing data in the cloud can be more secure than storing it in a physical server or data centre. If your laptop or computer is stolen, your data could be compromised by compromising the security of your home. If you have your data in the cloud, you can remove sensitive information remotely or move it to another account. It is difficult to break security measures on cloud platforms. Therefore, the security of the data is guaranteed.
Cloud providers specialize in data security and actively protect data by regularly updating their mechanisms. In addition, the cloud gives better control over the accessibility and availability of data, allowing only authorized users to access the data. Cloud storage security vendors provide secure data using advanced firewalls, event logging, internal firewall, encryption, physical security.

