Abstract
Digital Forensics might be a new term for some readers and some might be familiar with it. Since the technology has transitioned most of the daily work to online like banking details, customer details, phone details etc. So, the problems relating to the online has increased too like cybersecurity attacks, online theft. An evidence which is in the form relating to technology like details in the cloud, a USB storage can be considered as digital evidence. Now, Digital Forensic is a process of acquiring, preserving, and extracting the digital evidence. There are many tools which are available for free like Autopsy; if a user wants to learn about how Digital forensics work then this blog would dive into what Digital Forensics is and what tools can be used for digital evidence.
Introduction
In order to understand Digital Forensic, consider a scenario where a robbery took place inside an office but the robber and USB was found as an evidence. Now the robber deleted details from the USB or formatted the USB, so that he/she will not be evicted. Digital Forensics plays a vital role here from extracting the evidence to presenting the evidence in front of the law. A member of Digital Forensic team has to present all the evidence in a court and further court decides about the criminal. Now, there are three different steps involved in the Digital Forensics which are acquisition, preservation and extraction which are discussed below.
Steps Involving Digital Forensics
As mentioned in the above section that there are three steps involved in the Digital Forensics mainly which are preservation of evidence, acquisition of data and extraction of data. In the preservation of evidence, the evidence must be preserved in a hazmat bags, and they evidence must be handled with gloves. The evidence must be kept in proper temperature so that it does not affect the data in any way. The next step involved is acquisition of data and in this case the digital forensic tools come in practice. There are many digital forensic tools like Autopsy, FTK Imager, Volatility, Cellebrite etc. All these tools are very helpful but only Autopsy and FTK Imager are discussed in this blog in next section. The third step is extracting the data which is also done in the forensics tool and further providing them to a court in order to solve the case.
Digital Forensics Tools
The tools which are to be discussed are Autopsy and FTK Imager. Both tools are available for free of price on Autopsy’s and FTK Imager’s website. The purposes of these tools is to recover files which have been deleted already and for demonstration purposes a USB is used where files are deleted and then recovered using these software. The tools procedure is quite different but they both establish the same purpose which is recovering files. A file might be changed or did not recover properly but these tools does recover files properly. In order to check whether files restored are same or not, a user can check the hash of the file like MD5 hash or SHA hash and then compare it with the recovered file’s hash. There are many websites like OnlineMD5 Hash which can be used to check hash f the files. Following is the image of USB emptied after deleting files.
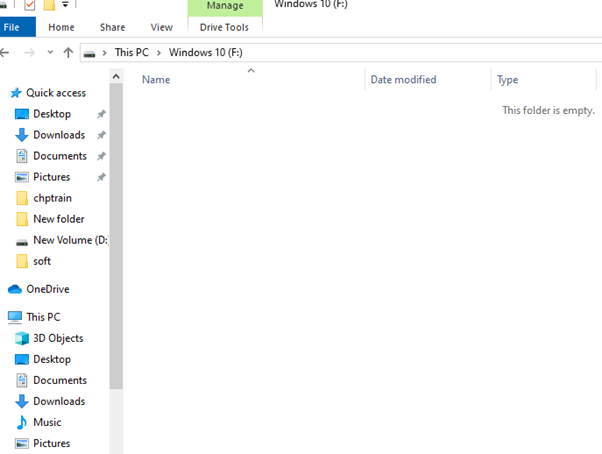
It is clear from the image above that there are no files in the USB and all the files were deleted permanently from the computer. Now using FTK Imager first, a new case can be created which is shown below:
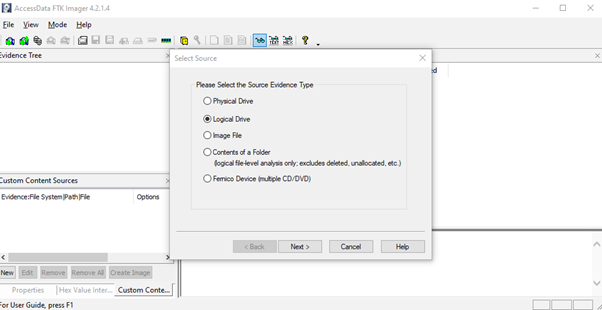
There are different types of destination files which can be recovered like Raw data, E01 data, AFF format and this case E01 data format is used. Images would take longer to be saved if there is more data in the USB which was deleted. The files would be saved in the destination folder as chose by the user. Then the case can be opened from File in the taskbar of the software and choosing the file saved. This would open all the files as shown below:
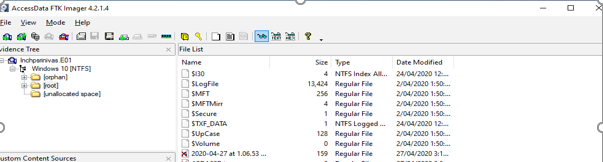
A user can search in all the directories and locate the files and further recover it.
The usage of Autopsy is quite different from FTK imager but it is much quicker and there are many options which might not be present in FTK Imager. The biggest difference is that Autopsy give the files straightaway in the main menu instead of opening from the saved files. The following image is the data source selection in Autopsy.
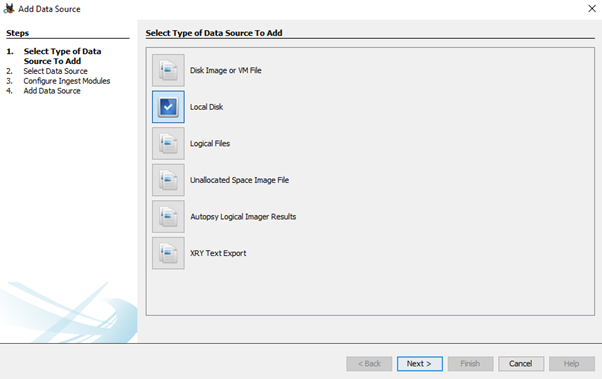
Now, the USB needs to be selected as source and then Autopsy gives a lot of options like which files need to be recovered or which needs to be excluded as shown below:
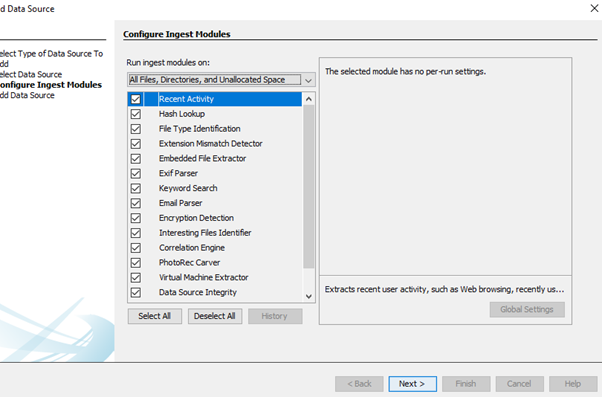
The procedure once begins, it starts giving files in the main menu. If a user has found its files then it can stop the procedure and recover the files or continue the procedure until find files or procedure is finished. It is recommendable to let the procedure finish off since some files might not be recovered properly. The files will be shown like in the image below:
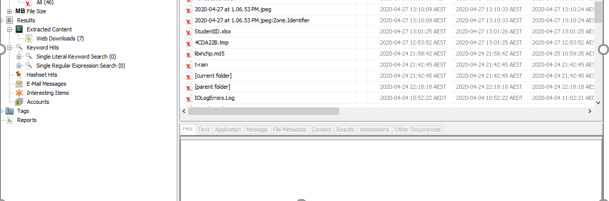
Then files can be exported into any folder. Another positive aspect of using Autopsy is that it can provide hash values in the software itself instead of using third-party website of software. The recovered files can be checked and use them as the case requires.
Conclusion
As most of the financials are moving online, the chances of thefts and crimes will increase too. The branch of digital forensics helps in gathering digital evidences and then recover the files which can be used against the perpetuator. It is important to note that there are many applications and according to what are the requirements, applications can be chosen. If a user wants to learn about the working of Digital Forensics; it is advisable to use a virtual machine like VmWare. Digital Forensics is certainly the future which will help in reducing solving crime rate in Australia and around the whole world.