Cybersecurity is a critical aspect of modern society as it protects individuals, organizations, and governments from online threats such as hacking, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime. The increasing reliance on technology has created new opportunities for cyber criminals to steal sensitive information, damage computer systems, and cause widespread disruption. As a result, organizations must take cybersecurity seriously in order to ensure their information and systems are protected.

At its core, cybersecurity is a combination of technology, processes, and people working together to secure digital assets and information. This requires a multi-layered approach that includes firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and other security measures. However, these technical solutions are only part of the equation. It is equally important to have effective policies and procedures in place to ensure that employees understand the risks and know how to avoid them.
One of the main advantages of a strong cybersecurity program is that it helps to prevent data breaches. Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, and can result in the loss of sensitive information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other personal data. A data breach can also harm an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of trust among customers and partners. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can reduce the risk of a data breach and minimize the damage that may result from a breach if it does occur.
Another advantage of cybersecurity is that it helps organizations to comply with regulations. Many industries are subject to strict regulations that require organizations to protect sensitive information and to report data breaches. For example, healthcare organizations must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which requires them to protect the privacy and security of patient health information. By implementing effective cybersecurity measures, organizations can ensure they are in compliance with these regulations and avoid costly fines and penalties.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, a strong cybersecurity program can also help organizations to improve their overall efficiency. By implementing security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption, organizations can reduce the risk of malware and other security incidents that can disrupt operations. This can lead to increased productivity, as employees are able to focus on their work without being interrupted by security incidents.
Cybersecurity is a critical aspect of modern society, and organizations must take it seriously in order to protect their information and systems. A strong cybersecurity program can help to prevent data breaches, comply with regulations, and improve overall efficiency. It is important for organizations to implement effective technical solutions, policies, and procedures, as well as to educate employees about the risks and how to avoid them. By taking a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity, organizations can help to ensure their digital assets and information are protected from online threats.
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. It has become one of the most prevalent forms of cybercrime in recent years, causing widespread disruption and financial losses for individuals and organizations alike.
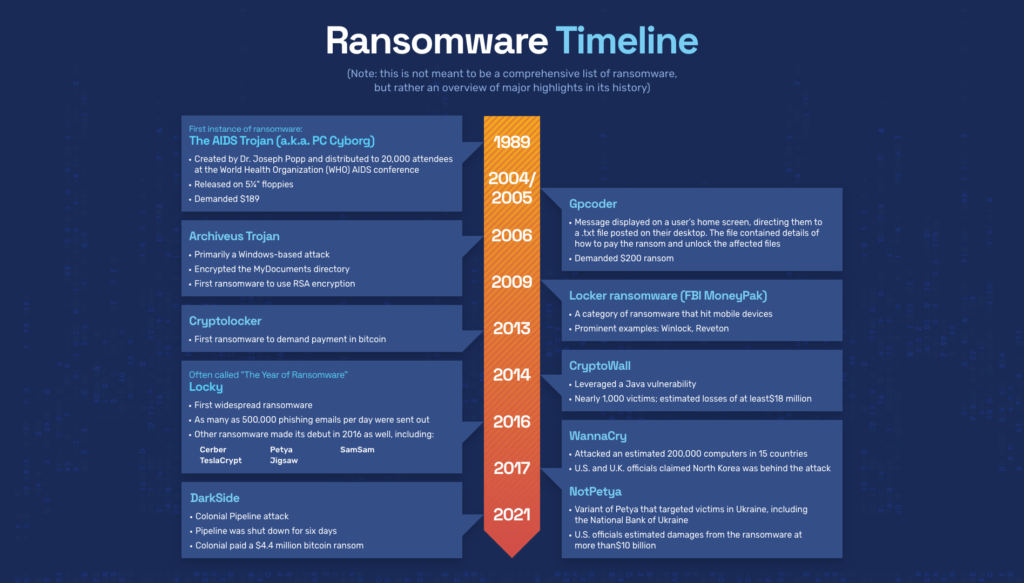
The first recorded instance of ransomware dates back to 1989, when a programmer named Joseph Popp distributed a virus called the AIDS Trojan. The virus encrypted the victim’s files and demanded a payment of $189 to obtain the decryption key. However, the ransomware was not very effective and did not cause widespread damage.
In the early 2000s, ransomware evolved to become more sophisticated and more dangerous. The first known instance of modern ransomware was the GpCode Ransomware, which appeared in 2006. This malware encrypted the victim’s files and demanded payment in exchange for the decryption key. Unlike earlier ransomware, GpCode used strong encryption algorithms, making it much more difficult for victims to recover their files without paying the ransom.
In recent years, ransomware has become a major threat to individuals and organizations. One of the main reasons for this is the growth of the dark web, which has made it easier for criminals to distribute ransomware and to receive payments anonymously. In addition, the rise of cryptocurrency has made it easier for criminals to demand payment, as they can receive payment without having to reveal their identity.
The evolution of ransomware has also been driven by the increasing use of cloud computing and the internet of things (IoT). These technologies have created new opportunities for attackers to spread ransomware and to cause widespread disruption. For example, the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 affected more than 200,000 computers in 150 countries, causing widespread disruption and financial losses.
The evolution of ransomware has led to the development of new security measures to protect against this threat. For example, organizations can implement backup and disaster recovery systems to reduce the impact of a ransomware attack. In addition, they can implement endpoint protection solutions, such as antivirus software and firewalls, to reduce the risk of infection.
In conclusion, the evolution of ransomware has been driven by technological advancements, the growth of the dark web, and the increasing use of cloud computing and the IoT. Ransomware has become one of the most prevalent forms of cybercrime, causing widespread disruption and financial losses for individuals and organizations. To protect against this threat, organizations must implement effective security measures and educate their employees about the risks and how to avoid them.
