Cognitive technology
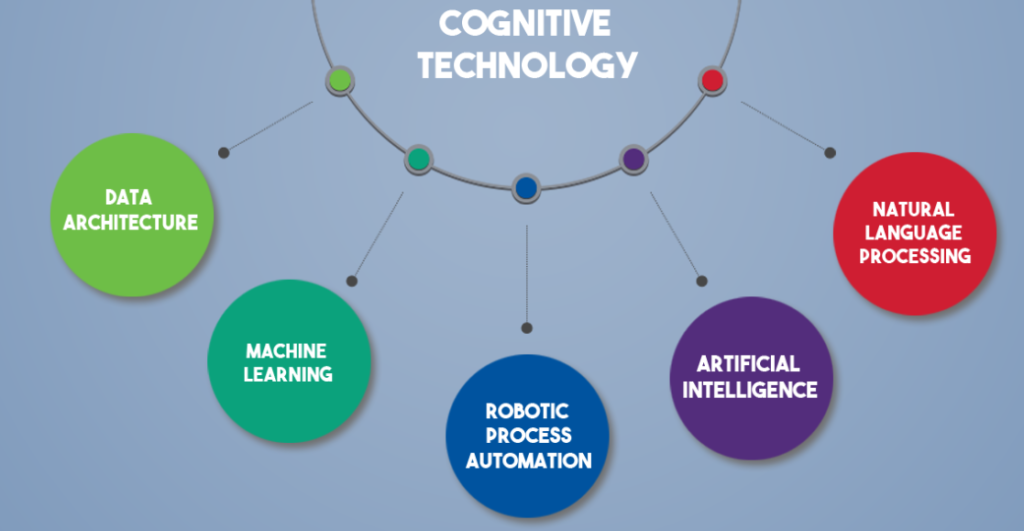
Algorithms, robotic process automation, machine learning, natural language processing, and natural language creation are all included in the wide category of cognitive technologies, or “thinking” technologies, which extends into the field of artificial intelligence (AI). The philosophical question of whether or not these technologies are actually thinking or intelligent is relevant. For our purposes, these are systems that, regardless of the fundamental structure of the mechanisms that result in those behaviors, appear to think, or behave intelligently, similarly to how humans do. Strong business incentives are provided by cognitive technologies. From routine (robotic process automation) to sophisticated and abstract tasks, they can be automated (machine learning and AI). They are able to identify small patterns in data and predict potential future events. Business tasks that were not previously thought to be automatable, like evaluating contracts, categorizing photographs, or spotting offensive information, are now being automated thanks to cognitive technologies.
Cognitive Capabilities Classification
Natural Language Understanding, Machine Learning, Speech-to-Text, Biometrics, and Handwriting Recognition are just a few of the many distinct Cognitive Technologies that are already in use. Even though these tools are still developing, the information technology sector has not yet established clear boundaries between these many technologies. We must comprehend how they will be used in the commercial context in order to categories them. Engagement, insight, and automation can be considered as the three main pillars that make up cognitive technology applications. These fundamental components allow cognitive technology to sense and shape processes, imitating and occasionally outperforming complicated human thought patterns.
Almost any industry can acquire and use a few of the technologies in these areas. These talents work together inside a single company to support integrated automation.
Cognitive Engagement : Cognitive technologies are frequently used in situations where a business interacts with clients or other end users. By providing mass consumer personalization at scale via human-like communication techniques like visual and linguistic cues, intelligent agents and avatars are employed to enhance the end-user experience. In order for downstream systems to recognize and respond to the user’s requests, natural language understanding (NLU) technologies receive natural language from users and ascertain the speech’s intent. However, Natural Language Generation (NLG) technologies reduce the cognitive load for the user by transforming structured data inside computer systems, such as financial reports, into a more understandable form. Communication by voice is made possible by speech recognition and speech synthesis (text-to-speech) technology.
RoboChat, a platform from NAB-owned UBank, is one instance of a cognitive system enhancing interaction. Customers can use an IBM Watson-powered chatbot to fill out challenging home loan applications with the aid of the Watson engine. With the system’s ability to accept simple to moderately complicated questions, users can converse with the system using normal language instead of the conventional search engine query “interest-only repayment.” Like any new employee, RoboChat picks up new skills as the day goes on. The system keeps track of customer service problems and successes. Human team members analyze the problems that RoboChat “couldn’t understand” and then give the computer direct remedies based on their analysis. This enables RoboChat to grow in knowledge with each iteration by learning from its errors.
Cognitive insights : Out of massive data sources, like Big Data platforms, these systems are able to create new patterns and linkages. From among billions of data points, they are able to analyze in real-time and produce valuable, actionable insights. The algorithms and outputs of cognitive insight technologies can be changed over a number of iterations, potentially millions, without the involvement of a human. The machine will modify its code during these iterations, improving the testing procedure for each subsequent iteration. As this goes on, the system will keep successful processes and eliminate unsuccessful ones. As a result, target system is recursively optimized.
Netflix uses machine learning to deliver customized recommendations to its ever-growing user base that are much more complicated than simple genre similarities. The user is sorted into a subset of “taste groups,” each of which has a few thousand subcategories, using algorithms that analyze both the individual’s past behavior and overall trends. Each user receives personalized classifications and forecasts when these tastes are compared to the constantly growing library of viewing alternatives. Over 80% of newly discovered shows that a typical user will watch are a result of this system, which is incredibly successful.
Cognitive automation: This group of technologies, which is the most advanced, includes those created to automate routine, well-defined processes. These systems typically contain a robust set of guiding principles and libraries that impose a strict framework around the “decisions” they take. Typically, cognitive automation is employed to mimic easier mental actions and processes. These procedures, including content tagging, fundamental data extraction, and rule-based planning, are frequently rhythmic in nature.
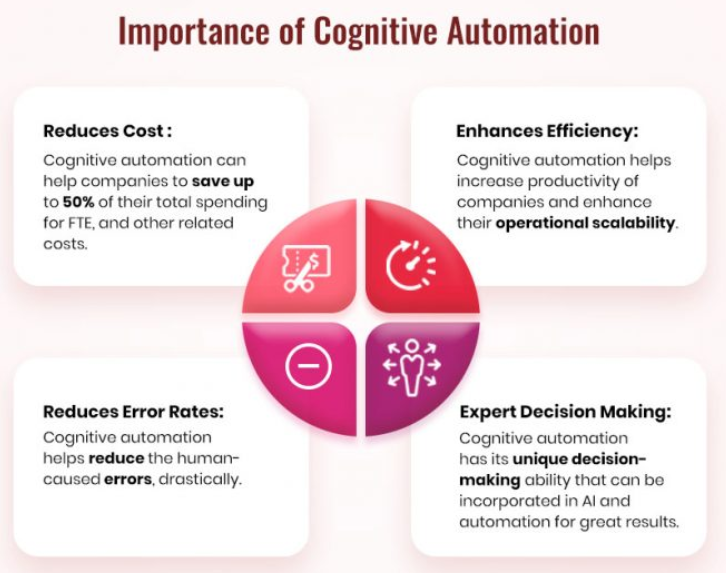
One of the most widely used types of cognitive automation is intelligent automation. This focuses on the direct substitution of computer software for human operations. IA is constrained to the settings set by their controller when acting alone. However, these processes may be maintained or even improved at a fully autonomous rate when paired with other strategies, such as machine learning. The Hong Kong subway is one example of how this has been put into practice. For more than 10,000 staff, an automated system planned and optimizes over 2,600 maintenance tasks each week. According to constraints like railway schedules and labor availability, this algorithm calculates millions of alternative options. The best maintenance schedule for each week is then determined.
Advantages of Cognitive Technology
By enabling a computer network to analyze and manage massive amounts of volumetric data, cognitive computing aids in the usage of a computer network for useful real-life applications. There are a number of benefits that cognitive computing offers, including the following:
- Simpler and more effective business processes
- Accurately analyze data
- Customer Interaction Has Increased
Conclusion
The field of artificial intelligence, which is constantly evolving, has given rise to cognitive technology. Applications for cognitive learning aspects become more obvious as AI becomes more prevalent in enterprises. While some of these systems, like Siri or Cortana, are consumer-facing, many others are not. The majority of cognitive technologies are designed to streamline internal company processes and unlock value from data that was previously hidden behind complexity or sheer volume.
