Today, at Let’s Tech IT Easy, we decided to start a new series that reflects the fast changing technology eco-system due to the “Cloud Computing”. Having reached this far, we realized that while everyone seems to have heard in some or the other way about “Cloud systems”, they still may not understand what actually does it mean. So, let’s take it easy and start with the first basic question…..What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networks, software, analytics, and intelligence, that deliver faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale over the Internet. You typically only pay for the cloud services you use, helping you lower your operational costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale your business as needed.
Cloud computing is a popular choice for people and businesses for a variety of reasons, including cost savings, increased productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and safety.
Click here for general IT Support services for Businesses
Evolution to cloud computing
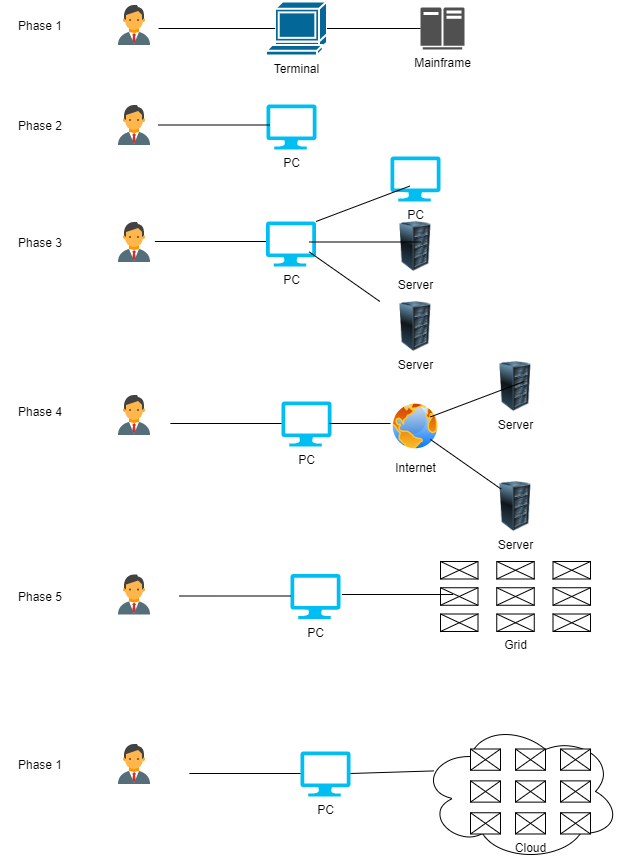
In phase 1, using dummy terminals, several users exchanged powerful mainframes. In phase 2, stand-alone PCs were strong enough to accommodate the needs of the majority of consumers. PCs, laptops, and servers were linked together via local networks in phase 3 to share resources and improve performance. Local networks were linked to other local networks that formed a global network in phase 4, such as the Internet to make use of remote software and services. In phase 5, via a distributed computing system, grid computing supported pooled computing resources and storage. Furthermore, in phase 6, cloud infrastructure offers shared services on the in a scalable and easy form, the Internet.
How does cloud computing work
Instead of owning their own computing infrastructure or data centres, companies can lease access to everything from applications to storage from a cloud provider.
One of the benefits of using cloud computing services is that businesses can avoid the initial cost and complexity of owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure and instead only pay for what they use when they use it. In turn, cloud service providers can realize significant economies of scale by providing the same services to a wide range of customers.
Organizations of all types, sizes and industries are using the cloud for a variety of use cases, including data backup, disaster recovery, email, virtual desktops, software development and testing, big data analytics, and customer web applications. For example, healthcare companies are using the cloud to develop more personalized therapies for their patients. Financial services companies use the cloud for real-time fraud detection and prevention. Video game makers also use the cloud to serve online games to millions of players around the world.
Layers of cloud computing
Infrastructure
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), a vendor provides physical computer hardware such as CPU processing, memory, data storage, and network connectivity. IAAS allows users to run selected operating system and software applications. Vendors generally control and maintain physical computer hardware. Users generally control and maintain operating systems and software applications. The actual IAAS suppliers are scaling their IAAS layer to such immense levels that the marginal cost of adding more GHz, GB, packaging, etc. converges to zero.
Platform
Platform as a service (PaaS), a vendor provides infrastructure in addition to services and web servers such as operating systems and server applications. PaaS enables customers to use the provider’s cloud infrastructure to deploy web applications and other customer-developed software using provider-supported programming languages. In general, the vendor controls and maintains physical computer hardware, operating systems, and server applications. In general, the user only controls and maintains user-developed software applications. This framework gives developers easy access to a complete ecosystem for creation and implementation, and also helps you to host the application you are developing.
Software
Software as a service (SaaS), vendor use their cloud infrastructure and cloud platforms to provide software applications to customers. These end-user applications are usually accessed by the web browser so that users do not have to install or maintain additional software. Typically, manufacturers control and manage hardware, operating systems, and software applications on a physical computer. Typically, customers control and manage only a limited number of application configuration settings for the user.
Development model
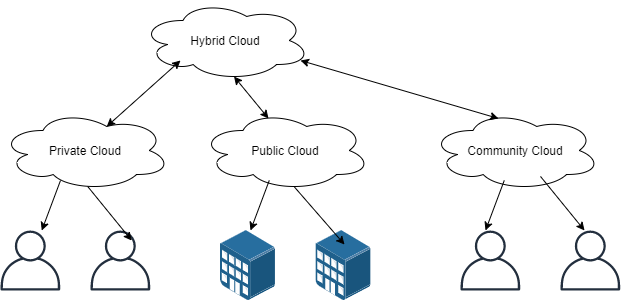
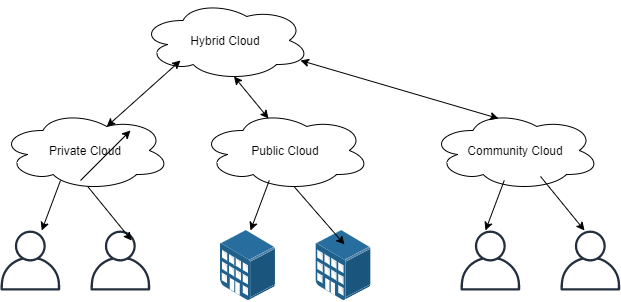
Public cloud
An organization uses one vendor’s cloud infrastructure used by many other organizations and other members of the public over the internet. This model offers the maximum potential return on economies of scale. However, this model has several risks that need to be considered.
Private cloud
Cloud Infrastructure and Services used is managed on the organization’s premises or off-site and managed by the organization or vendor. Compared to the public cloud model, the private cloud model has reduced the potential for cost. If the private cloud is properly implemented and maintained, it reduces the chances of security. A well-developed private cloud, managed by a vendor, can offer many benefits to the public cloud, but has greater control over security.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds connect public and private clouds, connected by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud helps your business optimize for more flexibility, more deployment options and your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Community cloud
In a community cloud, a shared infrastructure or cloud setting is shared by the culture with many organisations. There must be a shared purpose for all this organisation.
Benefits of cloud computing
- Business efficiency and Cost reduction
- Speed
- Deploy your business globally in minutes
- Performance
- Data security
- Disaster recovery
3 issues of cloud computing
Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
- Availability
- Confidentiality
- Access control
Cloud computing features
Resource pooling and elasticity
In cloud storage, to support a vast number of clients, services are shared. Cloud storage uses multi-tenancy where, due to demand, various services are dynamically distributed and de-allocated. It is not possible to know, from the user’s end, where the resource currently exists.
The distribution of services should be dynamic, in the sense that the demand should adjust appropriately and efficiently. If the demand increases many times on a single day, then the device should be elastic enough to satisfy the extra requirement, and when the demand reduces, it should revert to the usual level.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Cloud computing will guarantee users QoS in hardware / CPU terms. Memory power, performance, and bandwidth.
Pricing
There is no up-of-investment condition for cloud computing. No spending on capital is required. consumers pay for resources and capacity they use.
Click here to purchase any IT related software or hardware
Scalability and on-demand services
Cloud computing provides services and resources on demand, the provided resources are scalable over number of data centres.
Over the next few days, we will post some more blogs that would take this series ahead and explain various concepts about Cloud-Computing. Till then, let’s tech it easy….;)