CLOUD COMPUTING:
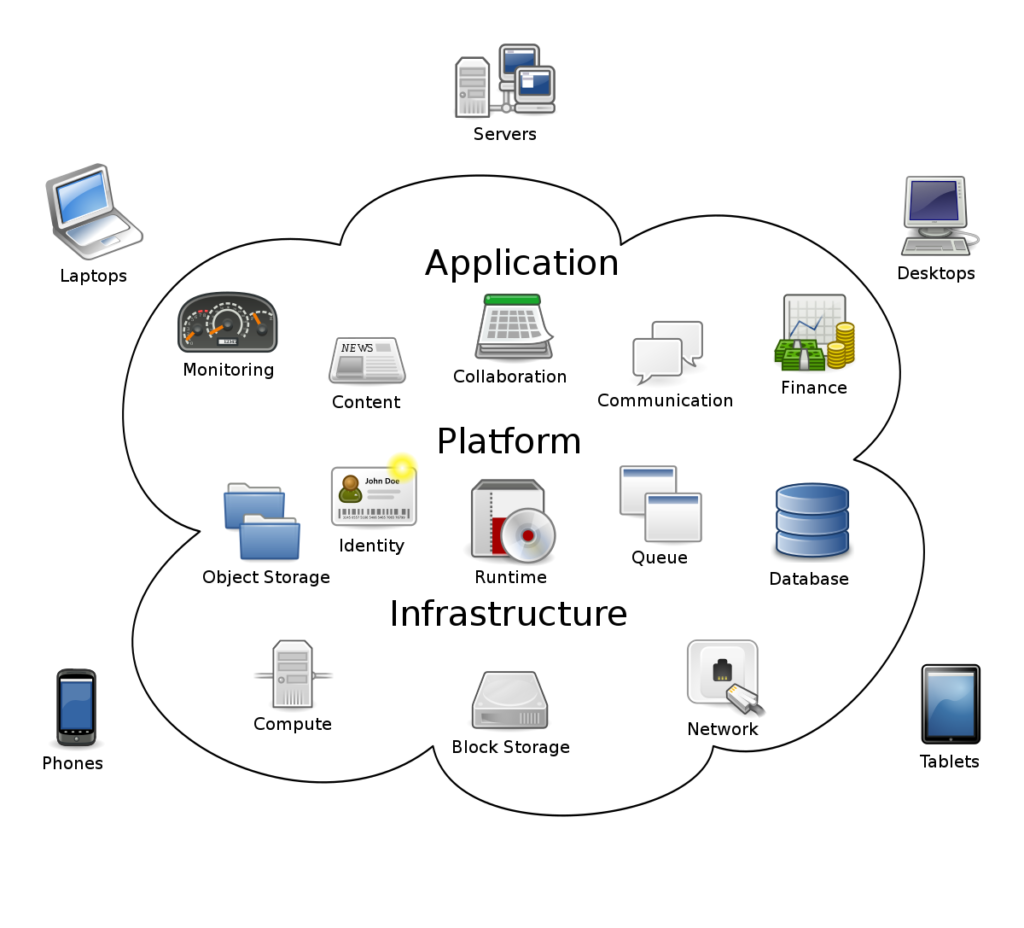
Simply described, cloud computing is the delivery of various services over the Internet. These resources include data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software, among other tools and applications.
Cloud-based storage allows users to save files to a remote database rather than keeping them on a proprietary hard drive or local storage device. As long as an electronic gadget has internet connections, it has access to data and the software programmes needed to execute it. By supplying the same services to a large number of people, in return cloud computing service companies can benefit from considerable economies of scale.
Cloud computing services today include everything from basic storage, networking, and processing power to natural language processing and artificial intelligence, as well as common office programmes. Almost any service that doesn’t require you to be physically near the computer gear you’re using can now be supplied through the cloud.
Cloud basic services:
The three basic types of cloud computing services are public, private, and hybrid. For a fee, public cloud services make their services available over the Internet. Private cloud services, on the other hand, limit the number of people who can use them. These services are a network-based system that provides hosted services. A hybrid option exists as well, which combines elements of both public and private services.
Let’s get in detail with these services,
- PUBLIC:
- The public cloud is the traditional cloud computing model, in which users can access a large pool of computing power via the internet (whether that is IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS). One of the most significant advantages is the ability to rapidly scale a service. The cloud computing providers have vast amounts of computing power that they share among a large number of customers via the ‘multi-tenant’ architecture.
- Because of their massive scale, they have enough spare capacity to easily cope if any particular customer requires more resources, which is why they are frequently used for less-sensitive applications that require a varying amount of resources.
- Computing functionality can range from common services such as email, apps, and storage to enterprise-grade operating systems and infrastructure environments used for software development and testing.
- The cloud vendor is in charge of creating, managing, and maintaining a pool of computing resources that is shared by multiple tenants from across the network.
Advantages of using public cloud:
- High scalability and flexibility to meet the demands of an unpredictable workload.
- Because the cloud vendor manages the infrastructure, the complexity and reliance on in-house IT expertise is reduced.
- Flexible pricing options based on various SLA offers
Disadvantages of using public cloud:
- The total cost of ownership (TCO) for large-scale usage, particularly for midsize to large enterprises, can rise exponentially.
- Because public clouds are inherently insecure, they are not suitable for sensitive mission-critical IT workloads.
- A lack of visibility and control over the infrastructure may not meet your compliance requirements.
- PRIVATE:
Because it is hidden behind the corporate firewall, private cloud allows organisations to reap some of the benefits of public cloud without having to worry about losing control over data and services. Companies can control where their data is stored and build the infrastructure in any way they want – primarily for IaaS or PaaS projects – to give developers access to a pool of computing power that scales on-demand without risking security.
Advantages of using private cloud:
- Organizations can run protocols, configurations, and measures to customise security based on unique workload requirements, allowing them to comply with stringent regulations.
- High scalability and efficiency to meet erratic demands while maintaining security and performance
- The private cloud is dependable in terms of SLA performance and efficiency
Disadvantages of using private cloud:
- When compared to public cloud alternatives, the private cloud is an expensive solution with a relatively high TCO, particularly for short-term use cases.
- Due to the high security measures in place, mobile users may have limited access to the private cloud.
- If the cloud data centre is limited to on-premise computing resources, the infrastructure may not be able to meet unpredictable demands.
- HYBRID:
In reality, hybrid cloud is probably where everyone is: a little bit of public, a little bit of private. Some data is in the public cloud, some projects are in the private cloud, there are multiple vendors, and there are various levels of cloud usage. Disaster recovery planning and the desire to avoid hardware costs when expanding their existing data centre are the primary reasons for choosing hybrid cloud.
Advantages of using hybrid cloud:
- Improved security posture as sensitive IT workloads run on dedicated resources in private clouds, while regular workloads are distributed across low-cost public cloud infrastructure as a cost-cutting measure.
- Public cloud systems can scale without exposing sensitive IT workloads to security threats.
- Maximum dependability is achieved by distributing services across various data centres, some public and others private.
Disadvantages of using hybrid cloud:
- As organisations operate and manage an evolving mix of private and public cloud architecture, additional infrastructure complexity is introduced.
- Switching between public and private funds can be difficult to track, resulting in wasteful spending.
- Strong compatibility and integration are required between cloud infrastructures from various locations and categories. This is a limitation of public cloud deployments, where organisations do not have direct control over the infrastructure.
COMPANY’S PROVIDING CLOUD COMPUTING:
Many companies are now offering cloud services and improving their performance on a daily basis. These Cloud Service Providers offer SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
So, let’s DISCUSS the world’s TOP 3 Cloud Service Providers,
- AWS:
Cloud computing services are delivered from massive data centres located all over the world. AWS categorises this as ‘regions’ and ‘availability zones.’ Each AWS region is a distinct geographic area, such as the EU (London) or the US West (Oregon), which AWS then divides into availability zones (AZs). An AZ is made up of one or more datacenters that are far enough apart that a single disaster will not take both offline, but close enough together to support business continuity applications that require rapid failover. AWS has over 50 AZs, each with multiple internet connections and power connections to multiple grids.
(Image reference: https://www.halcyontek.com/amazon-web-service.aspx)
- MICROSOFT AZURE:
Microsoft Azure allocates its resources in a slightly different manner. It provides regions, which it defines as a “set of data centres deployed within a latency defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network.” It also provides ‘geographies,’ which are typically composed of two or more regions that can be used by customers with specific data-residency and compliance requirements “to keep their data and apps closed

(Image reference: https://www.erpsoftwareblog.com/2020/10/an-overview-of-microsoft-azure-and-your-erp-pizza-as-a-service-example/)
- GOOGLE:
Google follows a similar model, dividing its cloud computing resources into regions, which are then further subdivided into zones, each of which includes one or more data centres from which customers can run their services. Google recommends that customers deploy applications across multiple zones and regions to help protect against unexpected failures. It currently has 15 regions made up of 44 zones:

(Image reference: https://www.blog.google/products/google-cloud/what-was-new-with-google-cloud-in-april-2020/)
If you still not sure or don’t know how and what cloud service you want to use for your organization, don’t worry, you can easily obtain help by clicking ‘Computer Repair on site (CROS)’here.

Cloud computing challenges:
- Although cloud performance is generally quite stable, there are times when the cloud infrastructure is under heavy load. This can be seen at certain times of the day, usually during business hours. In a cloud environment, an application’s performance is determined by network traffic and the resources that other virtual machines running on the same physical machine as the application’s virtual machine consume. It can be difficult to replicate the performance displayed from one run to the next.
- Because different cloud providers may provide different levels of services (for example, Google App Engine provides PaaS while Amazon EC2 provides IaaS, SaaS, and APIs), it may be difficult for a user to switch from one cloud provider to another. In other contexts, this is referred to as the “lock-in” problem. In general, IaaS is easier to switch to or from than PaaS, while SaaS is the most difficult. Data theft is a particular concern during an economic downturn because the number of security breaches has increased.
- Anyone considering putting their data in a third-party storage space would be concerned about privacy and data security. After all, users will have no idea where their data will be stored or who will have access to it within the cloud infrastructure. Some Cloud Computing providers may distribute their data centers across multiple countries. Data stored in these countries may be subject to different regulations and thus be protected or unprotected depending on the local governments.
HOW TO OVERCOME CLOUD COMPUTING CHALLENGES:
We face numerous problems while dealing with cloud computing some of them can be resolved easily but some are bit hard so we need to take those problems to the experts in that field where they can solve the problem intelligently and efficiently within no time. one of that type of professional team is ” Bench Mark IT Service”. https://www.benchmarkitservices.com/google-cloud-service-providers/.

They are dedicated to providing full cloud deployments using Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or Amazon Web Services. Google Cloud, which incorporates GSuite as part of its enterprise and business services, is quickly establishing itself as a leader in email hosting.
They assist enterprises in establishing cloud infrastructure, cloud hosting, virtual machine deployment in the cloud, data migration, machine administration, and other technical support difficulties. Allow us to spend more time on manufacturing rather than connecting things.