Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networks, software, analytics, and intelligence, that deliver faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale over the Internet. You typically only pay for the cloud services you use, helping you lower your operational costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale your business as needed.
Cloud computing is a popular choice for people and businesses for a variety of reasons, including cost savings, increased productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and safety.
For cloud based solutions for the businesses like Google, AWS and Azure
How does cloud computing work
Instead of owning their own computing infrastructure or data centres, companies can lease access to everything from applications to storage from a cloud provider.
One of the benefits of using cloud computing services is that businesses can avoid the initial cost and complexity of owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure and instead only pay for what they use when they use it. In turn, cloud service providers can realize significant economies of scale by providing the same services to a wide range of customers.
Organizations of all types, sizes and industries are using the cloud for a variety of use cases, including data backup, disaster recovery, email, virtual desktops, software development and testing, big data analytics, and customer web applications. For example, healthcare companies are using the cloud to develop more personalized therapies for their patients. Financial services companies use the cloud for real-time fraud detection and prevention. Video game makers also use the cloud to serve online games to millions of players around the world.
Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
Benefits of cloud computing
Business efficiency and Cost reduction
By using the cloud infrastructure, you do not need to spend large amounts of money to buy and maintain equipment. This significantly reduces the investment cost. You do not need to build hardware, facilities, utilities, or a large data centre to grow your business. You also do not need large IT teams to handle your cloud data centre operations, as you can enjoy the experience of your cloud provider’s employees.
Speed
Most cloud computing services are self-service and on-demand, so even large amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, usually with just a few clicks. This gives companies more flexibility and relieves the burden on resource planning.
Deploy your business globally in minutes
With the cloud, you can expand into new geographies and deploy a global solution in minutes. Most of the cloud computing services has infrastructure all over the world, so you can deploy your application to multiple physical locations with a few clicks. Keeping applications close to the end users reduces latency and improves performance.
Performance
The largest cloud computing services operate in a global network of secure data centres, regularly updated to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several advantages over a single enterprise data centre, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Data security
Data breaches and other cybercrimes can destroy a company’s revenue, customer loyalty and brand status. This is one of the major concerns of every business. Cloud services provide advanced security features by storing and handling your data securely.
Click here for cyber security related issues of businesses
Cloud storage vendors implement basic protections for their platforms and the data they process, such as authentication, access control and encryption. Therefore, most enterprises supplement this protection with their own additional security measures to enhance data protection in the cloud and restrict access to sensitive information in the cloud.
Disaster recovery
Along with data security, data loss is a major concern for all businesses. Storing your data in the cloud ensures that data is always available even if your devices, such as laptops or PCs, are damaged. Cloud-based services provide instant data recovery for all types of emergencies.
Relying on the traditional on-premise method means all your data is stored locally, on office computers. Despite your best efforts, computers can malfunction for several reasons – from malware and viruses, to age-related hardware degradation, to simple user error. But, if you upload your data to the cloud, it will not be accessible to any computer with internet connection, even if it is on your working computer.
Click her for general IT Support services for Businesses
Types of cloud computing services
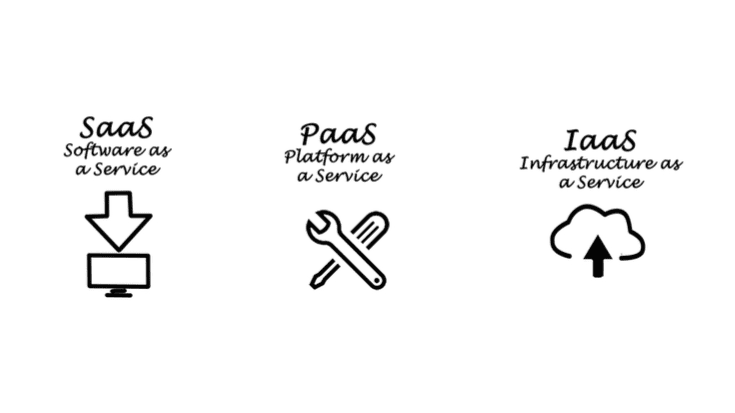
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
A vendor provides physical computer hardware such as CPU processing, memory, data storage, and network connectivity. IAAS allows users to run selected operating system and software applications. Vendors generally control and maintain physical computer hardware. Users generally control and maintain operating systems and software applications.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Vendor provides infrastructure in addition to services and web servers such as operating systems and server applications. PaaS enables customers to use the provider’s cloud infrastructure to deploy web applications and other customer-developed software using provider-supported programming languages. In general, the vendor controls and maintains physical computer hardware, operating systems, and server applications. In general, the user only controls and maintains user-developed software applications.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Vendor use their cloud infrastructure and cloud platforms to provide software applications to customers. These end-user applications are usually accessed by the web browser so that users do not have to install or maintain additional software. Typically, manufacturers control and manage hardware, operating systems, and software applications on a physical computer. Typically, customers control and manage only a limited number of application configuration settings for the user.
Cloud development models
Public cloud
An organization uses one vendor’s cloud infrastructure used by many other organizations and other members of the public over the internet. This model offers the maximum potential return on economies of scale. However, this model has several risks that need to be considered.
Private cloud
Cloud Infrastructure and Services used is managed on the organization’s premises or off-site and managed by the organization or vendor. Compared to the public cloud model, the private cloud model has reduced the potential for cost. If the private cloud is properly implemented and maintained, it reduces the chances of security. A well-developed private cloud, managed by a vendor, can offer many benefits to the public cloud, but has greater control over security.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds connect public and private clouds, connected by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud helps your business optimize for more flexibility, more deployment options and your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Community cloud
In a community cloud, a shared infrastructure or cloud setting is shared by
the culture with many organisations. There must be a shared purpose for all these organisations. Both these agencies or third parties control the group cloud. Often, the community cloud is used for national security purposes.
Future of cloud

Regardless of size, most organizations consider the cloud to be the first option for delivering a new application or feature. It turns out that no one wants to build and maintain an application on their servers or data centres, which means companies around the world are starting to see the benefits of a pay-as-you-go infrastructure.
Now that we live in a digital economy and the number of IoT devices is growing rapidly, we not only have access to information, we use it to make decisions in real time. A large amount of data generated in the cloud will need to be collected and processed.
Click here to purchase any IT related software or hardware
Gaps need to be taken care of in the future
- Privacy and Security: The data must be protected together in a form that addresses legal issues about the location of the data and is managed by the system.
- Adaptability by developing different programming models.
- Data, resources, app, and services needs legislation and licensing models depending on the place they are hosted
- Ability to detect failures, adapt to the required amount of resources, guarantee the continuous availability of said resources and meet customer expectations in terms of quality by creating new segmentation concepts and distributed programming models.
Conclusion
We see cloud computing now as a transition from using many large servers to one huge server, from distributed data (from the same company) to centralized. Cloud computing systems can be more efficient, we need to upgrade technologies to meet the needs of such useful systems. Before the use of these systems we recommend you do your own research. Cloud computing can be a benefit for some companies and a disaster for others, so when considering cloud computing we should do our own research and not rely solely on the research of others.