Secure web browsing is a game of changing tactics. Just when you think you’ve made your computer as safe to use as possible, the landscape changes. Cyber criminals are constantly developing new methods to hijack your system, and unless you stay ahead of the game you could find yourself with a very large problem. To secure your home computer well, you are suggested to contact your local computer expert like “Computer Repair Onsite”.
1.Install and use antivirus software.
Security experts agree across the board that a good first line of defense is to make use of antivirus software. Antivirus software will detect and remove viruses as well as prevent any new infections. Do your research, choose a software program that fits your needs, and use it. To purchase the antivirus software, you can go to the website like X-Tech Buy.
2. Use a firewall.
A firewall is an application that protects your computer from hackers gaining unauthorized access to your computer. Setting up a personal firewall will dramatically reduce the possibility of your computer being attacked by Internet threats.

3. Strong passwords are your friend.
A strong password is the equivalent of a deadbolt on a door. The more difficult it is to gain entrance to your accounts, the safer your accounts are. Make your passwords difficult to figure out, by using a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters, and most importantly, change them regularly.
Passwords are one of the biggest weak spots in the whole Internet security structure, but there’s currently no way around them. And the problem with passwords is that people tend to choose easy ones to remember (such as “password” and “123456”), which are also easy for cyber thieves to guess. Select strong passwords that are harder for cybercriminals to demystify. Password manager software can help you to manage multiple passwords so that you don’t forget them. A strong password is one that is unique and complex—at least 15 characters long, mixing letters, numbers and special characters.
4. Update your security software.
It’s not enough to install security software one time; you must install each update as it is made available. Cyber criminals are constantly finding new ways to infiltrate systems and launch new threats, and security software developers release updates to combat this trend. To update the security software, you can go to the website like X-Tech Buy.
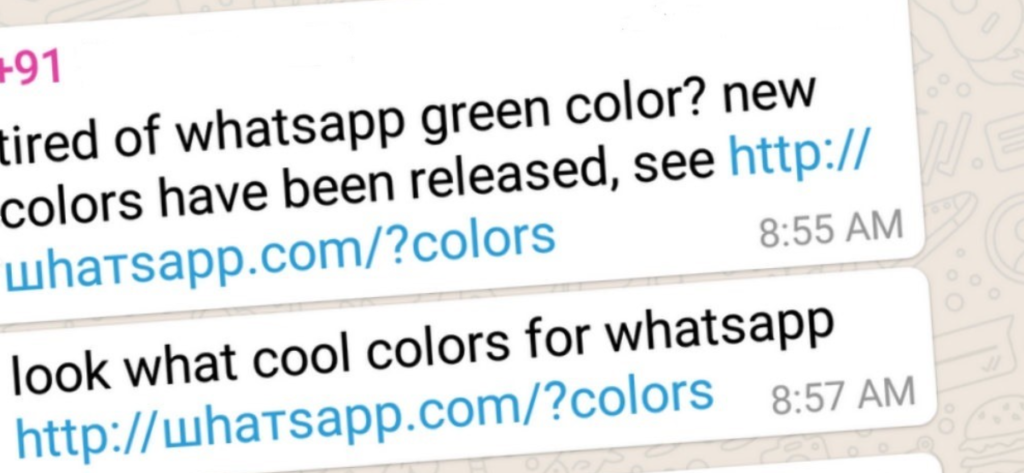
5. Be wary of clicking links in email or instant messages.
Viruses spread easily through links in instant messages and email attachments. Even if you know and trust the person who sent it, it’s possible the link is infected and the sender is unaware of it.
6. In fact, be wary of clicking links, period.
Free toolbars, popup windows offering freebies, sidebar ads on websites, links in public forums – clicking any of these could open your computer to a host of issues. Just don’t do it. That free trial of a new game isn’t worth it.
Unsafe surfing can also lead to other threats—from embarrassing personal comments or images that, once online, are nearly impossible to erase, to getting mixed up with people you’d rather have had nothing to do with.
Here are the Top 10 Internet safety rules to follow to help you avoid getting into trouble online (and offline).
7. Keep Personal Information Professional and Limited
Potential employers or customers don’t need to know your personal relationship status or your home address. They do need to know about your expertise and professional background, and how to get in touch with you. You wouldn’t hand purely personal information out to strangers individually—don’t hand it out to millions of people online.
8. Keep Your Privacy Settings On
Marketers love to know all about you, and so do hackers. Both can learn a lot from your browsing and social media usage. But you can take charge of your information. As noted by Lifehacker, both web browsers and mobile operating systems have settings available to protect your privacy online. Major websites like Facebook also have privacy-enhancing settings available. These settings are sometimes (deliberately) hard to find because companies want your personal information for its marketing value. Make sure you have enabled these privacy safeguards, and keep them enabled.
9. Practice Safe Browsing
You wouldn’t choose to walk through a dangerous neighbourhood—don’t visit dangerous neighbourhoods online. Cybercriminals use lurid content as bait. They know people are sometimes tempted by dubious content and may let their guard down when searching for it. The Internet’s demimonde is filled with hard-to-see pitfalls, where one careless click could expose personal data or infect your device with malware. By resisting the urge, you don’t even give the hackers a chance.
10. Make Sure Your Internet Connection is Secure. Use a Secure VPN Connection
When you go online in a public place, for example by using a public Wi-Fi connection, PCMag notes you have no direct control over its security. Corporate cybersecurity experts worry about “endpoints”—the places where a private network connects to the outside world. Your vulnerable endpoint is your local Internet connection. Make sure your device is secure, and when in doubt, wait for a better time (i.e., until you’re able to connect to a secure Wi-Fi network) before providing information such as your bank account number.
To further improve your Internet browsing safety, use secure VPN connection (virtual private network). VPN enables you to have a secure connection between your device and an Internet server that no one can monitor or access the data that you’re exchanging.
Recommended VPN Providers
- NordVPN
- ExpressVPN
- Private Internet Access
- PureVPN
- Perfect Privacy
11. Be Careful What You Download
A top goal of cybercriminals is to trick you into downloading malware—programs or apps that carry malware or try to steal information. This malware can be disguised as an app: anything from a popular game to something that checks traffic or the weather. As PC World advises, don’t download apps that look suspicious or come from a site you don’t trust.
12. Make Online Purchases From Secure Sites
Any time you make a purchase online, you need to provide credit card or bank account information—just what cybercriminals are most eager to get their hands on. Only supply this information to sites that provide secure, encrypted connections. As Boston University notes, you can identify secure sites by looking for an address that starts with https: (the S stands for secure) rather than simply http: They may also be marked by a padlock icon next to the address bar.
13. Be Careful What You Post
The Internet does not have a delete key, as that young candidate in New Hampshire found out. Any comment or image you post online may stay online forever because removing the original (say, from Twitter) does not remove any copies that other people made. There is no way for you to “take back” a remark you wish you hadn’t made, or get rid of that embarrassing selfie you took at a party. Don’t put anything online that you wouldn’t want your mom or a prospective employer to see.
14. Be Careful Who You Meet Online
People you meet online are not always who they claim to be. Indeed, they may not even be real. As InfoWorld reports, fake social media profiles are a popular way for hackers to cozy up to unwary Web users and pick their cyber pockets. Be as cautious and sensible in your online social life as you are in your in-person social life.
15. Keep Your Antivirus Program Up To Date
Internet security software cannot protect against every threat, but it will detect and remove most malware—though you should make sure it’s to date. Be sure to stay current with your operating system’s updates and updates to applications you use. They provide a vital layer of security.
16. Bookmark important sites.
If there are sites you visit regularly, it’s a good idea to bookmark them in your browser. A mistyped address could take you to a false site that mirrors the site you intended to go to, but with malicious code that can harm your computer and compromise your information. Bookmarked addresses take you to the same site every time.
Most importantly, realize that the care you take to protect yourself in your everyday life extends to your online life. Don’t share personal information unless you are absolutely certain that where you share it is secure. Be aware that any information you share over a public wireless hot spot (say, at your favorite coffee shop) is not secure and can be seen by anyone looking at information as it travels over that network. Just as you wouldn’t leave your debit card on the dashboard of your unlocked car, don’t make your information easy to attain.
17.Manage Your Cookies
Cookies are a way for websites to store certain bits of information in your browser. Their original purpose was to make browsing more convenient for users, by storing login information for example. They have certainly achieved that purpose, but have also morphed into “tracking cookies”. These let websites track you after you’ve left their sites.
Clearing cookies that you don’t want or need is the best way to keep sites from tracking you once you’ve navigated to new, unrelated websites.
18.Use Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is when a service requires two measures of verifying your identity. This could mean you need a password and a link sent to your email, or a code text messaged to you to log in. Adding this second layer of protection is a reliable way to keep your data safe.
19.Browser Extensions
Opinions are a bit mixed on this one. While adding extensions, or add-ons, to your browser can protect you, it also just opens up your data to another third party. It’s important to do your research before installing.
20.Private Search Engines
These search engines work like normal, popular search engines except they make your privacy a priority. Generally, private search engines don’t track your searches or link your search terms to your personal data. These search engines also use encryption to hide your search terms locally and from other users on your network. Try these out and see if you like a certain one best:
- Search Encrypt
- StartPage
- DuckDuckGo
Who Are You Protecting Yourself From?
Hackers
The term “hacker” is definitely overused to the point that the term’s meaning is a bit cloudy. However, hackers are individuals trying to gain access to your information for personal or political gain. These cyber-criminals use a number of methods but their motivation is mainly getting your financial information, passwords, or social security number. They then use this information for identity theft or to access your bank accounts. If you somehow have also been a target of the hackers, you must approach a reliable cyber security expert like BITS
Advertisers
Much of the internet is built around advertising. To make their ads more effective or to get insight into how you interact with their websites, companies and businesses use the massive amounts of data they collect.
Google operates the largest advertising network in the world. With its analytics software and advertisements on a majority of the internet’s websites, Google knows a lot about you. If the idea of one company knowing most of what you do on the internet makes you uncomfortable, you are not alone.
NSA & Other Governmental Groups
Unfortunately, governments around the world have decided they need to track their citizens on the internet and through other means. Edward Snowden revealing the NSA’s surveillance methods shocked many people. In countries under authoritarian regimes, this is sadly the norm.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
The companies who provide internet service also monitor how people use the web. Congress passed a bill that allows ISPs to sell data about their user’s habits on the internet. This could lead to your browsing data ending up in third parties’ hands. ISPs can arguably access the most information about you because they see all of your internet activity, not just the browsing on specific websites.
Conclusion: Be Vigilant About Your Internet Privacy
Privacy and security on the internet are constantly evolving. What keeps you safe one day may change completely the next. Because the internet is generally an open platform, new threats emerge all the time. Technology and opinions surrounding it are constantly changing. It’s important to get second (and third) opinions on the products you use and the protection measures you take.