Introduction
The advancement in modern technologies and the use of IoT have been reaching new heights with every minute passing. By using these devices and technologies, a huge amount of data is gathered and analyzed; this data is known as big data. This data can be of different types such as structured, semi-structured or unstructured. All these data types are useful in extracting useful insights that can be used for various purposes. Big data analytics has the tendency to provide organizations with deep insights from large volumes of data gathered from multifarious data sources. The example of the results of big data analytics can be seen in the day to day lives. For example, when a user searches for shoes on Google or any other search engine, all other applications or websites on the user’s device start showing advertisements for shoes. This is a result of big data analytics practices using which the user’s data, search daily searches, and daily activities are analyzed and related topics are displayed to the users.
Five V’s of Big Data
To understand the concept of big data in detail, the key attributes of big data, also known as the five V’s of big data are very important.
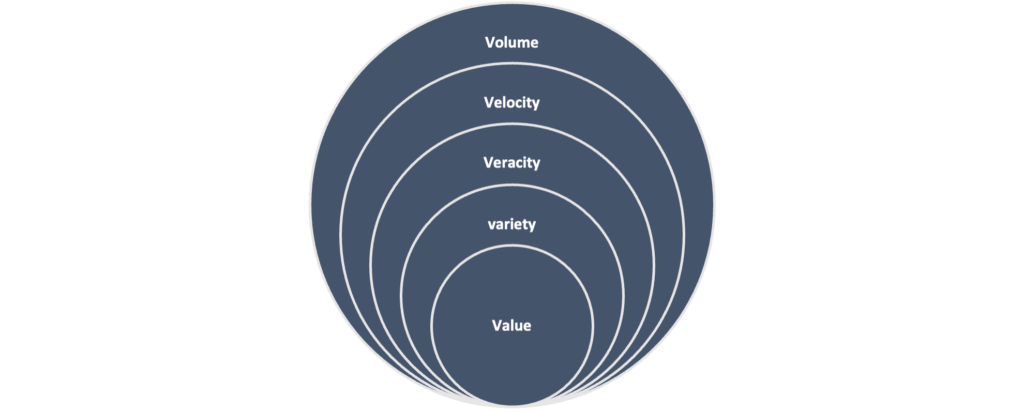
- Volume- It refers to the size or amount of data gathered or stored. The data gathered from social media feeds, and clickstreams on a web application or IoT devices are available in larger volumes (AltexSoft, 2021).
- Velocity- It refers to the speed at which the data is generated, stored and processed. Some of the data related to smart devices often operate in real-time and require real-time evaluation (Gutta, 2022).
- Variety- The variety of data refers to different forms or types of data gathered from different sources such as structured, semi-structured and unstructured data.
- Structured Data- Properly organized data with defined length and format is considered a structured form of data that can be stored in relational databases. Examples- Bank Statements.
- Semi-Structured Data- Semi organized data that is difficult to be organized in a relational database is referred to as semi-structured data. In this type of data, the subject or topic is in organized form but the data within does not have an organized structure. Examples- XML data.
- Unstructured Data- Unorganized data with no defined length and format is considered as unstructured data and it is very difficult to analyze. Examples- Pdf, Media logs.
- Value- The most important attribute and characteristic of big data is the value of the gathered data. For business purposes, data with no value is useless and is substantially removed from the available data sets so as to minimize the chances of extended data processing time. It is important to extract valuable information from the collected data through big data analytics techniques (AltexSoft, 2021).
- Veracity- It refers to the quality and accuracy of the data gathered from different sources. The inconsistencies and uncertainties in the data can cause problems in extracting valuable information from that data (Gutta, 2022).
Big Data Analytics
Gathering of large volumes of data has no use till it has any value. The process of extracting valuable insights or information from different variety of data using data analysis tools and methods such as data mining, predictive analysis, deep learning etc. is called Big data analysis. Various software applications used for storage and processing of big data are Hadoop, Apache Spark, NoSQL etc. Big data analysis plays a major role in identifying trends, correlations and unique patterns in raw data and drawing useful and meaningful full information from that data using some familiar analysis techniques such as clustering and regression (Elgendy & Elragal, 2014).
Working on big Data Analysis
The big data analysis process includes the following five steps to process the data and draw useful insights from a large volume of data.
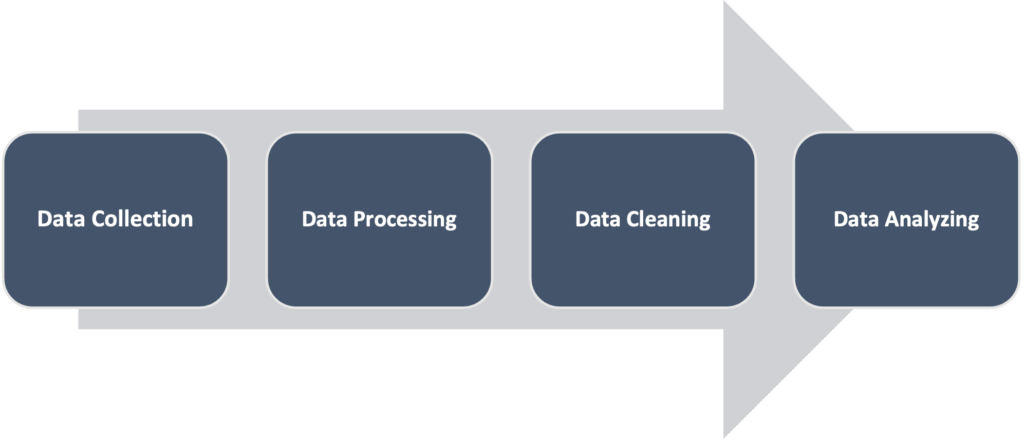
- Data Collection- The first process in big data analysis is to collect data from different sources such as cloud storage servers, mobile applications, IoT sensors and many more. The data collected from these sources are raw and of varying formats such as structured, semi-structured and unstructured (tableau, 2021).
- Data Processing- After collecting different types of data from various data sources, it needs to be organized into standardized data which has a high degree of consistency so as to get accurate results. After organizing the data, the processing is done using batch processing and stream processing options. Batch processing is used for that data whose turnaround time between collection and processing is longer. Stream Processing option is used for small batches of data to shorten the turnaround time and provide fast results. This processing option is mainly focused on the real-time analysis of data.
- Data Cleaning- Irrespective of the volume and velocity of data, it requires cleaning or scrubbing to remove the duplicate, incomplete and inaccurate data to improve the data analysis process. Uncleaned data may lead to inappropriate and flawed insights.
- Data Analyzing- After collecting, processing and cleaning of data, the analysis process begins. In this process, the unique patterns, trends and insights are extracted using various methods and tools such as-
- Data Mining- Data mining is the process of identifying unique patterns and relationships from large data sets. Using data mining techniques, the raw data collected from various sources are converted into meaningful insights that can assist the decision-making process (tableau, 2021).
- Predictive Analysis- Predictive analysis techniques are used by organizations to analyze historical data, and find patterns and trends in that data. These trends help the organization to make an informed decision for future business processes. Also, these techniques help the organization in identifying the potential risks and threats based on the historical data analysis.
- Deep Learning- This technique is used for analyzing the data using Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning based on the human neural network (Mahdavinejad et al., 2018).
References
- AltexSoft. (2021). Big Data Analytics: How It Works, Tools, and Real-Life Applications. AltexSoft. Retrieved from https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/big-data-analytics-explained/
- Elgendy, N., & Elragal, A. (2014). Big Data Analytics: A Literature Review Paper. Advances In Data Mining. Applications And Theoretical Aspects, 214-227. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08976-8_16
- Gutta, S. (2022). The 5 V’s of Big Data. Medium. Retrieved from https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/the-5-vs-of-big-data-2758bfcc51d
- tableau. (2021). Retrieved from https://www.tableau.com/learn/articles/big-data-analytics
- Mahdavinejad, M., Rezvan, M., Barekatain, M., Adibi, P., Barnaghi, P., & Sheth, A. (2018). Machine learning for internet of things data analysis: a survey. Digital Communications And Networks, 4(3), 161-175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2017.10.002

