Making a virtual replica of something, whether a desktop, server or network, is a technique known as virtualisation. Testing and development, disaster recovery, and workload consolidation are some uses for this virtualised computer system representation. The software that enables virtual machine creation and operation on servers is virtualisation software.
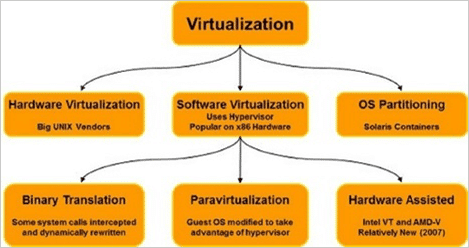
The main advantage of adopting virtual machine software is running multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single server or desktop computer, which was previously not feasible with conventional hardware. Microsoft’s most recent virtualisation offering, Hyper-V, has taken the role of earlier models, including Microsoft Virtual Server, Windows Virtual PC, and Microsoft Virtual PC. As there are many virtualisation software which is popular In 2018, some of them are mentioned below:
1. Microsoft HyperV
2. VMware vSphere
3. Citrix XenServer
4. Red hat KVM
1. Microsoft HyperV:
Launched in 2008, Hyper-V helps expand or establish a private cloud environment. It promotes effective hardware utilisation, improves business continuity, and makes development and testing more efficient.
Features of Microsoft Hyper-V are:
- Nested virtualisation
- Discrete device assignment
- Cloud backup
- Supports containerisation
- Quality of service (QoS) for software-defined networks
- Supports re-sizing of virtual hard disks, memory, and CPU while the VM is running
- Live migration & Storage Migration
- Storage Quality of Service (QoS)
- Windows PowerShell Direct (new)
Some of the advantages that it has are:
- It allows us to combine various workloads on fewer systems; Hyper-V improves our energy usage and conserves physical space.
- Users may relocate virtual guests across pieces of hardware thanks to Hyper-adaptability V’s with no downtime.
- Redundancy and consistent application availability are provided via failover clustering.
- Users can run many VMs thanks to the platform’s dynamic memory management.
- The platform uses Microsoft’s Active Directory to provide streamlined security administration.
Similarly, it also has some disadvantages like:
- Linux doesn’t get enough support
- When the operating system receives security upgrades, users are required to shut down all virtual machines (VMs).
2. VMware vSphere:
To virtualise our servers and deliver applications, VMware vSphere provides a bare-metal environment. VMware ESXi and VMware Vcenter Server are the virtualisation components that make up the vSphere module.
The ESXi hypervisor enables quick provisioning of virtual resources and performance optimisation through page sharing and compression. The vCenter server also centralises management of the ESXi devices linked to the network.
Features of VMware vSphere are:
- The VMs are operated using the ESXi hypervisor.
- Users may manage ESXi hosts and control processes on VMs using the vCenter Server.
- Cloud assets are protected using the Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication service provided by vCenter.
- vCenter service users and their actions are verified using Security Token Service (STS) certificates.
- When the central vCenter server is down, high availability is ensured through vSphere Cluster Services (vCLS).
- Users of the Vmotion technology may smoothly switch VMs between physical hosts and data repositories without affecting their services.
- Driver hardening guarantees that processes keep running even if input/output devices have issues.
- Users may create alerts, configure permissions, and monitor network activities using managed inventory items.
Some of the advantages that it has are:
- The functionality of vSphere may be increased by users by adding vSphere components via plugins.
- Accessing vSphere components is made simple by the client interface provided by vSphere.
- The hardware layer comes with built-in fault tolerance.
- Users can always regain services thanks to the software’s snapshots.
- The vendor support on the platform is excellent.
Similarly, it also has some disadvantages like:
- When compared to alternative virtualisation providers, the VMware licence is more expensive.
- Because vSphere is a complicated platform, it needs substantial training to comprehend and use it.
- Hardware that VMware does not support cannot be used with the platform.
3. Citrix XenServer:
Based on Xen Project Hypervisor, XenServer is an open-sourced bare-metal virtualisation platform. It comprises enterprise-grade features that help enterprises easily handle workloads, combined OS, and networking configurations.
XenServer provides improved virtualised graphics with NIVIDA and Intel and allows the execution of multiple computer operating systems on the same computer hardware.
Features of Citrix XenServer:
- Host Failure Protection
- Multi-server management
- Dynamic Memory Control
- Active Directory Integration
- Role-Based Administration and Control (RBAC)
- In Memory read caching
- Live VM migration & Storage XenMotion
Some of the advantages that it has are:
- Small and medium-sized businesses can afford licence charges.
- Since it is an open-source platform, companies are free from the problems associated with vendor lock-in.
- The platform includes a simple to use, intuitive graphical user interface.
- Using the snapshot functionality, users may restore operations and defend sensitive data from threats.
- The platform is simple to set up and does not require lengthy setups.
- Citrix Hypervisor supports 3D graphics through its virtual GPU suppliers.
Similarly, it also has some disadvantages like:
- USB device support is only minimal
- lacks a cutting-edge management solution for centralised control of virtual machines
- Citrix XenServer must use PowerShell scripts to automate processes, which might be difficult for non-technical users.
- Moving virtual machines from an open-source environment to the commercial XenServer platform is difficult and time-consuming.
4. Red hat KVM:
Users may instal their applications on Red Hat’s OpenShift Kubernetes platform, built on enterprise KVM and Linux. Red Hat Virtualization platform enables demanding workloads.
Red Hat Virtualization relied on container technology to provide customers with more options for creating, transferring, and expanding data-intensive applications that demand high availability, low latency, and zero downtime.
Features of Red hat KVM:
- Red Hat Virtualization supports mixed applications running on VMs and containers.
- Users may break new apps into container microservices and apply traditional VM workloads to them.
- Users may run virtual machines (VMs) in Kubernetes thanks to RedHat’s open-source KubeVirt service.
Some of the advantages that it has are:
- Because the platform is open-source, users may avoid problems caused by vendor locks.
- Live migration and high availability for apps are included in their base licence.
- The platform is simple to use and update and enables consistent administration.
Similarly, it also has some disadvantages like:
- Slow deliveries of security patches
Any firm may profit significantly from virtualisation, which is a vital tool. Finding the appropriate virtualisation software for your purposes and comprehending how it will affect your organisation in the short- and long-term are the keys.
The choices available to network experts, IT managers, CTOs, and CIOs change as virtualisation develops into new forms that are more accessible than ever. This information should assist you in choosing the product that will best meet the requirements of your business.

