BACK END OF DATA PROCESSING:
What is data processing?
The conversion of data into a useful and desired format is known as data processing. Companies’ access to the data that can sharpen their competitive edge and give key business insights is limited without data processing. That is why it is critical for all businesses to comprehend the importance of processing all of their data and how to do it. This conversion, or “processing,” is done either manually or automatically, according to a predetermined sequence of actions. The majority of the processing is done automatically, using computers and other data processing technologies. The output data, often known as “processed” data, can be acquired in a variety of formats. Image, graph, table, vector file, audio, charts, and any other required format are examples of these formats. The final form is determined by the software or approach utilised. Automatic data processing is what it’s called when it’s done by itself. Data centers are crucial because they allow for processing, storage, access, sharing, and analysis of data.
When data is collected and transformed into useable information, it is called data processing. Data processing is usually done by a data scientist or a team of data scientists, and it is critical that it is done correctly so that the end product, or data output, is not harmed. This method can be used to sort an increasing amount of data. This aids in gaining a clearer picture of the subject and a better comprehension of it. This can lead to increased productivity and profits in a variety of industries. Data security, machine learning, data science, network security, and other areas of advancement necessitate a concentrated approach for trustworthy, precise, and cost-effective processing. Every organisation, particularly those that demand real-time processing, requires a dependable and efficient data centre. These facilities host vital infrastructure and provide the reliable processing necessary to keep services operational.
Why to do data processing?
For businesses to develop better business plans and gain a competitive advantage, data processing is critical. Employees throughout the organisation can understand and use the data if it is converted into a comprehensible format such as graphs, charts, and texts. Data processing takes raw data and converts it into more understandable formats (graphs, papers, etc.) that computers can understand and use. Because of the myriad new rules and purposes related with data, data processing is becoming a hot topic. Personal information, customer data, health information, contact information, location data, and other types of data are collected by large corporations and multinational corporations (MNCs) in a variety of ways. As a result of the collecting of this data, there is growing concern about how it is acquired and used. Collecting, keeping, and analysing sensitive data such as income, medical records, and location data is becoming a global concern. New legislation is being drafted to regulate what data is gathered and how it is used while keeping user privacy in mind.
Data processing cycle:
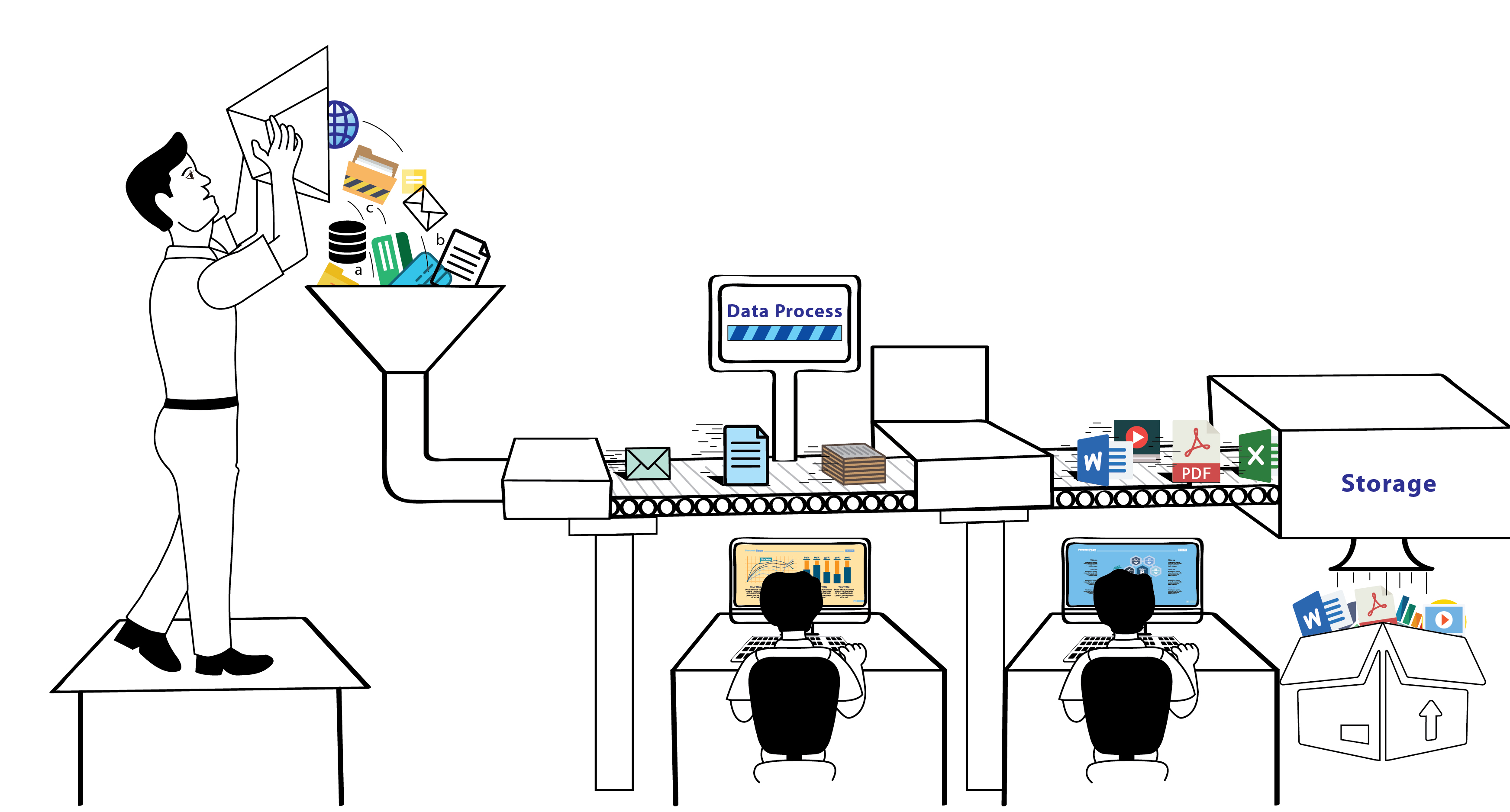
Any activity that necessitates data collection necessitates data processing. The information gathered must be saved, sorted, processed, analysed, and displayed. The data processing cycle is made up of several steps in which raw data (input) is fed into a process (CPU) that generates actionable insights (output). Each step is performed in a specified order, although the procedure is repeated in a cyclic fashion. The output of the first data processing cycle can be saved and used as the input for the subsequent cycle. This entire procedure can be broken down into six basic stages:
- Collection: The initial stage in data processing is data collection. Data is gathered from various sources, such as data lakes and data warehouses. It’s critical that the data sources used are reliable and well-constructed, so that the data collected is of the highest possible quality. The type of raw data gathered has a significant impact on the final product. As a result, raw data should be collected from defined and accurate sources in order for the conclusions to be legitimate and useable. Money numbers, website cookies, a company’s profit/loss accounts, user activity, and so on are examples of raw data.
- Preparation: After the data has been acquired, the data preparation stage begins. The stage of data preparation, sometimes known as “pre-processing,” is when raw data is cleaned up and structured in preparation for the next stage of data processing. Raw data is thoroughly verified for mistakes during the preparation process. This step’s goal is to get rid of faulty data and start generating high-quality data for the greatest business intelligence. The act of sorting and filtering raw data to remove unneeded and erroneous data is known as data preparation or data cleaning. Raw data is reviewed for errors, duplicates, miscalculations, and missing data before being translated into a format appropriate for analysis and processing.
- Input: The raw data is transformed to a machine-readable format and sent into the processing unit in this stage. This can take the form of data entry via a keyboard, scanner, or any other type of input device. The clean data is then entered into its intended destination and translated into a language that it can comprehend. The initial stage in the transformation of raw data into usable information is data entry.
- Data processing: The data entered into the computer in the previous stage is processed for interpretation in this stage. Machine learning algorithms are used to process the data, albeit the method may vary slightly depending on the source of the data and its intended application. To obtain a suitable outcome, the raw data is treated to various data processing methods using machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms.
- Output: The data entered into the computer in the previous stage is processed for interpretation in this stage. Machine learning algorithms are used to process the data, albeit the method may vary slightly depending on the source of the data and its intended application. To obtain a suitable outcome, the raw data is treated to various data processing methods using machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms.
- Storage: Storage is the final step in the data processing cycle, where data and metadata are saved for later use. This enables easy access to and retrieval of information whenever it is needed, as well as direct use of the information as input in the next data processing cycle. Furthermore, compliant with data protection legislation such as GDPR necessitates correctly maintained data. When data is correctly saved, individuals of the organisation may access it quickly and readily when they need it.
Conclusion:
For corporations, researchers, institutions, and individual users, data processing includes a wealth of information. With the increasing amount of data collected every day, more data scientists and data engineers are required to aid in the understanding of this data. New rules and guidelines have been enacted in response to growing concerns about user privacy and the acquisition of sensitive data. These regulations vary by country and regulate how data is processed, shared, and used by businesses.
If you are not sure about doing this you can simply take the help of experts here. here we can get the solution to all the software and hardware problems.

We may think it is an easy process to handle data and process it is not so easy, but it can lead us to more problems by choosing the wrong step so we have to advise experts on such matters. One of the experts on the current problems is the “BENCHMARK IT SERVICES” team. In this case you find solutions and support for various data, hardware and software problems simply by explicit and professional contact and explanation of exactly what we need.

