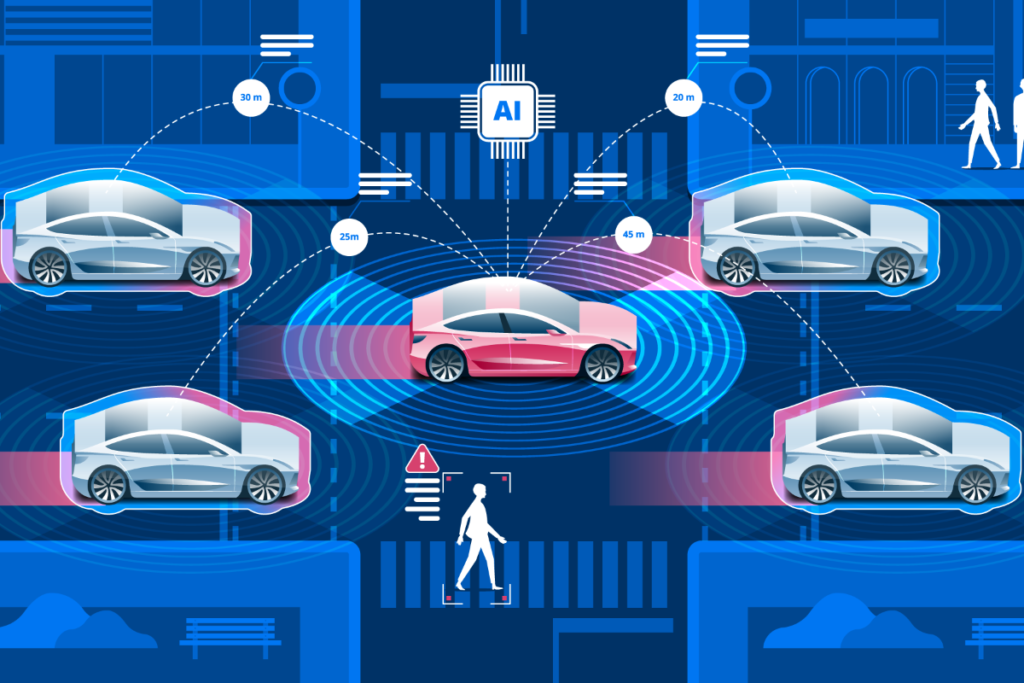
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, are vehicles that are capable of navigating and driving themselves without the need for human input. These vehicles use a combination of technologies such as sensors, cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS to navigate and make decisions.
Currently, there are different levels of autonomous vehicles, with Level 5 being fully autonomous and Level 0 being a traditional car with no self-driving capabilities. Most companies developing autonomous vehicles are currently focusing on Level 3 to Level 4, which allows for some self-driving features such as highway cruise control and automatic emergency braking.
There are several companies currently working on developing autonomous vehicles, including Tesla, Waymo (Alphabet), GM Cruise, and Uber. These companies are testing and deploying autonomous vehicles in various settings, such as on public roads and in controlled testing environments.
These vehicles have the potential to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and increase fuel efficiency. However, there are also concerns about the technology, such as cybersecurity risks and the potential for job loss in the transportation industry.
Autonomous vehicles use a variety of features and technologies to navigate and make decisions on the road. Some of the key features of autonomous vehicles include:
- Sensors: Autonomous vehicles use a variety of sensors such as cameras, lidar, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to gather data about their environment. These sensors provide information about the vehicle’s surroundings, including the location of other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles.
- GPS: Autonomous vehicles use GPS to determine their location and to plan their route.
- Computer Vision: Autonomous vehicles use computer vision to interpret the data gathered by the sensors and make decisions. Computer vision algorithms enable the vehicle to identify objects, such as traffic lights, road signs, and other vehicles, and understand their significance.
- Machine Learning: Autonomous vehicles use machine learning algorithms to make decisions based on the data they gather. These algorithms allow the vehicles to learn from their experiences and improve their decision-making over time.
- Communication: Autonomous vehicles use communication technologies such as V2V (vehicle-to-vehicle) and V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure) to share information with other vehicles and with traffic infrastructure such as traffic lights.
- Control systems: Autonomous vehicles use complex control systems to control the vehicle’s speed, direction, and braking. These systems use information from the sensors and the vehicle’s computer to make decisions about how to safely control the vehicle.
- Emergency backup systems: Autonomous vehicles have a backup plan in case of system failure, such as human takeover or emergency braking.
- Cybersecurity: Autonomous vehicles have a robust cybersecurity system to protect the vehicle and the passengers from hacking and unauthorized access.
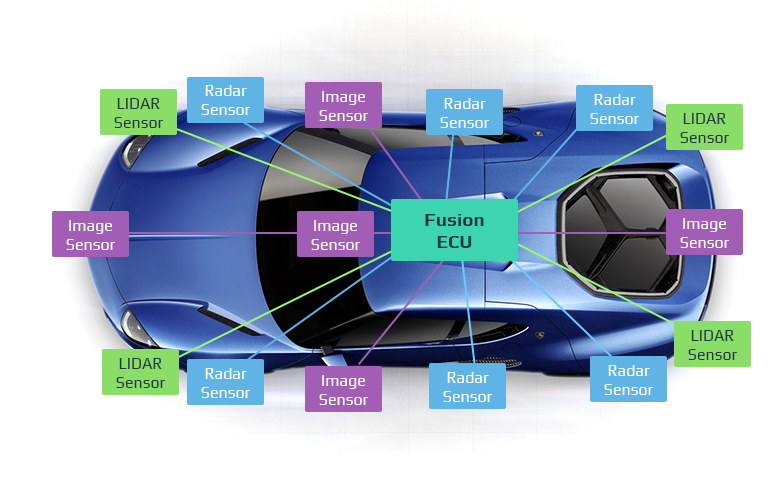
While autonomous vehicles have the potential to improve safety and efficiency on the road, there are also several limitations to the technology that need to be addressed. Some of the limitations of autonomous vehicles include:
- Complexity of the technology: Autonomous vehicles use a large number of sensors and algorithms to make decisions, which can make the technology difficult to develop and maintain.
- Environmental factors: Autonomous vehicles rely on sensors and cameras to gather data, which can be affected by environmental factors such as poor lighting, bad weather, and debris on the road.
- Safety concerns: Autonomous vehicles still have a risk of accidents, and there are concerns about how the vehicles will handle complex or unusual driving situations.
- Cybersecurity risks: Autonomous vehicles are vulnerable to cyber attacks, which could compromise the safety of the vehicle and its passengers.
- Ethical concerns: Autonomous vehicles raise ethical concerns about responsibility in the event of an accident, such as who would be held liable in case of an accident caused by the vehicle.
- Job Loss: Autonomous vehicles could lead to job loss for human drivers and other workers in the transportation industry.
- High cost: Autonomous vehicles are still expensive to produce, and the cost of the technology may be prohibitive for some individuals and companies.
- Limited availability: Autonomous vehicles are not yet widely available to the general public, and it may be several years before they are widely adopted.
- Limited infrastructure: Autonomous vehicles require a well-developed infrastructure such as road signs and traffic lights that are equipped with sensors, which is not available in some areas.
- Regulation: Autonomous vehicles are still in the early stages of development and there is a lack of clear regulation and standards for the technology.
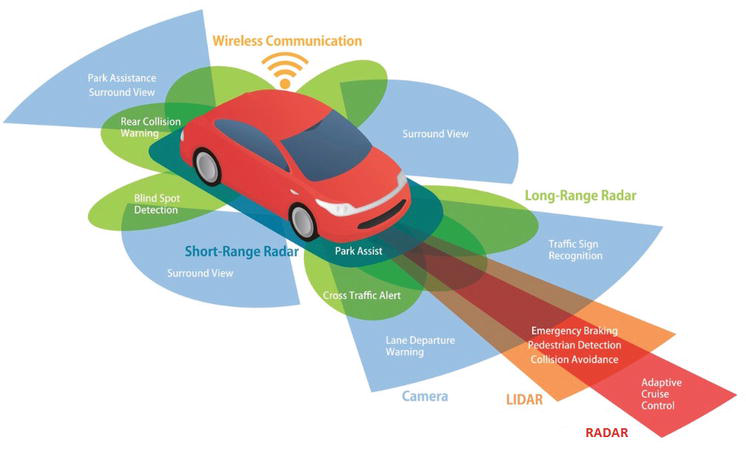
The legality of autonomous vehicles varies by country and region. In some places, autonomous vehicles are allowed on the road for testing and development purposes, but there may be restrictions on where and when they can be operated. In other places, autonomous vehicles are not yet legal for operation on public roads.