Safeguarding Business in the Digital Age: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Cybersecurity
Introduction
In today’s digital era, businesses are more interconnected than ever before, relying heavily on technology for operations, communication, and data storage. While this technological advancement brings numerous benefits, it also exposes businesses to the ever-growing threat of cyber attacks. Cybersecurity has become a critical concern for organizations of all sizes, as the potential consequences of a breach can be devastating. In this blog, we will delve into the cybersecurity-related issues faced by businesses and explore strategies to fortify their defenses.
The Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape
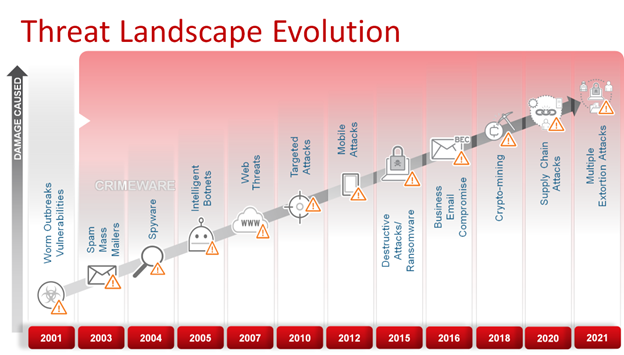
Cyber threats have evolved significantly over the years, becoming more sophisticated and diverse. Hackers are constantly developing new methods to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. Phishing attacks, ransomware, and data breaches have become commonplace, targeting businesses across industries. The financial, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors are particularly attractive to cybercriminals due to the sensitive information they handle.
One of the challenges faced by businesses is the increasing complexity of attacks. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) involve persistent, targeted attacks that can go undetected for extended periods. As businesses embrace cloud computing, IoT devices, and interconnected networks, the attack surface expands, providing more entry points for malicious actors.
The Human Element: A Weakest Link

While technology plays a significant role in cybersecurity, the human element remains a critical factor. Employees can inadvertently compromise security through actions such as clicking on malicious links, falling victim to social engineering tactics, or neglecting basic security protocols. Recognizing the importance of cybersecurity awareness and training is crucial for businesses to mitigate these risks.
Implementing a robust cybersecurity culture within an organization involves regular training sessions, simulated phishing exercises, and creating awareness about the latest threats. Employees should understand the potential consequences of their actions and the importance of following security best practices. By fostering a security-conscious culture, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
Securing the Perimeter: Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
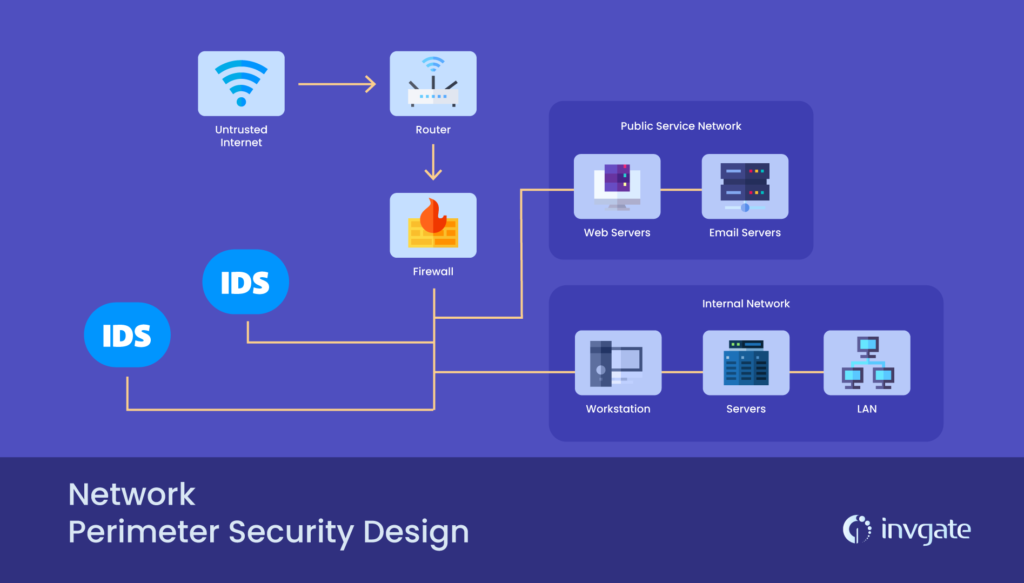
Building a strong defense against cyber threats starts with securing the network perimeter. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are foundational elements of network security. Firewalls act as barriers between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Intrusion Detection Systems, on the other hand, monitor network or system activities for malicious behavior or policy violations. They analyze traffic patterns, log files, and other relevant data to detect and respond to potential threats. Combining firewalls and IDS provides a multi-layered defense mechanism that helps businesses proactively identify and mitigate cyber threats.
The Role of Encryption in Data Protection

Data is a valuable asset for businesses, and protecting it from unauthorized access is paramount. Encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. By converting data into unreadable code that can only be deciphered with the appropriate encryption key, businesses can safeguard their information, even if it falls into the wrong hands.
End-to-end encryption is particularly important when transmitting sensitive data over networks. Secure communication channels using protocols like SSL/TLS ensure that data remains confidential during transit. Additionally, businesses should implement encryption for data at rest, whether stored on servers, in the cloud, or on employee devices.
Embracing Zero Trust Security Model
As traditional perimeter-based security models prove increasingly insufficient in today’s dynamic threat landscape, the Zero Trust model has gained prominence. The Zero Trust approach assumes that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Instead of relying solely on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust emphasizes continuous verification of identity and strict access controls.
Implementing Zero Trust involves authenticating and authorizing every user and device attempting to access the network. This approach minimizes the risk of lateral movement within the network, making it more challenging for attackers to gain unauthorized access. With the rise of remote work and the prevalence of mobile devices, a Zero Trust security model becomes even more critical in ensuring comprehensive protection.
Incident Response and Business Continuity Planning

Despite the best preventive measures, no system is completely immune to cyber threats. Therefore, having a robust incident response plan and business continuity strategy is essential for minimizing the impact of a cybersecurity incident.
Incident response involves a coordinated effort to detect, respond to, and recover from a security breach. This includes identifying the nature and scope of the incident, containing the threat, eradicating the root cause, and implementing measures to prevent future occurrences. Rapid and effective incident response is crucial in limiting the damage caused by a cyber attack.
In parallel, a well-defined business continuity plan ensures that critical operations can continue in the event of a disruption. This includes regularly backing up essential data, establishing redundant systems, and having a clear communication plan to keep stakeholders informed during a crisis. By proactively planning for resilience, businesses can significantly reduce downtime and financial losses associated with cyber incidents.
Conclusion
As businesses navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, cybersecurity must be at the forefront of their priorities. The evolving threat landscape requires a proactive and adaptive approach to safeguard sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and ensure business continuity. By investing in advanced technologies, fostering a cybersecurity-aware culture, and developing comprehensive strategies for incident response and business continuity, businesses can fortify their defenses against the ever-present and evolving cyber threats. In an interconnected world, the resilience of a business is intrinsically tied to its ability to secure and protect its digital assets.
