What is most important for any technology? The users. The ease of using technology and understanding the way to use it efficiently is what makes a technology either a hit or flop. At the very least we can consider the user interface to be the screens or visual elements that enable the users to interact with the technology. Whereas, user experience is the personal experience that a person feels while using the technology or service.
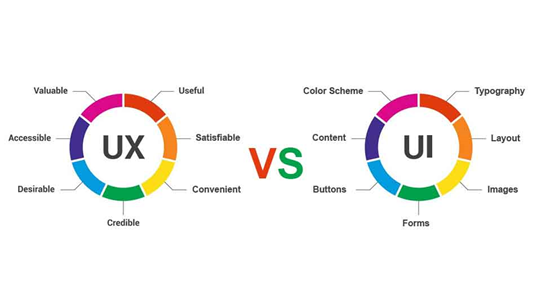
Fig. Link: https://www.webtrickshome.com/public/blog/180817102549uxvsuifeatured.jpg
Even when they are not new terms, they are easily misunderstood by normal people as being the same. But they are very different, to say the least.
User Interface:
In easy words, U(ser) I(nterface) is any medium that allows a user to interact with the technology. This could mean from screens to keyboards, sounds, or even light. To understand it in more detail let us discuss a little about its history. In the early days of computers, there was a command-line interface that let you enter some commands in order to access and use any technology. The graphical interface that we use nowadays was not yet developed in the 1970s. It was pretty hectic to use a computer back in those days. Back in the early days to use a computer one must know programming language which was practically not possible resulting in being one among the many reasons for computers to be out of common people’s reach. After roughly a decade G(raphical) U(ser) I(nterface) the know now. With this development, the interaction with a computer became easier to interact with the help of visual commands like buttons or icons.
Fig. Link: https://www.zibtek.com/blog/content/images/2020/07/image-5.png
This development broke through the limitation of people that could use a personal computer. Then apple released its product that included a point and click the mouse in 1984 which made the product’s the first commercially successful personal computer. It was then recognized that if the system is hard to interact with it would never leave the shop shelves. To tackle this issue UI designers came to light. With the passing of time technology grew and will continue to do so. As long as the computer remains in our daily life the work of a UI designer would never be over. Now they do not only have to watch over the computer interface but others like mobile apps, or websites are also their domain.
User Experience:
For the improvement of U(ser) I(nterface) UX was evolved. When there are technologies out for user interaction everything depended upon this interaction, how they feel about the product, their experience of using it either positive, negative, or neutral. This affects not only the product but all the names that are involved with the same like their manufacturers, distributors, and even developers.
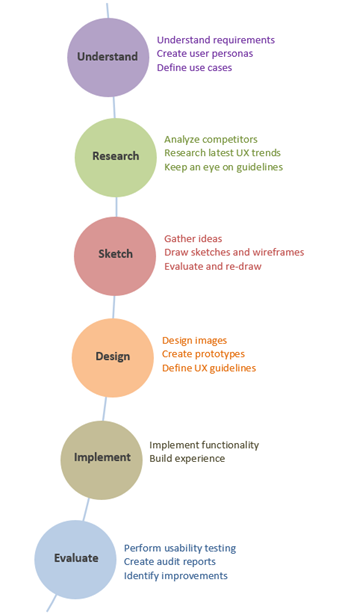
Fig. Link: https://miro.medium.com/max/924/1*w7ZVcRMhinJUjb5VRHfCpw.png
User research is the first step in U(ser) Ex(perience) design. U(ser) Ex(perience) designers must understand their intended audience and determine precisely what users require from the product they are building. User personas are created by U(ser) Ex(perience) designers as they gain this comprehension. Personas assist users in understanding the aims, aspirations, and limits of intended users. These insights enable them to provide innovative solutions that are the most effective for their users. U(ser) EX(perience) designers collaborate closely with U(ser) I(nterface) designers, U(ser) EX(perience) researchers, marketers, and production departments to properly appreciate their users via study and testing. Based on monitoring and evaluation of consumer surveys, they use the insights gathered to iterate and enhance experiences indefinitely. The definitions of U(ser) EX(perience) and UI indicate that they are linked structural form, although they are not. The visual elements of creation, as well as the overall sense it transmits, are more important in UI design. However, even the most beautiful design UI will result in a poor user experience if the U(ser) EX(perience) is poor.
UX and UI Designers:
Many businesses have recently discovered that clever architecture provides a strategic edge and are ready to invest extensive amounts in producing a great consumer experience. As a response, the position of U(ser) EX(perience) designer evolved and is now in great demand. In a nutshell, UX design is a human-centered approach to product layout. U(ser) EX(perience) designers are in charge of understanding the demands of the intended user and assuring that the organization generates products that fit those needs. U(ser) EX(perience) design is a diverse discipline in which U(ser) EX(perience) designers may work on several phases of product production such as market research, inspiration, modeling, and testing.
U(ser) EX(perience) designing begins with extended research of user requirements. Emotional intelligence is an important ability for U(ser) EX(perience) designers to have. It assists U(ser) EX(perience) designers in understanding and uncovering the underlying requirements and sentiments of the individuals for whom they are developing. Identifying the aim of a product and creating a realistic solution is all part of design strategies. U(ser) EX(perience) are continually active within the product’s implementation. They communicate with all team members to ensure that the model design is on track.
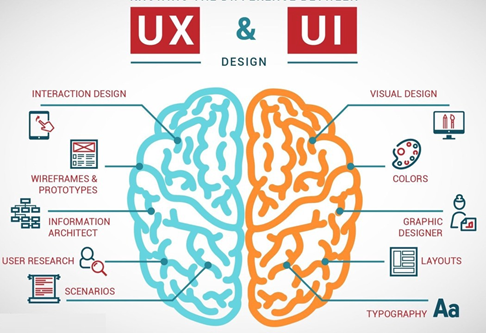
Fig. Link: https://img.techentice.com/media/2020/03/ui-ux.jpeg
The function of U(ser) I(nterface) designers are mainly concerned with the visual display of data. To build interfaces with a nice appearance and feel, U(ser) I(nterface) designers need to have visual elements, creative style, and marketing design abilities. U(ser) I(nterface) designers often transform the user flow and schematic capture for specific screens generated by U(ser) EX(perience) designers into something visually pleasing. A good designer keeps pursuing perfection as they know details are most important and monitored. A visually great design will get them nowhere if there are problems with the design. So, they must have the skills to solve issues. Be able to examine and conduct strong market evaluations of their goods and visual design selections. Ensure that the UI design appears well on all screen sizes and resolutions. U(ser) I(nterface) designers typically collaborate closely with UX designers and the technical team. Strong communication skills are essential to comprehend conceptual and operational.
Conclusion:
Presumably, you already grasp the subtle distinctions between U(ser) I(nterface) and U(ser) EX(perience). Yes, both are related, but they are not the same. U(ser) EX(perience) design is more quantitative. It has its origins in perceptual human behavior and social psychology. The visual effects if a product is visually attractive are more important in U(ser) I(nterface) software.
